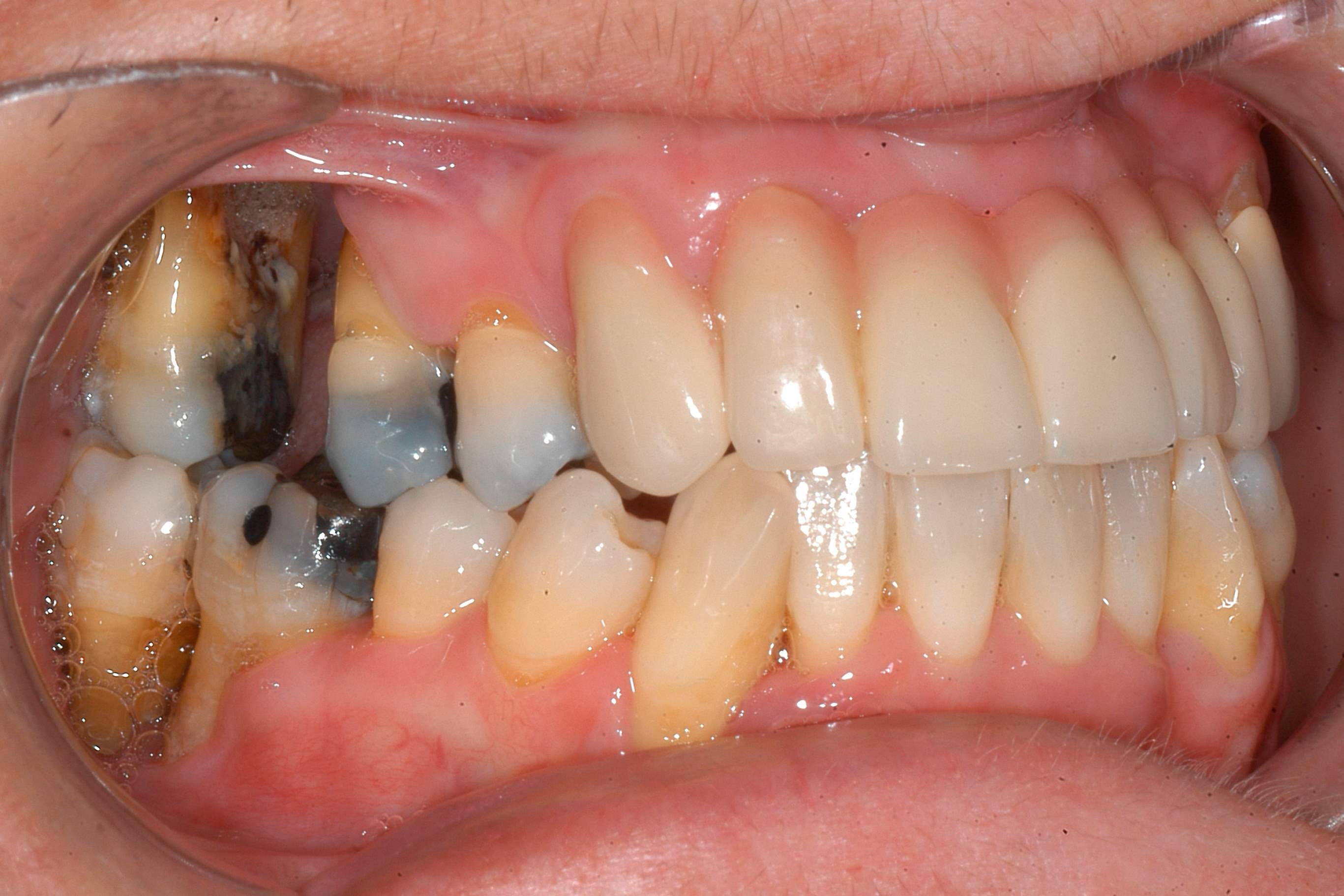
Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (pEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues, leading to severe dental and gum issues. Imagine having teeth that seem to fall out without much effort or gums that bleed easily. This condition can make everyday activities like eating and speaking quite challenging. pEDS isn't just about dental problems; it also involves joint hypermobility, skin that bruises easily, and other systemic issues. Understanding this syndrome can help those affected manage symptoms better and improve their quality of life. Let's dive into 40 facts about Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome to shed light on this complex condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (pEDS) is a rare genetic disorder causing severe gum disease, loose teeth, joint hypermobility, and other symptoms. Diagnosis and management involve genetic testing, dental care, and emotional support.
- Living with pEDS requires regular monitoring, adaptive devices, gentle skin care, and a positive outlook. Support groups, low-impact exercises, and hydration are essential for managing symptoms and improving overall well-being.
