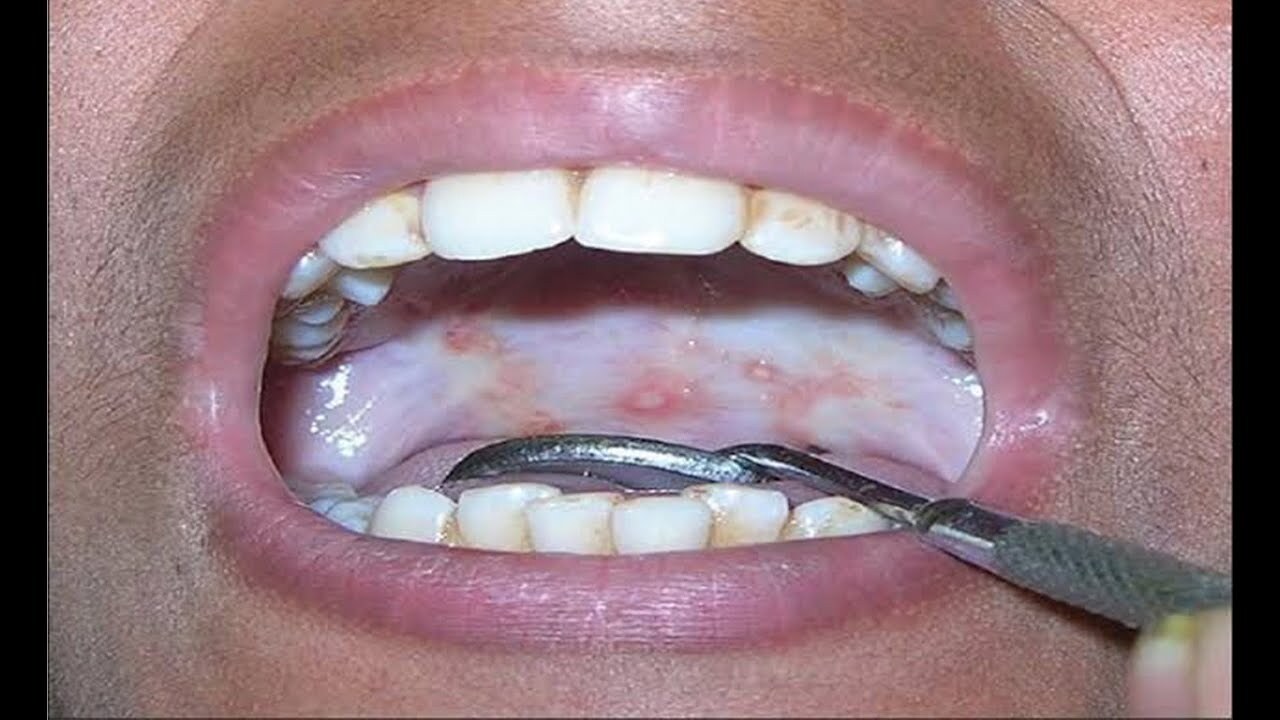
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF) is a chronic, progressive condition affecting the mouth. It causes the tissues in the mouth to become stiff, leading to difficulty in opening the mouth and swallowing. This condition is often linked to the chewing of betel nut, a common practice in some cultures. Symptoms include a burning sensation, restricted mouth opening, and a leathery texture of the oral tissues. Early diagnosis is crucial to manage the symptoms and prevent further complications. Treatment options range from lifestyle changes to medical interventions. Understanding OSMF can help in recognizing the signs early and seeking appropriate care.
Key Takeaways:
- Oral Submucous Fibrosis is a serious condition that can lead to oral cancer if not treated early. Betel nut chewing, spicy foods, and poor oral hygiene are major risk factors.
- Managing Oral Submucous Fibrosis involves stopping betel nut chewing, taking nutritional supplements, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals. Support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
What is Oral Submucous Fibrosis?
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF) is a chronic, progressive condition affecting the mouth. It primarily involves the mucous lining of the oral cavity, leading to stiffness and restricted mouth opening. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition:
-
OSMF is a potentially malignant disorder. This means it can transform into oral cancer if not treated promptly.
-
Betel nut chewing is a major cause. The habit of chewing betel nut, common in South Asian countries, significantly increases the risk of developing OSMF.
-
It affects both genders. Although more prevalent in males, females are also susceptible to OSMF.
-
Symptoms include burning sensation. Patients often experience a burning sensation in the mouth, especially when consuming spicy foods.
