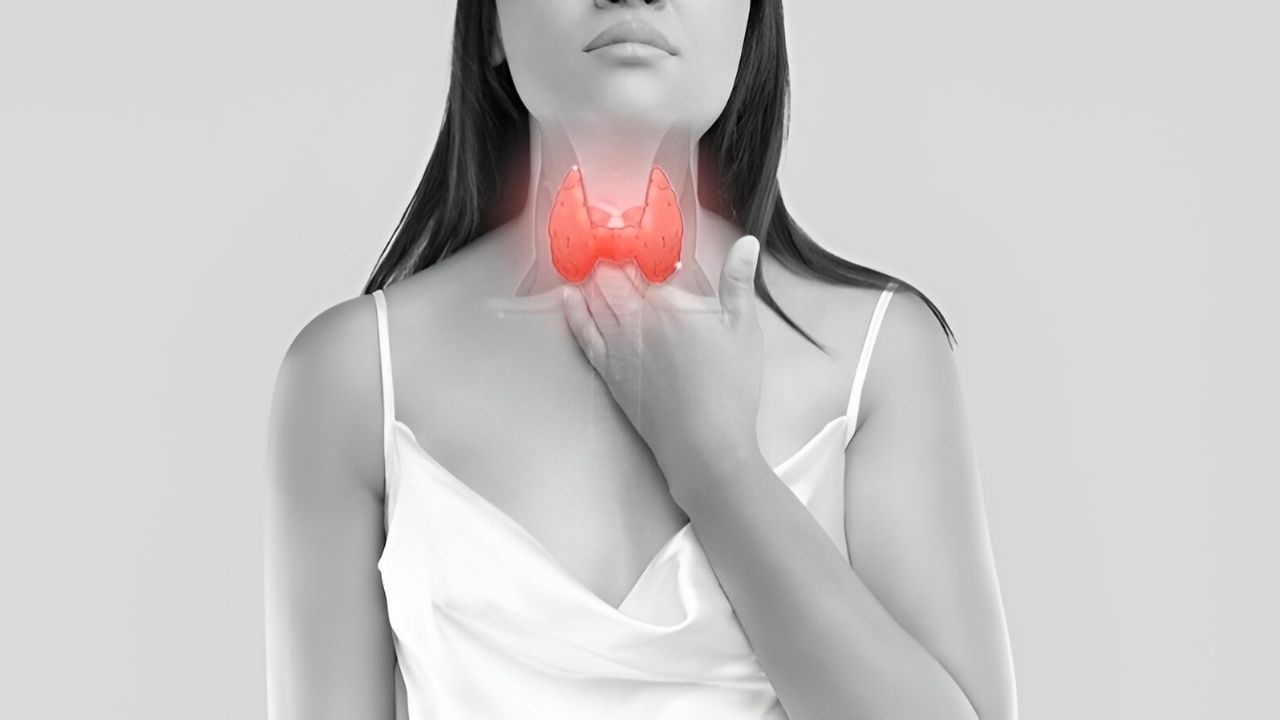
Why is iodine deficiency a concern? Iodine is a vital nutrient that helps the thyroid gland produce hormones crucial for growth, metabolism, and brain development. Without enough iodine, the body struggles to make these hormones, leading to various health issues. Iodine deficiency can cause goiter, hypothyroidism, and developmental delays in children. Pregnant women are especially at risk, as their iodine needs increase to support the developing baby. This deficiency is a global issue, affecting millions, particularly in regions where iodine-rich foods are scarce. Salt iodization has helped reduce the problem, but it remains prevalent in some areas. Understanding iodine's role and ensuring adequate intake is key to maintaining good health. Let's explore some interesting facts about iodine deficiency and its impact on the body.
Key Takeaways:
- Iodine is super important for our bodies, especially for our thyroid. Not having enough iodine can cause big problems, like making us tired and even affecting how smart we are!
- We can get iodine from foods like seafood, dairy, and iodized salt. It's important for everyone to eat a balanced diet to make sure we get enough iodine and stay healthy.
What is Iodine Deficiency?
Iodine deficiency occurs when the body doesn't get enough iodine, a vital mineral needed for thyroid function. This can lead to various health issues. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Essential for Thyroid Hormones
Iodine is crucial for producing thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, growth, and development. -
Goiter Formation
A lack of iodine can cause the thyroid gland to enlarge, forming a goiter. This is often visible as a swelling in the neck. -
Cognitive Impairment in Children
Children born to iodine-deficient mothers may suffer from cognitive impairments, affecting learning and development. -
Cretinism Risk
Severe iodine deficiency during pregnancy can lead to cretinism, a condition characterized by stunted physical and mental growth. -
Common in Developing Countries
Iodine deficiency is more prevalent in developing countries where access to iodine-rich foods is limited.
How Does Iodine Deficiency Affect Health?
The impact of iodine deficiency on health can be profound, affecting various bodily functions and overall well-being.
-
Hypothyroidism
Insufficient iodine can lead to hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones, causing fatigue and weight gain. -
Increased Miscarriage Risk
Pregnant women with iodine deficiency face a higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. -
Hearing Loss
In some cases, iodine deficiency can contribute to hearing loss, particularly in children. -
Delayed Puberty
Adolescents with iodine deficiency may experience delayed puberty due to hormonal imbalances. -
Increased Cholesterol Levels
Hypothyroidism from iodine deficiency can lead to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing heart disease risk.
Sources of Iodine
Understanding where iodine comes from can help prevent deficiency. Here are some common sources.
