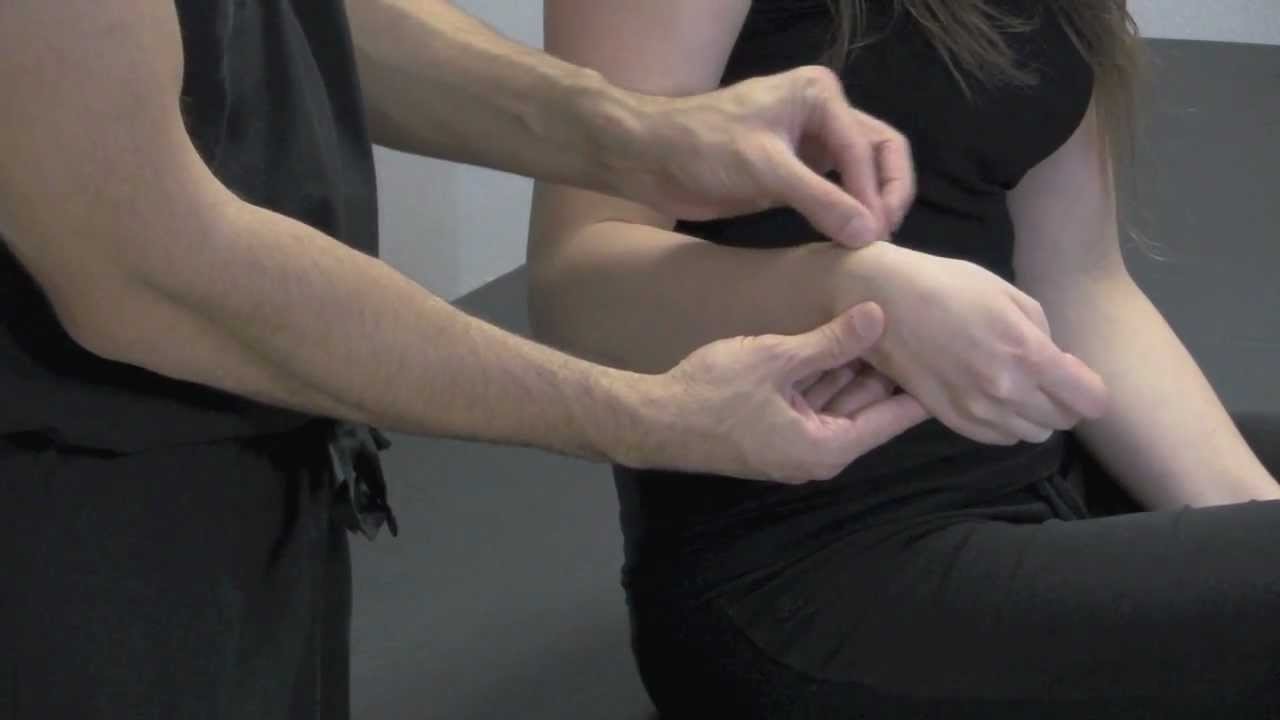
Ever wondered about the Finkelstein Test? This intriguing assessment, often used in medical settings, helps diagnose conditions like De Quervain's tenosynovitis. Named after American surgeon Harry Finkelstein, it involves a simple yet effective maneuver. Patients make a fist with their thumb tucked inside their fingers, then the wrist is bent towards the little finger. If pain occurs, it indicates inflammation of the tendons in the wrist. This test is quick, non-invasive, and provides immediate results. Understanding the Finkelstein Test can help you recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate treatment. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 50 fascinating facts about this essential diagnostic tool!
Key Takeaways:
- The Finkelstein Test is a simple and quick way for doctors to check for a painful wrist condition called De Quervain's tenosynovitis. It helps them figure out if there's inflammation in the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist.
- If you want to avoid De Quervain's tenosynovitis, take breaks during repetitive tasks, use ergonomic tools, and practice proper hand and wrist positioning. Strengthening hand and wrist muscles through exercises can also help prevent this painful condition.
