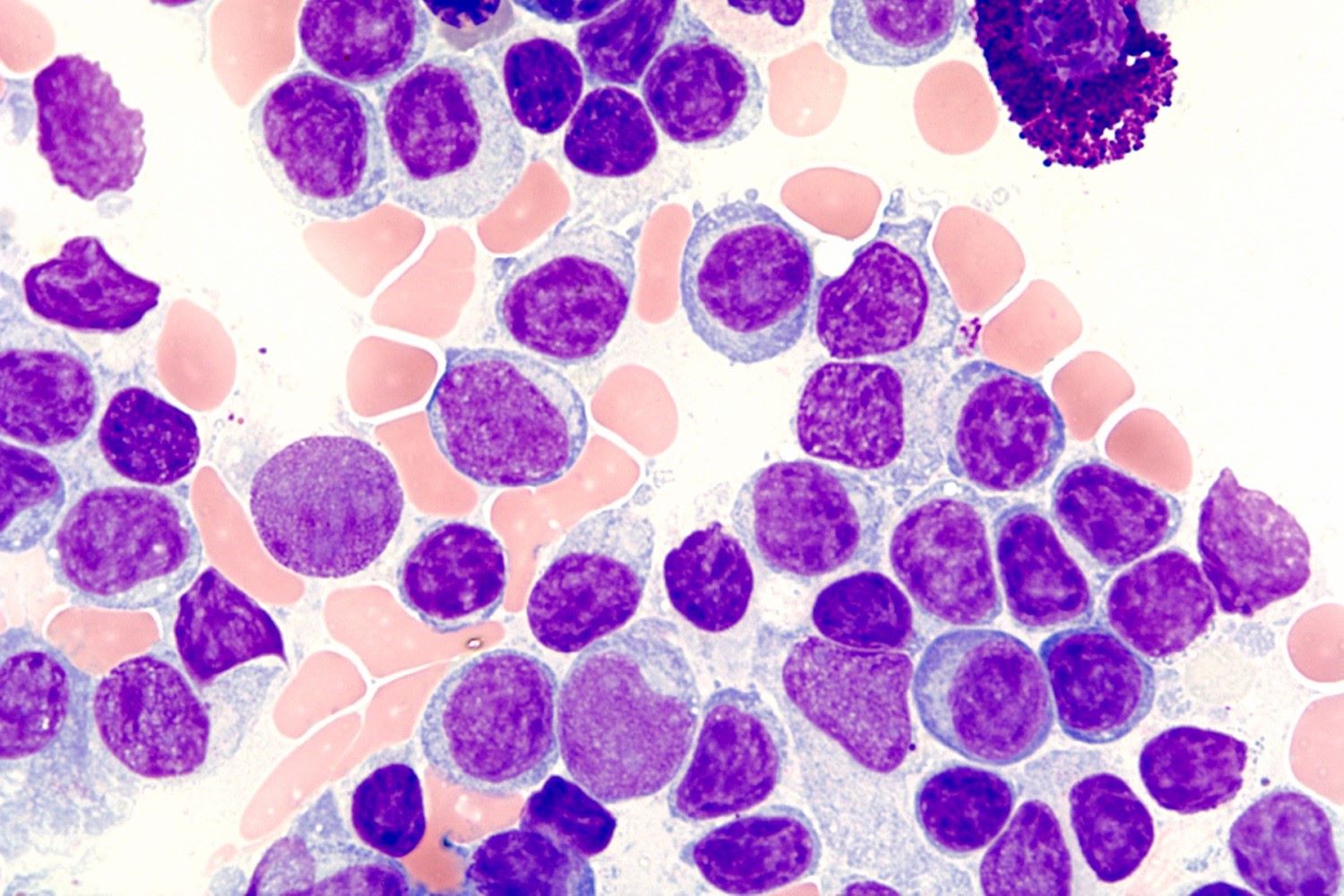
What is Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma? It's a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma that affects white blood cells. These cells, called B-cells, become abnormal and multiply uncontrollably. This condition often leads to the production of a protein called monoclonal immunoglobulin M (IgM), which can cause blood to thicken. This thickening may result in symptoms like fatigue, bleeding, and vision problems. Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma is sometimes associated with Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, a specific type of this lymphoma. Diagnosis usually involves blood tests, bone marrow biopsies, and imaging studies. Treatment options vary, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and sometimes stem cell transplants. While it can be challenging to manage, many patients live with this condition for years. Understanding this disease helps in making informed decisions about treatment and care.
Key Takeaways:
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma is a slow-growing cancer that mainly affects older adults, and it can have varying symptoms. Understanding its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for managing the disease effectively.
- Living with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma involves regular check-ups, healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking support from others. Ongoing research and global collaboration are essential for improving treatment and understanding of the disease.
Understanding Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma (LPL) is a rare type of cancer that affects white blood cells. It can be tricky to understand, but knowing some key facts can help make sense of it.
-
LPL is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. This means it starts in the lymphatic system, which is part of the body's immune system.
-
It mainly affects older adults. Most people diagnosed with LPL are over 60 years old.
-
LPL is slow-growing. Unlike some cancers, LPL progresses slowly, which can affect treatment decisions.
-
Waldenström's macroglobulinemia is a common form of LPL. This condition involves high levels of a protein called IgM in the blood.
-
Symptoms can vary widely. Some people experience fatigue, weight loss, or night sweats, while others might not have noticeable symptoms.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes LPL and who might be at risk can provide insight into this complex disease.
