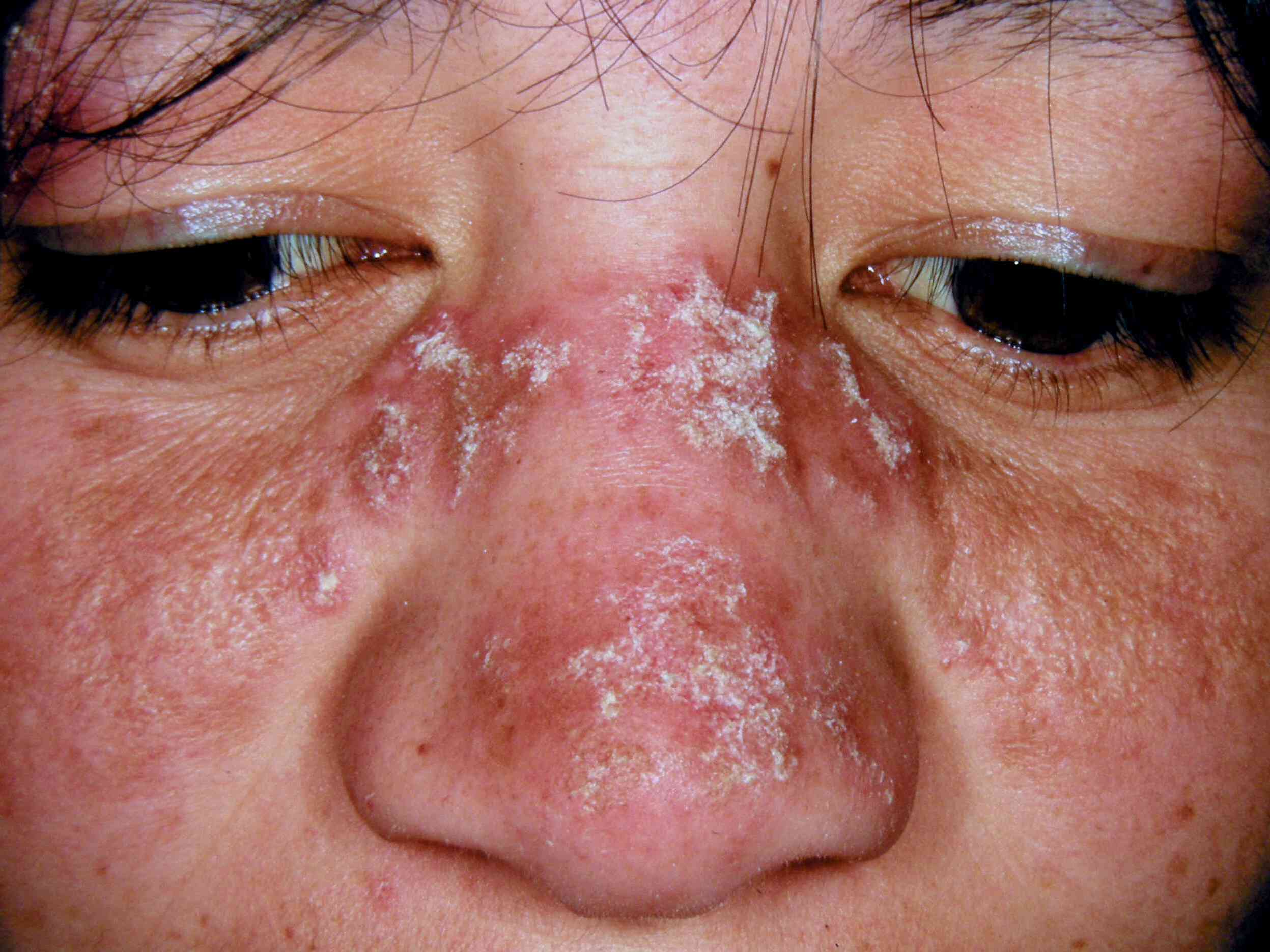
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, scalp, and ears. But what exactly is DLE? It's a form of lupus that causes red, inflamed patches on the skin, which can lead to scarring and pigment changes. Unlike systemic lupus, DLE doesn't typically affect internal organs. This condition is more common in women and often appears between the ages of 20 and 40. What causes DLE? The exact cause remains unknown, but factors like genetics, sunlight exposure, and smoking can trigger or worsen symptoms. Understanding DLE is crucial for managing its impact on daily life. Let's dive into 50 facts that will help you grasp this condition better.