What is the Finkelstein Test?
The Finkelstein Test is a clinical examination used to diagnose De Quervain's tenosynovitis, a painful condition affecting the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist. This test helps doctors determine if inflammation or irritation is present in these tendons.
- Named after American surgeon Harry Finkelstein, who first described it in 1930.
- Primarily used to diagnose De Quervain's tenosynovitis.
- Involves the patient making a fist with the thumb tucked inside the fingers.
- The wrist is then bent towards the little finger.
- Pain during this movement indicates a positive test result.
- Often used alongside other diagnostic methods for accuracy.
- Helps differentiate De Quervain's from other wrist conditions.
- Simple and quick to perform in a clinical setting.
- No special equipment is needed.
- Can be performed by various healthcare professionals.
Symptoms of De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Understanding the symptoms of De Quervain's tenosynovitis can help in recognizing the need for the Finkelstein Test. This condition can cause significant discomfort and affect daily activities.
- Pain near the base of the thumb.
- Swelling on the thumb side of the wrist.
- Difficulty moving the thumb and wrist.
- A "sticking" or "stop-and-go" sensation in the thumb.
- Pain that worsens with thumb and wrist movement.
- Tenderness when pressing on the affected area.
- A visible lump or thickening over the tendons.
- Pain that radiates up the forearm.
- Weakness in the thumb and wrist.
- Difficulty gripping objects.
Causes and Risk Factors
De Quervain's tenosynovitis can develop due to various reasons. Knowing these causes and risk factors can help in preventing the condition and understanding who might be at risk.
- Repetitive hand or wrist movements.
- Overuse of the thumb.
- Direct injury to the wrist or tendons.
- Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Pregnancy and postpartum period.
- Middle-aged women are more commonly affected.
- Jobs or hobbies that involve repetitive hand motions.
- Previous wrist injuries.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Poor wrist ergonomics.
Treatment Options
Once diagnosed with De Quervain's tenosynovitis, several treatment options are available. These treatments aim to reduce pain and inflammation, allowing the tendons to heal.
- Resting the affected hand and wrist.
- Applying ice to reduce swelling.
- Using a splint to immobilize the thumb and wrist.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen.
- Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation.
- Physical therapy to strengthen the wrist and thumb.
- Avoiding activities that aggravate the condition.
- Surgery in severe cases to release the tendons.
- Stretching exercises to improve flexibility.
- Ergonomic adjustments to prevent recurrence.
Preventing De Quervain's Tenosynovitis
Prevention is always better than cure. By adopting certain habits and making lifestyle changes, the risk of developing De Quervain's tenosynovitis can be minimized.
- Taking frequent breaks during repetitive tasks.
- Using ergonomic tools and equipment.
- Practicing proper hand and wrist positioning.
- Strengthening hand and wrist muscles through exercises.
- Avoiding activities that strain the thumb and wrist.
- Using assistive devices to reduce strain.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress.
- Staying hydrated to keep tendons flexible.
- Wearing protective gear during high-risk activities.
- Seeking early treatment for wrist pain to prevent worsening.
Final Thoughts on Finkelstein Test
Finkelstein Test, a cornerstone in organic chemistry, helps identify halide ions in compounds. Named after Hans Finkelstein, this reaction swaps halides using a metal halide salt. It's a go-to method for chemists due to its simplicity and efficiency. The test's versatility makes it valuable in both academic research and industrial applications. Understanding this reaction can deepen your grasp of chemical processes and reactions. Whether you're a student or a professional, knowing the ins and outs of the Finkelstein Test can be a game-changer. It’s not just about swapping halides; it’s about unlocking a deeper understanding of chemical behavior. So, next time you encounter a halide, remember the Finkelstein Test and its pivotal role in chemistry. Keep exploring, keep experimenting, and let the Finkelstein Test be a tool in your scientific toolkit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
