Horner Syndrome is a rare condition affecting the nerves connecting the brain to the eye and face. This syndrome can cause a drooping eyelid, constricted pupil, and lack of sweating on one side of the face. Horner Syndrome often results from damage to the sympathetic nerves, which can occur due to various reasons like neck trauma, tumors, or even certain surgeries. Understanding this condition is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. In this blog post, we'll explore 50 intriguing facts about Horner Syndrome that will help you grasp its complexities, symptoms, and potential treatments. Ready to dive in? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Horner Syndrome affects the nerves connecting the brain to the eye and face, causing symptoms like drooping eyelids and constricted pupils. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Causes of Horner Syndrome include trauma, tumors, and stroke, with treatment involving addressing the underlying cause, medications, and physical therapy. Support groups and lifestyle changes can also help manage the condition.
What is Horner Syndrome?
Horner Syndrome is a rare condition that affects the nerves connecting the brain to the eye and face. It can cause a variety of symptoms, often related to the eyes and facial muscles. Here are some fascinating facts about this intriguing condition.
- Horner Syndrome is also known as oculosympathetic palsy.
- It was first described by Swiss ophthalmologist Johann Friedrich Horner in 1869.
- The syndrome results from damage to the sympathetic nerves.
- It can affect people of all ages, including children.
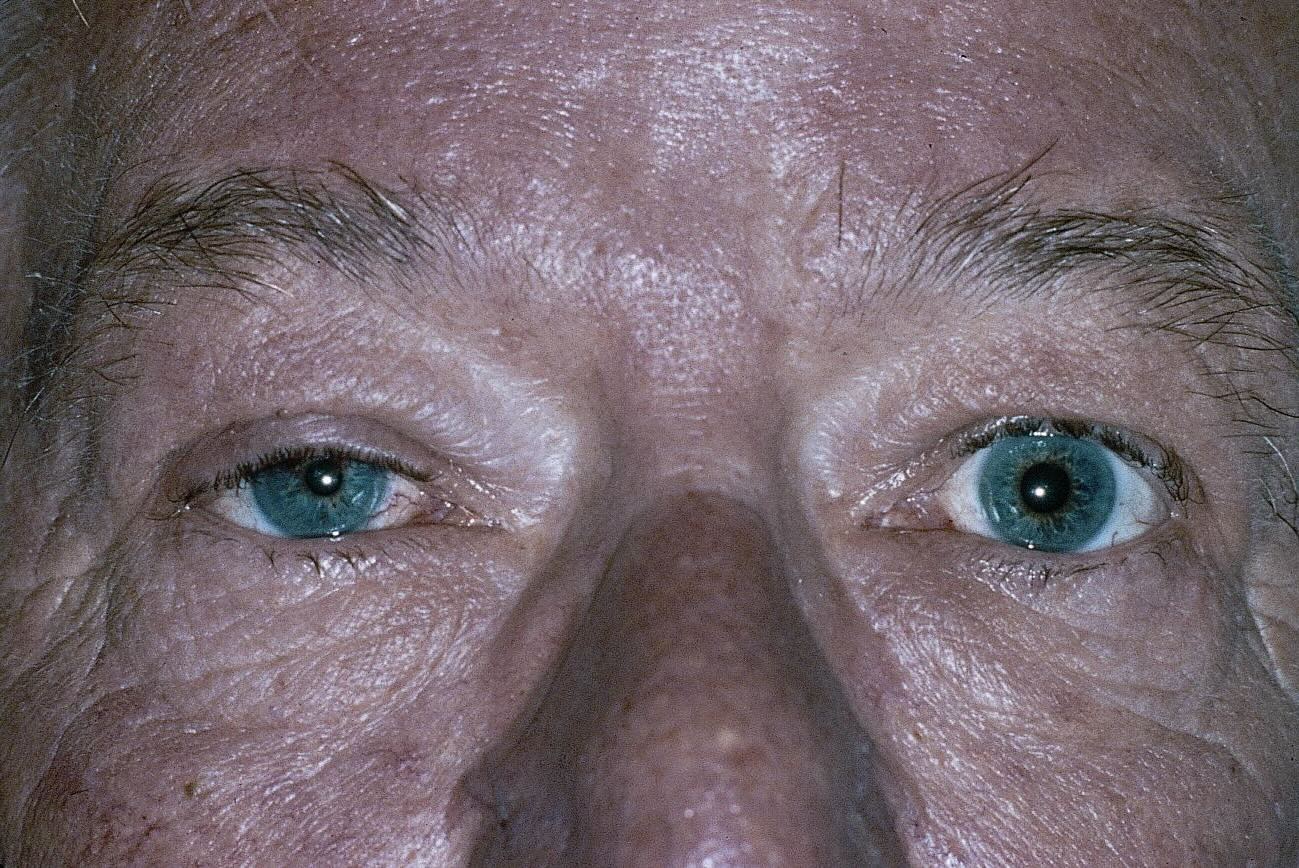
- Horner Syndrome often presents with a drooping eyelid, known as ptosis.