Key Takeaways:
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic skin condition that mainly affects the face, scalp, and ears. It's not contagious and can be managed with medications, lifestyle changes, and support.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of DLE can prevent complications. Lifestyle adjustments, regular check-ups, and staying informed about the condition can improve quality of life for those living with DLE.
What is Discoid Lupus Erythematosus?
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic skin condition. It primarily affects the face, scalp, and ears. Understanding DLE can help manage its symptoms better.
- DLE is a type of lupus: Unlike systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), DLE mainly affects the skin.
- Autoimmune disorder: The body’s immune system attacks its own tissues.
- Chronic condition: Symptoms can last for years or even a lifetime.
- More common in women: Women are more likely to develop DLE than men.
- Affects all ages: Both children and adults can get DLE.
- Sun exposure triggers symptoms: UV light can worsen the condition.
- Red, scaly patches: These patches are the hallmark of DLE.
- Scarring is common: Lesions can leave permanent scars.
- Hair loss: Scalp involvement can lead to hair loss.
- Not contagious: DLE cannot be spread from person to person.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of DLE
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management. Diagnosis often involves a combination of clinical evaluation and tests.
- Butterfly rash: A rash across the cheeks and nose is common.
- Lesions on the scalp: These can lead to permanent hair loss.
- Thickened skin: Affected areas may become thick and crusty.
- Discoloration: Skin may become lighter or darker in affected areas.
- Itching and pain: Lesions can be itchy or painful.
- Photosensitivity: Skin reacts negatively to sunlight.
- Biopsy for diagnosis: A skin biopsy can confirm DLE.
- Blood tests: These can help rule out systemic lupus.
- Direct immunofluorescence: This test can detect immune deposits in the skin.
- Clinical evaluation: A dermatologist examines the skin for characteristic signs.
Treatment Options for DLE
Managing DLE involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Early treatment can prevent complications.
- Topical steroids: These reduce inflammation and redness.
- Antimalarial drugs: Hydroxychloroquine is commonly used.
- Immunosuppressants: These help control the immune system.
- Avoiding sun exposure: Wearing protective clothing and using sunscreen is crucial.
- Vitamin D supplements: These may be needed due to limited sun exposure.
- Regular check-ups: Monitoring by a dermatologist is important.
- Moisturizers: These can help soothe dry, scaly skin.
- Laser therapy: Used for treating scars and lesions.
- Smoking cessation: Smoking can worsen DLE symptoms.
- Stress management: Stress can trigger flare-ups.
Living with DLE
Living with DLE requires adjustments and support. Understanding how to manage daily life can improve quality of life.
- Support groups: Connecting with others who have DLE can be helpful.
- Healthy diet: A balanced diet supports overall health.
- Regular exercise: Helps maintain physical and mental well-being.
- Mental health care: Counseling can help cope with the emotional impact.
- Education: Learning about DLE empowers patients.
- Skin care routine: Gentle, non-irritating products are best.
- Protective clothing: Long sleeves and hats protect against UV rays.
- Avoiding triggers: Identifying and avoiding personal triggers is key.
- Medication adherence: Taking medications as prescribed is crucial.
- Family support: Family understanding and support are important.
Research and Future Directions
Research continues to improve understanding and treatment of DLE. Advances in science offer hope for better management.
- Genetic studies: Research into genetic factors is ongoing.
- New medications: Development of new drugs is underway.
- Clinical trials: Participation in trials can provide access to new treatments.
- Biomarkers: Identifying biomarkers can help in early diagnosis.
- Patient registries: Collecting data helps researchers understand DLE better.
- Immunotherapy: New approaches in immunotherapy are being explored.
- Telemedicine: Virtual consultations provide easier access to specialists.
- Public awareness: Increasing awareness helps reduce stigma.
- Funding for research: More funding is needed for continued research.
- Collaborative efforts: Collaboration between researchers, doctors, and patients is essential.
Final Thoughts on Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) is a chronic skin condition that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing this disease. Early diagnosis and proper medical care can help control flare-ups and reduce scarring. Lifestyle changes, like avoiding sun exposure and quitting smoking, can also make a big difference.
Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is essential for those living with DLE. Staying informed about the latest research and treatments can empower patients to take an active role in their health. Remember, while DLE can be challenging, many people lead full, active lives with the right care and support. If you or someone you know is affected by DLE, don't hesitate to seek medical advice and support.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