-
Iodized Salt
One of the easiest ways to ensure adequate iodine intake is through iodized salt, which is widely available. -
Seafood
Fish and other seafood are rich in iodine, making them excellent dietary sources. -
Dairy Products
Milk, cheese, and yogurt contain iodine, contributing to daily intake. -
Eggs
Eggs are another good source of iodine, especially the yolk. -
Seaweed
Seaweed, particularly kelp, is one of the richest natural sources of iodine.
Global Efforts to Combat Iodine Deficiency
Efforts to reduce iodine deficiency have been implemented worldwide, with varying degrees of success.
-
Universal Salt Iodization
Many countries have adopted universal salt iodization programs to ensure populations receive adequate iodine. -
Public Health Campaigns
Educational campaigns raise awareness about the importance of iodine and encourage consumption of iodine-rich foods. -
Monitoring and Surveillance
Regular monitoring of iodine levels in populations helps identify and address deficiency issues. -
Fortification of Foods
In some regions, foods other than salt are fortified with iodine to improve intake. -
Research and Development
Ongoing research aims to develop new strategies for preventing and treating iodine deficiency.
Historical Context of Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency has been recognized for centuries, with historical records highlighting its impact.
-
Ancient Remedies
Ancient civilizations used seaweed and other iodine-rich substances to treat goiters. -
Discovery of Iodine
Iodine was discovered in 1811 by French chemist Bernard Courtois, leading to a better understanding of its role in health. -
Goiter Belt in the U.S.
In the early 20th century, parts of the United States were known as the "goiter belt" due to widespread iodine deficiency. -
Introduction of Iodized Salt
Iodized salt was introduced in the 1920s as a simple solution to combat iodine deficiency. -
World Health Organization's Role
The WHO has been instrumental in promoting iodine deficiency prevention efforts globally.
Signs and Symptoms of Iodine Deficiency
Recognizing the signs of iodine deficiency can lead to early intervention and treatment.
-
Fatigue and Weakness
Persistent tiredness and weakness can indicate an iodine deficiency affecting thyroid function. -
Weight Gain
Unexplained weight gain may be a result of a slowed metabolism due to low iodine levels. -
Hair Loss
Thinning hair or hair loss can occur when iodine levels are insufficient. -
Dry Skin
Dry, flaky skin might be a symptom of iodine deficiency, as thyroid hormones help regulate skin health. -
Cold Sensitivity
Feeling unusually cold, even in warm environments, can be linked to low iodine levels.
Iodine Deficiency in Different Populations
Iodine deficiency affects various groups differently, with unique challenges and considerations.
-
Pregnant Women
Pregnant women require more iodine to support fetal development, making them more susceptible to deficiency. -
Infants and Children
Young children need adequate iodine for brain development and growth, making deficiency particularly harmful. -
Vegetarians and Vegans
Those following plant-based diets may struggle to get enough iodine without careful planning. -
People in Iodine-Deficient Regions
Individuals living in areas with iodine-poor soil may have limited access to iodine-rich foods. -
Elderly Population
Older adults may experience iodine deficiency due to changes in diet and decreased absorption.
Preventing Iodine Deficiency
Taking steps to prevent iodine deficiency can improve health outcomes and quality of life.
-
Balanced Diet
Consuming a balanced diet that includes iodine-rich foods helps maintain adequate levels. -
Use of Iodized Salt
Incorporating iodized salt into meals is a simple way to boost iodine intake. -
Regular Health Check-Ups
Routine health check-ups can detect iodine deficiency early, allowing for timely intervention. -
Supplements
Iodine supplements may be necessary for those unable to get enough through diet alone. -
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the importance of iodine can encourage healthier dietary choices.
Myths and Misconceptions About Iodine Deficiency
Misunderstandings about iodine deficiency can lead to confusion and misinformation.
-
Myth: Only Coastal Areas Have Enough Iodine
While coastal areas often have more iodine-rich foods, iodine deficiency can still occur without proper diet. -
Myth: Iodine Deficiency is Rare
Despite efforts to reduce it, iodine deficiency remains a significant public health issue worldwide. -
Myth: Iodized Salt is Unhealthy
Iodized salt is safe and effective for preventing iodine deficiency when used in moderation. -
Myth: All Salt Contains Iodine
Not all salt is iodized, so it's important to check labels to ensure adequate iodine intake. -
Myth: Iodine Supplements are Always Necessary
Supplements are not always needed if a balanced diet provides enough iodine.
Future of Iodine Deficiency Prevention
Looking ahead, the fight against iodine deficiency continues with new strategies and innovations.
-
Technological Advances
New technologies may improve iodine fortification methods and monitoring. -
Global Collaboration
International cooperation can enhance efforts to reduce iodine deficiency worldwide. -
Sustainable Solutions
Sustainable approaches to iodine fortification can ensure long-term success. -
Personalized Nutrition
Advancements in personalized nutrition may help tailor iodine intake to individual needs. -
Continued Research
Ongoing research will provide insights into better prevention and treatment of iodine deficiency.
The Final Word on Iodine Deficiency
Iodine deficiency is a big deal for health. It can mess with your thyroid, which affects everything from growth to metabolism. Iodine is crucial for pregnant women and kids, as it helps brain development. Lack of it can lead to serious issues like goiter or even intellectual disabilities. The good news? It's preventable. Eating foods like seafood, dairy, and iodized salt can help maintain healthy levels. Many countries have programs to add iodine to salt, making it easier for everyone to get enough. But, not everyone has access to these fortified foods, so awareness is key. If you're worried about your iodine levels, a simple test can tell you where you stand. Staying informed and making small dietary changes can make a huge difference. Keep an eye on your iodine intake and encourage others to do the same.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
