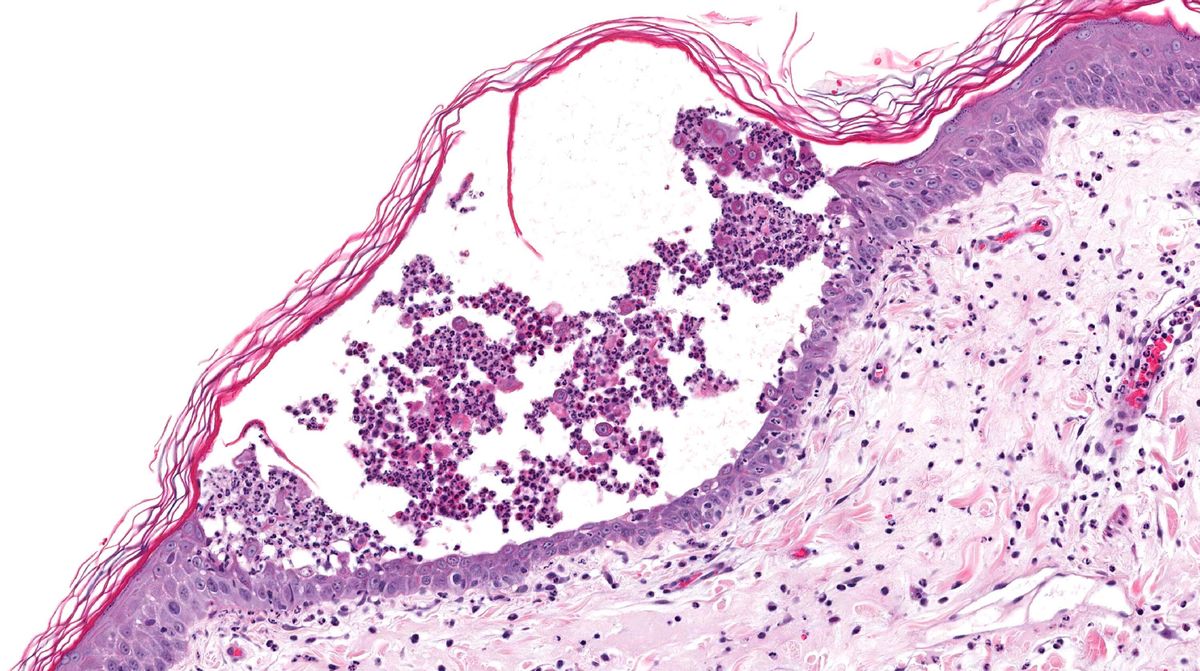
Pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder that causes painful blistering on the skin and mucous membranes. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, leading to the separation of skin layers. While it can affect anyone, it often appears in middle-aged or older adults. Symptoms include blisters that easily burst, leaving raw areas prone to infection. Diagnosing pemphigus involves a combination of clinical examination, biopsy, and blood tests. Treatment typically includes corticosteroids and immunosuppressants to reduce inflammation and prevent further damage. Managing this condition requires ongoing medical care and monitoring. Understanding pemphigus is crucial for those affected and their families, as it helps in navigating the challenges of living with a chronic illness. Awareness and education can lead to earlier diagnosis and better management, improving quality of life for those impacted.
Key Takeaways:
- Pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder causing painful blisters. It has different types, triggers, and treatments. Understanding its symptoms and seeking support are crucial for managing the condition effectively.
- Research into pemphigus is ongoing, offering hope for better treatments. Joining support groups and staying informed can help those affected cope with the condition.
Understanding Pemphigus
Pemphigus is a rare autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and mucous membranes. It can be a challenging condition to manage, but understanding its intricacies can help those affected and their loved ones. Here are some fascinating facts about pemphigus.
-
Autoimmune Nature: Pemphigus occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in the skin and mucous membranes. This leads to painful blisters and sores.
-
Types of Pemphigus: There are several types, including pemphigus vulgaris, pemphigus foliaceus, and paraneoplastic pemphigus. Each type has unique characteristics and symptoms.
-
Pemphigus Vulgaris: This is the most common form, often starting in the mouth before spreading to the skin. It can be severe and requires medical attention.
-
Pemphigus Foliaceus: This type primarily affects the skin, causing scaly sores and blisters. It is generally less severe than pemphigus vulgaris.
-
Paraneoplastic Pemphigus: Associated with certain cancers, this form is rare and can affect multiple body systems, not just the skin.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what triggers pemphigus can help in managing the condition. While the exact cause is unknown, several factors can increase the risk.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Some people may inherit a genetic tendency to develop pemphigus, although it is not directly passed from parent to child.
-
Environmental Triggers: Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to specific chemicals or drugs, may trigger the onset of pemphigus.
-
Age Factor: Pemphigus is more common in middle-aged and older adults, although it can occur at any age.
-
Ethnic Predilection: People of Mediterranean or Jewish descent have a higher incidence of pemphigus.
-
Drug-Induced Pemphigus: Some medications, like penicillamine and ACE inhibitors, have been linked to the development of pemphigus.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to a quicker diagnosis and better management of pemphigus.
-
Blister Formation: The hallmark symptom is the formation of blisters on the skin and mucous membranes that are easily ruptured.