- Another common symptom is miosis, or constricted pupil.
- Anhidrosis, or lack of sweating, can occur on the affected side of the face.
- The condition can be congenital or acquired.
- Trauma, tumors, or stroke can cause acquired Horner Syndrome.
- Congenital cases are often linked to birth trauma.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how doctors diagnose Horner Syndrome is crucial for early detection and treatment.
- A noticeable difference in pupil size, called anisocoria, is a key symptom.
- The affected eye may appear sunken, a condition known as enophthalmos.
- Light sensitivity, or photophobia, can occur in the affected eye.
- Doctors use a cocaine test to diagnose Horner Syndrome.
- Apraclonidine drops can also help confirm the diagnosis.
- Imaging tests like MRI or CT scans are often used to find the underlying cause.
- A thorough neurological exam is essential for diagnosis.
- Blood tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions.
- The syndrome can sometimes be mistaken for other eye disorders.
- Early diagnosis can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Causes and Risk Factors
Horner Syndrome can result from various causes, each with its own set of risk factors.
- Neck or chest surgery can damage sympathetic nerves, leading to Horner Syndrome.
- Car accidents are a common cause of traumatic Horner Syndrome.
- Tumors in the neck or chest, such as neuroblastoma, can cause the condition.
- Stroke affecting the brainstem can lead to Horner Syndrome.
- Multiple sclerosis is another potential cause.
- Cluster headaches are sometimes associated with Horner Syndrome.
- Carotid artery dissection, a tear in the artery, is a serious cause.
- Lung cancer, particularly Pancoast tumors, can lead to Horner Syndrome.
- Infections like tuberculosis can damage the sympathetic nerves.
- Genetic mutations are a rare cause of congenital Horner Syndrome.
Treatment and Management
Managing Horner Syndrome involves addressing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms.
- Treating the underlying cause often resolves the symptoms.
- Surgery may be required to remove tumors or repair nerve damage.
- Medications can help manage symptoms like pain or inflammation.
- Physical therapy may improve muscle function and reduce ptosis.
- Eye drops can help manage anisocoria and light sensitivity.
- Regular follow-up with a neurologist is crucial for monitoring progress.
- Support groups can provide emotional support and resources.
- Lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers for cluster headaches, can help.
- Early intervention improves the chances of recovery.
- In some cases, symptoms may persist despite treatment.
Interesting Facts and Historical Tidbits
Horner Syndrome has a rich history and some lesser-known facts that make it even more intriguing.
- Johann Friedrich Horner initially described the syndrome while studying ptosis.
- The syndrome is sometimes called Bernard-Horner Syndrome in Europe.
- Horner Syndrome can occur in animals, including dogs and cats.
- The condition is more common in males than females.
- Horner Syndrome can be a sign of a life-threatening condition, such as carotid artery dissection.
- The syndrome can sometimes resolve on its own without treatment.
- Horner Syndrome can be part of a larger syndrome, such as Wallenberg syndrome.
- The condition can affect one or both sides of the face, though unilateral cases are more common.
- Horner Syndrome can be a diagnostic challenge due to its varied presentation.
- Research is ongoing to better understand the condition and improve treatments.
Final Thoughts on Horner Syndrome
Horner Syndrome, while rare, offers a fascinating glimpse into the human body's complexities. This condition, resulting from nerve damage, can affect the eye and facial muscles. Symptoms like drooping eyelids, constricted pupils, and reduced sweating on one side of the face are telltale signs. Though it can be alarming, Horner Syndrome often points to underlying issues that need attention. Diagnosing it involves a series of tests, including imaging studies, to pinpoint the cause. Treatment focuses on addressing the root problem, which can range from neck injuries to tumors. Understanding Horner Syndrome highlights the importance of nerve pathways and their role in our daily functions. Awareness and early detection can make a significant difference in managing this condition. Stay informed, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice if you notice any unusual symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
