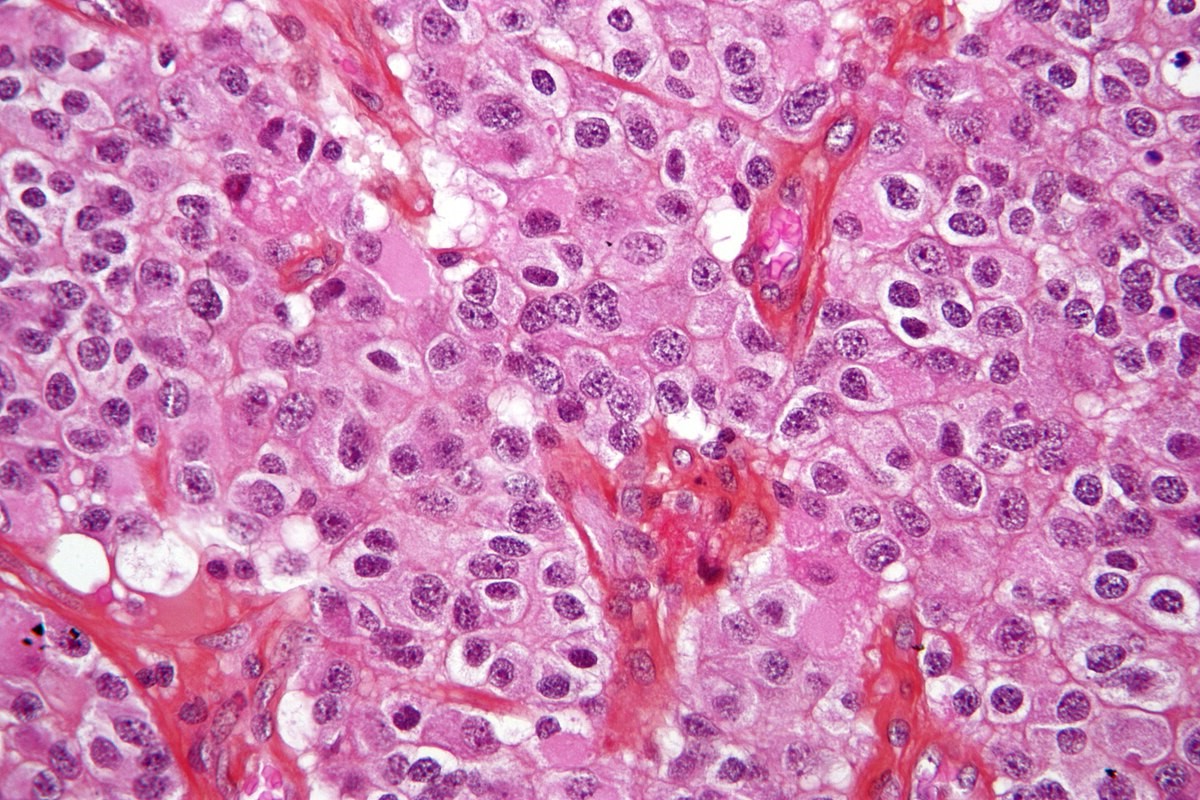
What is an oligodendroglioma? It's a type of brain tumor that starts in cells called oligodendrocytes. These cells are part of the central nervous system, helping to produce a substance called myelin, which protects nerve fibers. Oligodendrogliomas are considered rare and typically grow slowly, but they can vary in behavior and severity. They often occur in adults, with a higher incidence in those aged 40 to 60, though they can appear at any age. Symptoms might include headaches, seizures, or changes in behavior, depending on the tumor's location. Diagnosis usually involves imaging tests like MRI and a biopsy to confirm the type of tumor. Treatment options often include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, tailored to the individual's specific situation. Understanding oligodendroglioma is crucial for managing the condition effectively and improving quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Oligodendroglioma is a rare brain tumor that affects adults aged 30-50, with symptoms like headaches and seizures. Treatment options include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy, with survival rates varying based on tumor grade and genetic markers.
- Living with oligodendroglioma involves joining support groups, addressing mental health, making lifestyle adjustments, and involving family members in care. Despite challenges, patients can find joy and pursue their passions with the right support.
What is Oligodendroglioma?
Oligodendroglioma is a rare type of brain tumor that originates from oligodendrocytes, the cells responsible for producing myelin in the central nervous system. Understanding this condition can be crucial for those affected and their families. Here are some intriguing facts about oligodendroglioma.
-
Rare Occurrence: Oligodendrogliomas account for only about 2% of all brain tumors, making them quite uncommon.
-
Origin: These tumors develop from oligodendrocytes, which are cells that provide support and insulation to nerve fibers in the brain.