What is Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (pEDS) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects connective tissues, leading to various symptoms, particularly in the gums and teeth. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Origin: pEDS is caused by mutations in the C1R and C1S genes. These genes are responsible for producing proteins that help form connective tissues.
-
Inheritance Pattern: This syndrome follows an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. This means only one copy of the mutated gene from either parent can cause the disorder.
-
Early-Onset Periodontitis: One of the hallmark symptoms is severe gum disease, known as periodontitis, which starts in childhood or adolescence.
-
Loose Teeth: Due to weakened connective tissues, individuals with pEDS often experience loose teeth at an early age.
-
Gum Recession: Gums may recede significantly, exposing more of the tooth and increasing the risk of tooth loss.
-
Fragile Skin: Skin may be unusually soft, stretchy, and prone to bruising and tearing.
-
Joint Hypermobility: Many people with pEDS have joints that move beyond the normal range, leading to frequent dislocations and sprains.
-
Delayed Wound Healing: Wounds may take longer to heal, and scars can be thin and wide.
-
Easy Bruising: Individuals with pEDS often bruise easily due to fragile blood vessels.
-
Thin Skin: The skin may appear translucent, especially on the hands and feet.
Symptoms Beyond the Mouth
While pEDS primarily affects the gums and teeth, it can also cause a variety of other symptoms throughout the body.
-
Chronic Pain: Joint and muscle pain are common due to hypermobility and frequent injuries.
-
Fatigue: Many individuals experience chronic fatigue, which can impact daily activities.
-
Gastrointestinal Issues: Digestive problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), are often reported.
-
Heart Valve Problems: Some people with pEDS may develop issues with their heart valves, requiring medical monitoring.
-
Eye Problems: Fragile blood vessels in the eyes can lead to vision issues or easy bruising around the eyes.
-
Hernias: The weakened connective tissue can result in hernias, where an organ pushes through the muscle or tissue holding it in place.
-
Prolapsed Organs: Organs such as the bladder or uterus may prolapse, or slip out of place.
-
Varicose Veins: Weakened blood vessels can lead to varicose veins, which are swollen and twisted veins visible under the skin.
-
Flat Feet: Due to joint hypermobility, flat feet are a common occurrence.
-
Dental Crowding: Teeth may be crowded or misaligned, requiring orthodontic treatment.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosing and managing pEDS can be challenging due to its rarity and the variety of symptoms it presents.
-
Genetic Testing: Confirming a diagnosis often involves genetic testing to identify mutations in the C1R and C1S genes.
-
Clinical Evaluation: A thorough clinical evaluation by a specialist familiar with Ehlers-Danlos syndromes is crucial.
-
Dental Care: Regular dental check-ups and aggressive periodontal treatment are essential to manage gum disease.
-
Orthodontic Treatment: Braces or other orthodontic devices may be needed to address dental crowding and misalignment.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help manage joint pain and improve mobility.
-
Pain Management: Chronic pain may require a combination of medications, physical therapy, and other interventions.
-
Cardiac Monitoring: Regular heart check-ups are important to monitor for potential valve issues.
-
Nutritional Support: A balanced diet and possibly supplements can help manage gastrointestinal symptoms and overall health.
-
Psychological Support: Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, so psychological support or counseling may be beneficial.
-
Patient Education: Educating patients and their families about the condition and its management is crucial for improving quality of life.
Living with Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Living with pEDS requires ongoing management and support, but many individuals lead fulfilling lives with the right care.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others with similar experiences.
-
Adaptive Devices: Using adaptive devices, such as braces or splints, can help manage joint instability.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular medical and dental check-ups are essential to catch and address issues early.
-
Exercise: Low-impact exercises, like swimming or yoga, can help maintain joint health and overall fitness.
-
Avoiding Injury: Taking precautions to avoid injuries, such as using protective gear during activities, is important.
-
Skin Care: Gentle skin care routines can help manage fragile skin and prevent injuries.
-
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can help maintain skin and joint health.
-
Medication Management: Keeping track of medications and their effects is crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
-
Emergency Plan: Having an emergency plan in place for sudden health issues can provide peace of mind.
-
Positive Outlook: Maintaining a positive outlook and focusing on what can be controlled can improve overall well-being.
Final Thoughts on Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (pEDS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects connective tissues, leading to severe dental issues, fragile skin, and joint problems. Understanding the symptoms and seeking early diagnosis can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Regular dental check-ups, maintaining good oral hygiene, and consulting with specialists can help manage the condition effectively. Genetic counseling is also crucial for families with a history of pEDS to understand the risks and implications. While there is no cure, advancements in medical research continue to offer hope for better treatments and management strategies. Staying informed and proactive is key to navigating the challenges posed by pEDS. Remember, knowledge is power, and being aware of the facts can make a significant difference in managing this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