-
Restricted mouth opening is a key sign. As the disease progresses, the mouth's opening becomes increasingly limited.
-
It can affect speech. Severe cases of OSMF can lead to difficulties in speaking due to restricted tongue movement.
-
Swallowing becomes challenging. The fibrosis can make swallowing food and liquids difficult.
-
OSMF is irreversible. Once the fibrosis sets in, it cannot be completely reversed, only managed.
-
Early diagnosis is crucial. Detecting OSMF in its early stages can prevent progression and potential malignant transformation.
-
Biopsy confirms diagnosis. A tissue biopsy is often required to confirm the presence of OSMF.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of OSMF can help in prevention and early intervention. Here are some key points:
-
Genetic predisposition plays a role. Some individuals may be genetically more susceptible to developing OSMF.
-
Nutritional deficiencies contribute. Lack of essential nutrients like iron and vitamins can exacerbate the condition.
-
Tobacco use is a risk factor. Both smoking and smokeless tobacco use can increase the risk of OSMF.
-
Chronic irritation is harmful. Continuous irritation from rough teeth or ill-fitting dentures can contribute to OSMF.
-
Spicy foods can aggravate symptoms. Consuming very spicy foods can worsen the burning sensation associated with OSMF.
-
Alcohol consumption is linked. Regular alcohol intake can increase the risk of developing OSMF.
-
Poor oral hygiene is a factor. Neglecting oral hygiene can contribute to the development and progression of OSMF.
-
Environmental factors matter. Exposure to certain environmental toxins and pollutants can increase the risk.
-
Autoimmune responses may be involved. Some studies suggest that autoimmune responses could play a role in OSMF.
-
Hormonal imbalances can influence. Hormonal changes, especially in women, may affect the progression of OSMF.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is essential for managing OSMF effectively. Here are some important facts:
-
Early symptoms are subtle. Initial symptoms may include mild discomfort and a burning sensation in the mouth.
-
White patches may appear. The presence of white patches or lesions in the mouth can be an early sign of OSMF.
-
Fibrous bands form. As the disease progresses, fibrous bands develop in the oral mucosa, leading to stiffness.
-
Mouth ulcers are common. Recurrent mouth ulcers can be a symptom of OSMF.
-
Loss of pigmentation occurs. The affected areas may lose their normal pigmentation, appearing pale or white.
-
Difficulty in chewing. Patients often find it hard to chew food due to restricted mouth opening.
-
Nasal voice may develop. In advanced cases, the voice may become nasal due to restricted oral cavity space.
-
Saliva production decreases. Reduced saliva production can lead to dry mouth and further complications.
-
Pain in the ears. Some patients experience referred pain in the ears due to the fibrosis.
-
Regular dental check-ups are vital. Routine dental visits can help in early detection and management of OSMF.
Treatment and Management
Managing OSMF involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and regular monitoring. Here are some key points:
-
Cessation of betel nut chewing is crucial. Stopping the habit of chewing betel nut is essential to prevent further progression.
-
Nutritional supplements can help. Taking supplements to address nutritional deficiencies can aid in managing OSMF.
-
Steroid injections are used. Intralesional steroid injections can help reduce inflammation and fibrosis.
-
Physiotherapy is beneficial. Mouth exercises and physiotherapy can improve mouth opening and mobility.
-
Surgical intervention may be needed. In severe cases, surgery may be required to release fibrous bands and improve mouth opening.
-
Antioxidants are prescribed. Antioxidant supplements can help in reducing oxidative stress and managing OSMF.
-
Regular monitoring is essential. Continuous monitoring by healthcare professionals is crucial to manage the condition effectively.
-
Avoiding irritants is important. Patients should avoid irritants like spicy foods, tobacco, and alcohol.
-
Pain management is necessary. Pain relief medications may be prescribed to manage discomfort and pain.
-
Support groups can help. Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing OSMF.
Final Thoughts on Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Oral Submucous Fibrosis (OSMF) is a serious condition that affects many people, especially in regions where betel nut chewing is common. Understanding the symptoms and risk factors can help in early detection and treatment. OSMF can lead to severe complications like difficulty in eating, speaking, and even an increased risk of oral cancer. Regular dental check-ups and avoiding risk factors like tobacco and betel nut can significantly reduce the chances of developing this condition.
If you or someone you know shows signs of OSMF, seeking medical advice promptly is crucial. Early intervention can make a big difference in managing the disease and improving quality of life. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and take proactive steps to protect your oral health. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to preventing and managing health issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
