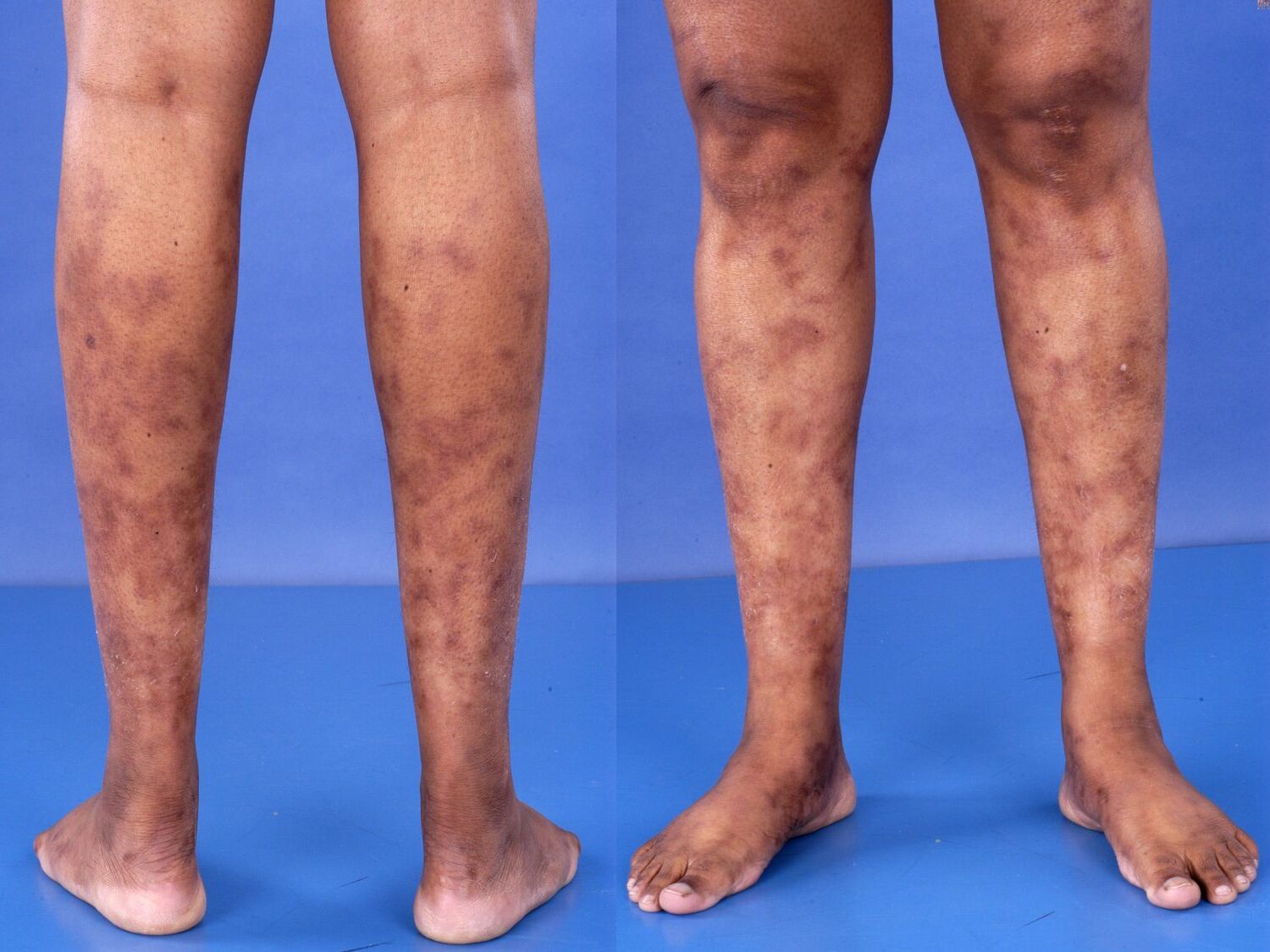
Periarteritis Nodosa is a rare but serious disease that affects small and medium-sized arteries, causing them to become inflamed and damaged. This inflammation can lead to a variety of symptoms, depending on which organs are involved. Common symptoms include fever, fatigue, weight loss, muscle pain, and abdominal pain. The exact cause of periarteritis nodosa remains unknown, but it is believed to be related to an abnormal immune response. Diagnosis often involves blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes a biopsy of affected tissue. Treatment typically includes medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. Understanding this condition is crucial for early detection and effective management.
Key Takeaways:
- Periarteritis Nodosa is a rare disease causing inflammation in blood vessels, affecting organs and tissues. It can be managed with treatments and lifestyle changes, but regular monitoring is crucial.
