Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome, is a genetic disorder that affects blood vessels. HHT causes abnormal blood vessel formation, leading to frequent nosebleeds, skin telangiectasias (small red spots), and arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) in organs like the lungs, liver, and brain. HHT affects approximately 1 in 5,000 people worldwide, making it relatively rare but significant. Symptoms can vary widely, even within the same family, making diagnosis challenging. Early detection and treatment are crucial to managing complications. This article will provide 50 intriguing facts about HHT, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, treatments, and ongoing research. Whether you're newly diagnosed, a caregiver, or just curious, these facts will offer valuable insights into HHT.
Key Takeaways:
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is a rare genetic disorder causing abnormal blood vessel formation, leading to symptoms like nosebleeds and organ complications. Treatment and regular monitoring are essential for managing HHT.
- Living with HHT requires lifestyle adjustments, proactive healthcare, and support from healthcare providers and family members. Staying informed, hydrated, and connected with support groups can help manage the condition effectively.
What is Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia?
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is a genetic disorder affecting blood vessels. It leads to abnormal blood vessel formation, causing various health issues. Here are some fascinating facts about HHT.
- HHT is also known as Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome.
- It affects approximately 1 in 5,000 people worldwide.
- The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- Mutations in the ENG, ACVRL1, and SMAD4 genes cause HHT.
- Symptoms often appear in childhood or adolescence.
- Nosebleeds are the most common symptom, affecting over 90% of patients.
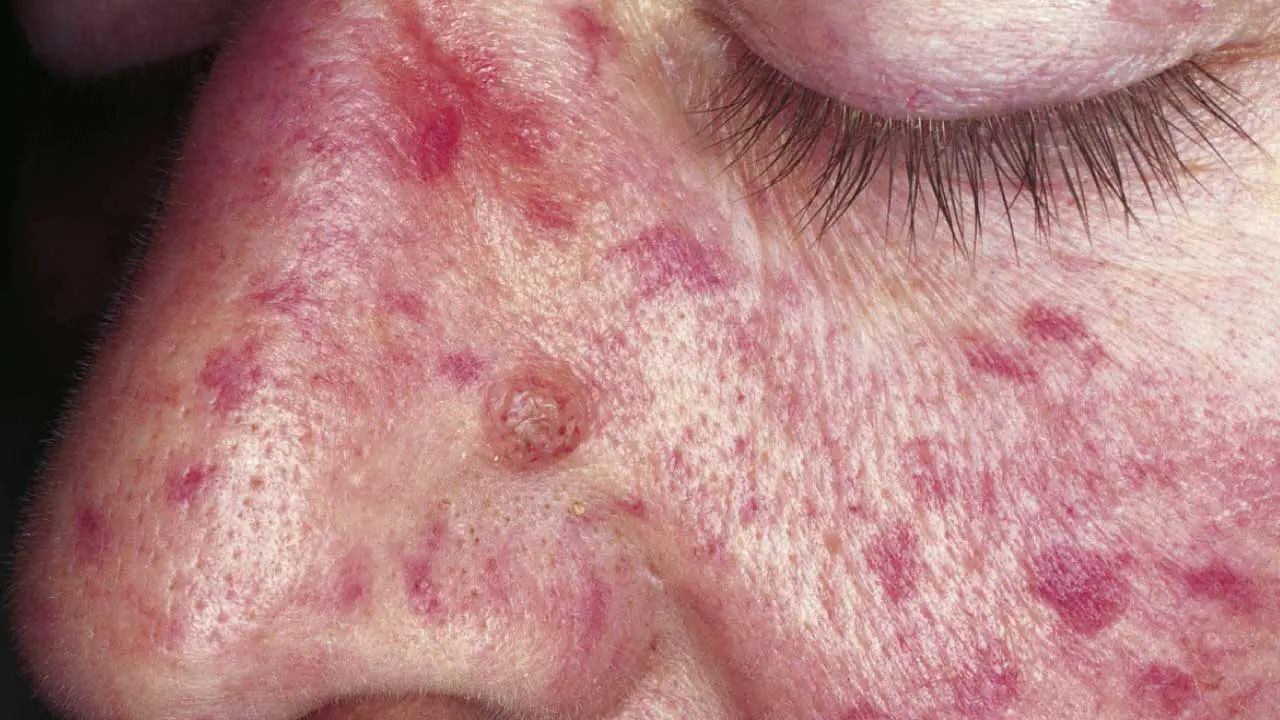
- Telangiectasias, small red spots on the skin, are another hallmark.
