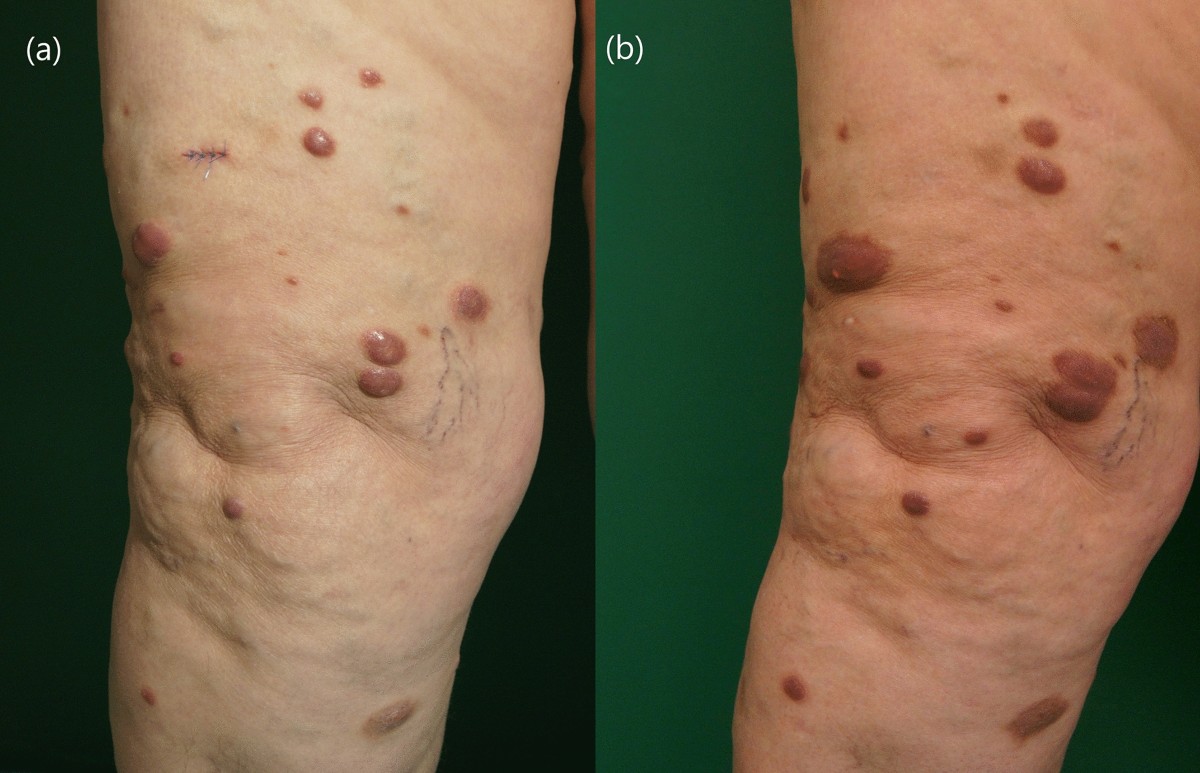
Rosai–Dorfman Disease might sound like a mouthful, but it's a rare disorder that affects the lymph nodes. What exactly is Rosai–Dorfman Disease? It's a condition where a type of white blood cell called histiocytes builds up in the lymph nodes, causing them to swell. This disease can also affect other parts of the body, like the skin, bones, and even the central nervous system. While it mostly shows up in children and young adults, anyone can get it. Symptoms can range from painless swollen lymph nodes to fever, weight loss, and night sweats. Understanding this disease can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment.
Key Takeaways:
- Rosai-Dorfman Disease is a rare condition causing lymph node swelling and other symptoms. It can affect anyone, but is most common in children and young adults. Treatment options include observation, steroids, and surgery.
- Research is ongoing to better understand and treat Rosai-Dorfman Disease. Some patients may experience spontaneous remission, while others may have a chronic, relapsing course. Support groups and clinical trials offer hope for the future.
What is Rosai-Dorfman Disease?