- Research and awareness efforts are essential to better understand and support those affected by Periarteritis Nodosa. Collaboration and education can improve diagnosis, treatment, and patient well-being.
What is Periarteritis Nodosa?
Periarteritis Nodosa (PAN) is a rare disease that affects the arteries. It causes inflammation and damage to the blood vessels, which can lead to serious health issues. Here are some important facts about this condition.
- PAN is a type of vasculitis, which means it involves inflammation of blood vessels.
- The disease primarily affects medium-sized arteries, which supply blood to organs and tissues.
- PAN can cause aneurysms, which are bulges in the walls of blood vessels that can burst and cause internal bleeding.
- The exact cause of PAN is unknown, but it is believed to involve an abnormal immune response.
- PAN is more common in men than women.
- The disease can occur at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in people between 40 and 60 years old.
- PAN can affect various organs, including the kidneys, heart, liver, and intestines.
- Symptoms of PAN can vary widely depending on which organs are affected.
- Common symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, muscle and joint pain.
- Skin lesions, such as ulcers or nodules, can also occur in people with PAN.
Diagnosing Periarteritis Nodosa
Diagnosing PAN can be challenging due to its varied symptoms. Doctors use a combination of tests and clinical evaluations to identify the disease.
- Blood tests can show elevated levels of inflammatory markers, which suggest the presence of inflammation.
- Imaging studies, such as angiography, can reveal abnormalities in blood vessels.
- A biopsy, where a small sample of tissue is taken and examined under a microscope, can confirm the diagnosis.
- Doctors may also use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans to look for signs of organ damage.
- In some cases, a nerve conduction study may be performed to assess nerve function.
Treatment Options for Periarteritis Nodosa
While there is no cure for PAN, various treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Corticosteroids, such as prednisone, are often used to reduce inflammation.
- Immunosuppressive drugs, like cyclophosphamide or azathioprine, can help control the immune system.
- In severe cases, plasmapheresis, a procedure that removes antibodies from the blood, may be used.
- Pain management strategies, including medications and physical therapy, can help alleviate discomfort.
- Regular monitoring and follow-up care are essential to manage the disease effectively.
Complications of Periarteritis Nodosa
If left untreated, PAN can lead to serious complications that affect various parts of the body.
- Kidney damage is a common complication, which can lead to high blood pressure and kidney failure.
- Heart problems, such as heart attacks or heart failure, can occur due to damage to the coronary arteries.
- Gastrointestinal issues, including bowel perforation or bleeding, can result from damage to the blood vessels in the intestines.
- Peripheral neuropathy, a condition that affects the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord, can cause pain, weakness, and numbness.
- Skin ulcers and gangrene can develop due to poor blood flow to the skin.
Living with Periarteritis Nodosa
Managing PAN requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and support.
- A healthy diet and regular exercise can help improve overall health and reduce inflammation.
- Avoiding smoking and limiting alcohol intake can help prevent further damage to blood vessels.
- Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce stress and improve well-being.
- Support groups and counseling can provide emotional support and help patients cope with the challenges of living with a chronic illness.
- Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the disease and adjust treatment as needed.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is essential to better understand PAN and develop new treatments.
- Scientists are studying the genetic factors that may contribute to the development of PAN.
- Research is also focused on identifying new biomarkers that can help diagnose the disease earlier.
- Clinical trials are testing new medications and therapies to improve treatment outcomes.
- Advances in imaging technology are helping doctors better visualize blood vessel abnormalities.
- Collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and patients is crucial to advancing our understanding of PAN.
Raising Awareness about Periarteritis Nodosa
Increasing awareness about PAN can help improve diagnosis, treatment, and support for those affected by the disease.
- Educational campaigns can help inform the public and healthcare professionals about the signs and symptoms of PAN.
- Advocacy groups can provide resources and support for patients and their families.
- Fundraising efforts can support research and help develop new treatments.
- Social media and online platforms can help connect patients and provide a sense of community.
- Sharing personal stories and experiences can help raise awareness and reduce the stigma associated with chronic illnesses.
Final Thoughts on Periarteritis Nodosa
Periarteritis Nodosa, or PAN, is a rare but serious disease that affects small and medium-sized arteries. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can make a huge difference in managing the condition. Early diagnosis is key to preventing severe complications. Treatments often include medications like corticosteroids and immunosuppressants, which help reduce inflammation and control the immune system.
Living with PAN can be challenging, but support from healthcare providers, family, and friends can make it easier. Staying informed and proactive about your health is crucial. Regular check-ups and following your treatment plan can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Remember, while PAN is rare, awareness and education can lead to better outcomes for those affected. Stay vigilant, seek medical advice if you notice symptoms, and support research efforts to find better treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