- These spots commonly appear on the face, lips, tongue, and fingers.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding can occur due to telangiectasias in the digestive tract.
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal connections between arteries and veins.
How Does HHT Affect the Body?
HHT can impact various organs and systems in the body. Understanding these effects helps in managing the condition better.
- AVMs can occur in the lungs, brain, liver, and spine.
- Pulmonary AVMs can lead to serious complications like stroke or brain abscess.
- Brain AVMs may cause seizures, headaches, or hemorrhagic stroke.
- Liver AVMs can result in high-output heart failure.
- Spinal AVMs might cause back pain or neurological deficits.
- Chronic anemia is common due to frequent bleeding episodes.
- Iron deficiency anemia often requires iron supplements or blood transfusions.
- HHT patients may experience fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Regular screening for AVMs is crucial for early detection and treatment.
- Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis and identify affected family members.
Treatment and Management of HHT
While there is no cure for HHT, various treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Nosebleeds can be managed with humidifiers, nasal ointments, and laser therapy.
- Severe nosebleeds may require nasal packing or surgical intervention.
- Telangiectasias can be treated with laser therapy or electrocautery.
- Iron supplements or intravenous iron infusions help manage anemia.
- Blood transfusions may be necessary for severe anemia.
- Embolization is a procedure used to treat AVMs in the lungs and brain.
- Liver AVMs might require medical management or liver transplantation.
- Regular follow-ups with a multidisciplinary team are essential.
- Patients should avoid medications that increase bleeding risk, like aspirin.
- Genetic counseling is recommended for affected families.
Living with HHT
Living with HHT requires awareness, lifestyle adjustments, and proactive healthcare.
- Patients should inform their healthcare providers about their condition.
- Wearing medical alert jewelry can be helpful in emergencies.
- Avoiding high-altitude locations reduces the risk of complications from pulmonary AVMs.
- Maintaining good oral hygiene is important to prevent gum bleeding.
- Regular dental check-ups are crucial for early detection of oral telangiectasias.
- Staying hydrated helps reduce the frequency of nosebleeds.
- Using a saline nasal spray keeps nasal passages moist.
- Patients should monitor their hemoglobin levels regularly.
- Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educating family members about HHT helps in early recognition of symptoms.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of HHT. Here are some key areas of focus.
- Researchers are exploring new medications to reduce bleeding episodes.
- Gene therapy holds potential for correcting the underlying genetic mutations.
- Clinical trials are investigating the efficacy of anti-angiogenic drugs.
- Advances in imaging techniques improve detection of AVMs.
- Collaboration between international HHT centers enhances research efforts.
- Patient registries help track disease progression and treatment outcomes.
- Public awareness campaigns aim to increase early diagnosis rates.
- Funding for HHT research is crucial for developing new therapies.
- Advocacy groups work to improve access to specialized care for HHT patients.
- Continued education for healthcare providers ensures better management of HHT.
Final Thoughts on Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT) is a rare genetic disorder that affects blood vessels, leading to frequent nosebleeds, skin abnormalities, and potential complications in organs like the lungs, liver, and brain. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options can help manage the condition better. Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing severe complications. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for families affected by HHT.
Staying informed about the latest research and maintaining regular check-ups with healthcare providers can make a significant difference. Support groups and resources are available for those living with HHT, offering community and guidance. Remember, knowledge and proactive care are key to managing HHT effectively. Stay vigilant, seek medical advice when needed, and connect with others who share similar experiences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