-
Location: They are most commonly found in the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
-
Age Factor: Typically, oligodendrogliomas are diagnosed in adults between the ages of 30 and 50.
-
Gender Prevalence: Men are slightly more likely to develop this type of tumor than women.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include headaches, seizures, and changes in personality or behavior.
-
Diagnosis: MRI and CT scans are often used to diagnose oligodendrogliomas.
-
Biopsy Confirmation: A biopsy is usually required to confirm the diagnosis and determine the tumor's grade.
-
Grading System: Oligodendrogliomas are graded based on their aggressiveness, with Grade II being less aggressive and Grade III being more aggressive.
-
Genetic Markers: The presence of certain genetic markers, such as 1p/19q co-deletion, can influence prognosis and treatment options.
Treatment Options for Oligodendroglioma
Treatment for oligodendroglioma varies depending on the tumor's grade and location. Here are some key facts about the treatment options available.
-
Surgery: Surgical removal is often the first step in treating oligodendrogliomas, especially if the tumor is accessible.
-
Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells, often used after surgery.
-
Chemotherapy: Drugs like temozolomide may be used to treat oligodendrogliomas, particularly those with specific genetic markers.
-
Watchful Waiting: In some cases, especially with slow-growing tumors, doctors may recommend monitoring the tumor before starting treatment.
-
Clinical Trials: Patients may have the option to participate in clinical trials to access new and experimental treatments.
-
Personalized Treatment: Treatment plans are often tailored to the individual, taking into account the tumor's genetic profile.
-
Side Effects: Treatments can have side effects, including fatigue, nausea, and cognitive changes.
-
Rehabilitation: Post-treatment rehabilitation may be necessary to help patients recover cognitive and physical functions.
-
Supportive Care: Palliative care can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life for patients with advanced tumors.
-
Multidisciplinary Approach: Treatment often involves a team of specialists, including neurosurgeons, oncologists, and radiologists.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Understanding the prognosis and survival rates for oligodendroglioma can provide insight into what patients and families might expect.
-
Prognosis Factors: Factors influencing prognosis include tumor grade, genetic markers, and patient age.
-
Survival Rates: The 5-year survival rate for Grade II oligodendroglioma is approximately 70-90%.
-
Grade III Survival: For Grade III, the 5-year survival rate drops to around 30-50%.
-
Genetic Influence: Tumors with the 1p/19q co-deletion generally have a better prognosis.
-
Recurrence: Oligodendrogliomas can recur, necessitating ongoing monitoring and potential additional treatment.
-
Long-term Monitoring: Regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests are crucial for detecting any changes in the tumor.
-
Quality of Life: Many patients maintain a good quality of life with appropriate treatment and support.
-
Research Advances: Ongoing research is focused on improving treatment outcomes and understanding the biology of these tumors.
-
Survivorship Care: Long-term care plans can help manage the physical and emotional challenges faced by survivors.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in personalized medicine and targeted therapies offer hope for improved outcomes.
Living with Oligodendroglioma
Living with oligodendroglioma involves adapting to changes and finding ways to maintain a fulfilling life. Here are some facts about managing life with this condition.
-
Support Networks: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others facing similar challenges.
-
Mental Health: Addressing mental health is important, as anxiety and depression can be common among patients.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support overall well-being.
-
Cognitive Challenges: Some patients may experience cognitive changes, requiring strategies to manage memory and concentration issues.
-
Work and Education: Patients may need to adjust their work or education plans to accommodate treatment and recovery.
-
Family Involvement: Family members often play a crucial role in providing care and support.
-
Financial Planning: Managing the financial aspects of treatment can be challenging, and seeking financial advice may be beneficial.
-
Legal Considerations: Patients may need to address legal matters, such as power of attorney and healthcare directives.
-
Advocacy: Getting involved in advocacy efforts can help raise awareness and support research funding.
-
Finding Joy: Despite the challenges, many patients find ways to enjoy life and pursue their passions.
Final Thoughts on Oligodendroglioma Facts
Understanding oligodendroglioma is crucial for anyone dealing with this condition. These tumors, though rare, present unique challenges and opportunities for medical advancements. Knowing that they often respond well to treatment provides hope, but early detection remains key. The genetic markers like 1p/19q co-deletion play a significant role in determining the best treatment options and prognosis.
Symptoms can vary, making awareness essential for early diagnosis. While surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy are common treatments, ongoing research continues to explore new avenues. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is invaluable for those affected.
Staying informed about the latest research and treatment options can empower patients and their families. With advancements in medical science, the outlook for those with oligodendroglioma continues to improve, offering hope for a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