-
The exact cause of LPL is unknown. Researchers are still trying to figure out why some people develop this cancer.
-
Genetic mutations play a role. Changes in certain genes, like MYD88, are often found in people with LPL.
-
Family history can increase risk. Having a close relative with LPL or another type of lymphoma might raise your chances of developing it.
-
Certain infections are linked to LPL. Infections like hepatitis C have been associated with a higher risk of LPL.
-
Environmental factors might contribute. Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation could potentially increase the risk.
Diagnosis and Testing
Diagnosing LPL involves several steps and tests to ensure accuracy.
-
Blood tests are crucial. These tests can detect abnormal levels of proteins and blood cells.
-
Bone marrow biopsy is often needed. This test helps confirm the presence of cancer cells in the bone marrow.
-
Imaging tests might be used. CT scans or MRIs can help determine the extent of the disease.
-
Flow cytometry analyzes cells. This test examines the characteristics of cells in the blood or bone marrow.
-
Genetic testing identifies mutations. Testing for specific genetic changes can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment Options
There are various ways to treat LPL, depending on the individual's situation.
-
Watchful waiting is sometimes recommended. If symptoms are mild, doctors might monitor the condition without immediate treatment.
-
Chemotherapy is a common treatment. Drugs are used to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
-
Targeted therapy focuses on specific proteins. These drugs aim to block the growth of cancer cells by targeting certain molecules.
-
Immunotherapy boosts the immune system. This treatment helps the body's natural defenses fight cancer.
-
Plasmapheresis removes excess proteins. This procedure filters the blood to reduce high levels of IgM protein.
Living with Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma
Managing life with LPL involves understanding the disease and making lifestyle adjustments.
-
Regular check-ups are important. Frequent visits to the doctor help monitor the disease and manage symptoms.
-
Healthy lifestyle choices can help. Eating well, exercising, and getting enough rest can improve overall health.
-
Support groups offer emotional help. Connecting with others who have LPL can provide comfort and advice.
-
Managing stress is crucial. Techniques like meditation or yoga can help reduce anxiety and improve well-being.
-
Staying informed empowers patients. Learning about LPL and its treatments can help patients make informed decisions about their care.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving LPL treatment and understanding.
-
Clinical trials test new treatments. Participating in trials can provide access to cutting-edge therapies.
-
Research focuses on genetic mutations. Scientists are studying how genetic changes affect LPL and its treatment.
-
New drugs are being developed. Researchers are working on medications that target specific aspects of LPL.
-
Immunotherapy is a growing field. Advances in this area hold promise for more effective treatments.
-
Collaboration improves outcomes. Researchers, doctors, and patients working together can lead to better understanding and management of LPL.
Myths and Misconceptions
Clearing up common myths can help people better understand LPL.
-
LPL is not contagious. You can't catch it from someone else.
-
It's not always hereditary. While family history can be a factor, not everyone with LPL has a relative with the disease.
-
LPL is not the same as leukemia. Although both affect blood cells, they are different types of cancer.
-
Symptoms can be subtle. Not everyone with LPL experiences severe symptoms.
-
Treatment is not one-size-fits-all. Each person's treatment plan is tailored to their specific needs.
Support and Resources
Finding support and resources can make living with LPL easier.
-
Cancer support organizations offer help. Groups like the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society provide information and support.
-
Online forums connect patients. These platforms allow people with LPL to share experiences and advice.
-
Counseling services are available. Professional counselors can help patients and families cope with the emotional impact of LPL.
-
Educational materials are accessible. Many organizations offer brochures, videos, and other resources about LPL.
-
Financial assistance programs exist. Some groups provide help with medical bills and other expenses related to treatment.
Global Perspective on LPL
LPL affects people worldwide, and understanding its global impact is important.
-
LPL is rare globally. It accounts for a small percentage of all lymphomas worldwide.
-
Incidence rates vary by region. Some areas have higher rates of LPL than others.
-
Access to treatment differs globally. Availability of treatments can vary based on location and healthcare systems.
-
Research is conducted worldwide. Scientists around the globe are working to better understand and treat LPL.
-
International collaboration is key. Sharing knowledge and resources can improve outcomes for people with LPL everywhere.
Personal Stories and Experiences
Hearing from those who have lived with LPL can provide valuable insights.
-
Patient stories offer hope. Many people with LPL live full, active lives despite their diagnosis.
-
Caregivers play a vital role. Support from family and friends is crucial for managing the disease.
-
Each journey is unique. No two experiences with LPL are exactly alike.
-
Sharing experiences helps others. By telling their stories, patients can inspire and educate others facing similar challenges.
-
Community support is invaluable. Being part of a supportive community can make a big difference in coping with LPL.
Final Thoughts on Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma
Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, a rare type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, presents unique challenges and insights for both patients and researchers. Understanding its symptoms, like fatigue and night sweats, helps in early detection and management. Treatment options, including chemotherapy and targeted therapies, offer hope for those affected. While the disease can be complex, ongoing research continues to improve outcomes and quality of life.
Staying informed about the latest advancements and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers are crucial steps for patients. Support from family, friends, and support groups can make a significant difference in navigating this journey. As science progresses, the future holds promise for more effective treatments and a deeper understanding of this condition. Knowledge empowers, and being proactive in learning about lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma can lead to better management and a brighter outlook.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