-
Painful Sores: These blisters can lead to painful sores, especially in the mouth, making eating and drinking difficult.
-
Skin Erosion: Once blisters rupture, they leave behind raw, painful areas that can become infected if not treated properly.
-
Nikolsky's Sign: A clinical test where slight rubbing of the skin causes the top layer to slip away, indicating pemphigus.
-
Biopsy for Diagnosis: A skin biopsy is often performed to confirm the diagnosis, looking for specific antibodies in the tissue.
Treatment Options
Managing pemphigus involves a combination of medications and lifestyle adjustments to reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
-
Corticosteroids: These are often the first line of treatment to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
-
Immunosuppressants: Drugs like azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil help control the immune response.
-
Biologic Therapies: Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody, has shown promise in treating pemphigus by targeting specific immune cells.
-
Topical Treatments: Creams and ointments can help manage skin symptoms and prevent infections.
-
Dietary Adjustments: Soft foods and avoiding spicy or acidic foods can help manage oral symptoms.
Living with Pemphigus
Living with pemphigus requires ongoing management and support. Here are some tips for coping with the condition.
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups with a dermatologist or rheumatologist are crucial for managing symptoms and adjusting treatments.
-
Support Groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice from others living with pemphigus.
-
Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so finding ways to relax and manage stress is important.
-
Skin Care Routine: Gentle skin care and avoiding harsh soaps or chemicals can help prevent irritation.
-
Sun Protection: Protecting the skin from sun exposure can prevent flare-ups and reduce the risk of skin damage.
Research and Future Directions
Research into pemphigus is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments and understanding the disease better.
-
Genetic Research: Studies are looking into the genetic factors that contribute to pemphigus, which could lead to targeted therapies.
-
New Medications: Researchers are developing new drugs that target specific pathways in the immune system to treat pemphigus more effectively.
-
Clinical Trials: Ongoing clinical trials are testing the safety and efficacy of new treatments, offering hope for better management options.
-
Patient Registries: These databases collect information from people with pemphigus to help researchers understand the disease and develop new treatments.
-
International Collaboration: Scientists worldwide are working together to share knowledge and advance pemphigus research.
Historical Context
Pemphigus has been recognized for centuries, with historical records providing insight into its impact and treatment over time.
-
Ancient Descriptions: Historical texts describe conditions resembling pemphigus, indicating its presence for centuries.
-
Early Treatments: Before modern medicine, treatments included herbal remedies and bloodletting, with limited success.
-
Medical Advances: The development of corticosteroids in the 20th century revolutionized pemphigus treatment, significantly improving patient outcomes.
-
Cultural Beliefs: In some cultures, pemphigus was thought to be a curse or punishment, leading to stigma and isolation.
-
Modern Understanding: Advances in immunology have transformed pemphigus from a mysterious ailment to a manageable condition.
Notable Cases
Throughout history, there have been notable cases of pemphigus that have brought attention to the condition.
-
Famous Figures: Some historical figures are believed to have suffered from pemphigus, although diagnoses were not confirmed.
-
Medical Case Studies: Documented cases in medical literature have helped shape the understanding and treatment of pemphigus.
-
Patient Advocacy: High-profile cases have led to increased awareness and advocacy for pemphigus research and support.
-
Media Coverage: Stories in the media have highlighted the challenges faced by those with pemphigus, raising public awareness.
-
Impact on Families: Notable cases have shown the impact of pemphigus on families, emphasizing the need for support and understanding.
Myths and Misconceptions
Despite increased awareness, several myths and misconceptions about pemphigus persist.
-
Contagion Myth: Pemphigus is not contagious. It is an autoimmune disorder, not an infectious disease.
-
Dietary Cures: While diet can help manage symptoms, there is no specific food or diet that can cure pemphigus.
-
Stress as a Cause: Stress can worsen symptoms but is not a direct cause of pemphigus.
-
Skin Care Products: No specific product can cure pemphigus, although gentle skin care can help manage symptoms.
-
Alternative Therapies: While some alternative therapies may offer symptom relief, they should not replace conventional medical treatment.
Support and Resources
Finding support and resources can make living with pemphigus more manageable.
-
Patient Organizations: Groups like the International Pemphigus & Pemphigoid Foundation provide support and resources for patients and families.
-
Educational Materials: Many organizations offer brochures, videos, and online resources to help people understand and manage pemphigus.
-
Healthcare Providers: Building a team of knowledgeable healthcare providers is crucial for effective management.
-
Online Communities: Social media and online forums offer a platform for connecting with others who have pemphigus.
-
Research Participation: Joining research studies can contribute to the understanding and treatment of pemphigus, benefiting future patients.
Final Thoughts on Pemphigus
Pemphigus, a rare autoimmune disorder, affects the skin and mucous membranes, causing blisters and sores. Understanding this condition is crucial for those affected and their loved ones. Early diagnosis and treatment can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. While pemphigus can be challenging, advancements in medical research offer hope for better treatments and outcomes. Patients should work closely with healthcare professionals to develop personalized care plans. Support from family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional strength and practical advice. Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options empowers patients to make informed decisions about their health. Though pemphigus presents unique challenges, a proactive approach and a strong support network can help individuals lead fulfilling lives. Remember, knowledge is power, and staying educated about pemphigus is a step toward managing this condition effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