Rosai-Dorfman Disease (RDD) is a rare disorder characterized by an overproduction of a type of white blood cell called histiocytes. These cells can accumulate in lymph nodes and other tissues, causing various symptoms.
- Rare Condition: RDD is considered a rare disease, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
- First Described in 1969: The disease was first identified by pathologists Juan Rosai and Ronald Dorfman.
- Histiocytes Overproduction: The hallmark of RDD is the overproduction of histiocytes, a type of immune cell.
- Lymph Node Swelling: One of the most common symptoms is painless swelling of the lymph nodes, particularly in the neck.
- Extranodal Involvement: RDD can affect other parts of the body, including skin, bones, and central nervous system.
- Unknown Cause: The exact cause of RDD remains unknown, though some researchers suspect a viral or genetic origin.
- Self-Limiting: In many cases, RDD is self-limiting and may resolve without treatment.
- Chronic Course: Some patients experience a chronic course with recurring symptoms.
- No Gender Preference: RDD affects both males and females equally.
- Pediatric Cases: While it can occur at any age, RDD is most commonly diagnosed in children and young adults.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how RDD is diagnosed can help in early detection and management of the disease.
- Fever: Some patients may experience fever as a symptom.
- Night Sweats: Night sweats are another common symptom associated with RDD.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur in some cases.
- Skin Lesions: Extranodal involvement can lead to skin lesions, which may be mistaken for other skin conditions.
- Bone Pain: When bones are affected, patients may experience bone pain or fractures.
- Neurological Symptoms: If the central nervous system is involved, symptoms can include headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits.
- Biopsy for Diagnosis: A biopsy of the affected tissue is often required to confirm the diagnosis.
- Imaging Tests: Imaging tests like CT scans or MRIs can help identify the extent of the disease.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may show elevated levels of certain immune cells.
- Misdiagnosis: Due to its rarity and varied symptoms, RDD is often misdiagnosed as other conditions.
Treatment Options
While some cases of RDD resolve on their own, others may require medical intervention.
- Observation: In cases where symptoms are mild, doctors may opt for a watch-and-wait approach.
- Steroids: Corticosteroids can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of affected lymph nodes or tissues may be necessary in some cases.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy drugs can be used in severe or refractory cases.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy is another option for treating localized disease.
- Immunotherapy: Newer treatments include immunotherapy, which targets the immune system.
- Antiviral Medications: If a viral cause is suspected, antiviral medications may be prescribed.
- Pain Management: Pain management strategies are important for patients experiencing bone pain or other discomforts.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility and quality of life.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: Treatment often involves a team of specialists, including oncologists, dermatologists, and neurologists.
Prognosis and Research
The prognosis for RDD varies, and ongoing research aims to better understand and treat this rare disease.
- Variable Prognosis: The prognosis for RDD varies widely depending on the extent and location of the disease.
- Spontaneous Remission: Some patients experience spontaneous remission without treatment.
- Chronic Disease: Others may have a chronic, relapsing course.
- Research Ongoing: Research is ongoing to better understand the underlying causes and develop new treatments.
- Genetic Studies: Some studies are exploring potential genetic factors involved in RDD.
- Clinical Trials: Clinical trials are testing new therapies and treatment approaches.
- Patient Registries: Patient registries help collect data and improve understanding of the disease.
- Support Groups: Support groups and online communities provide resources and support for patients and families.
- Awareness Campaigns: Awareness campaigns aim to educate healthcare providers and the public about RDD.
- Future Therapies: Advances in medical research hold promise for more effective treatments in the future.
Final Thoughts on Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman Disease, though rare, offers a fascinating glimpse into the complexities of the human body. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help those affected navigate their health journey more effectively. From its discovery by Juan Rosai and Ronald Dorfman to the various ways it manifests, this disease underscores the importance of medical research and awareness. While it primarily affects lymph nodes, it can also impact other organs, making early diagnosis crucial. Treatments vary, ranging from observation to more aggressive therapies like chemotherapy. Staying informed and consulting healthcare professionals can make a significant difference. Knowledge is power, especially when dealing with such a rare condition. Keep these facts in mind, and you'll be better prepared to understand and support those living with Rosai-Dorfman Disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
