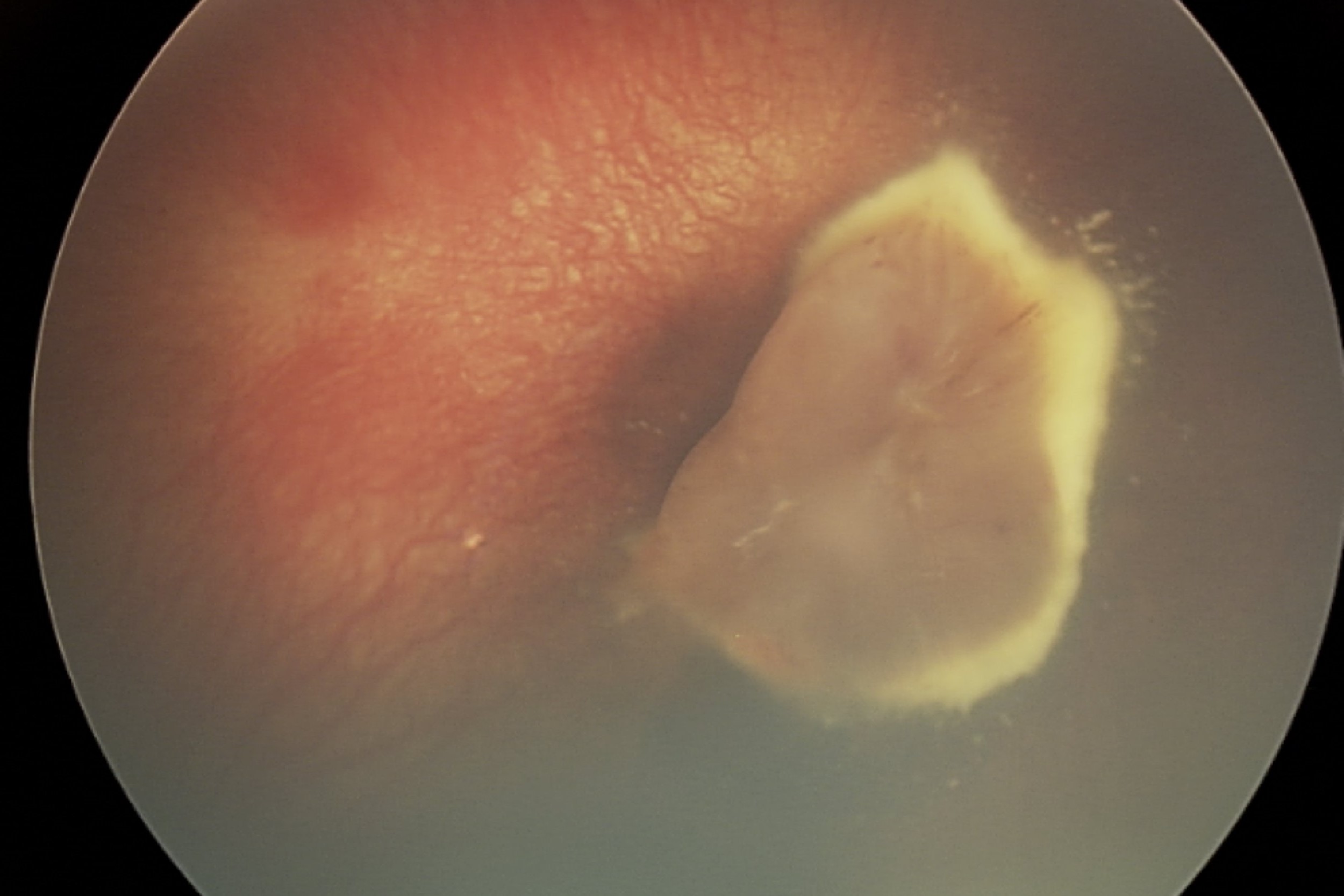
Norrie Disease is a rare genetic disorder that primarily affects the eyes and can lead to blindness. This condition is caused by mutations in the NDP gene, which plays a crucial role in the development of the retina. Symptoms often appear at birth or in early childhood, with affected individuals experiencing progressive vision loss. In addition to vision problems, some may also face hearing loss, developmental delays, or behavioral challenges. Norrie Disease is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern, meaning it mostly affects males, while females are typically carriers. Diagnosis involves genetic testing and thorough clinical evaluations. While there's no cure, early intervention and supportive therapies can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Understanding this condition is vital for those affected and their families, as it provides insight into potential challenges and available support.
Key Takeaways:
- Norrie Disease is a rare genetic disorder causing blindness, hearing loss, and developmental delays. Early diagnosis and supportive therapies can improve quality of life for affected individuals.
- Understanding the genetic aspects of Norrie Disease can aid in diagnosis and family planning. Genetic testing and counseling play crucial roles in managing the condition.
What is Norrie Disease?
Norrie Disease is a rare genetic disorder primarily affecting the eyes and sometimes causing other developmental issues. Named after Gordon Norrie, a Danish ophthalmologist, this condition is often diagnosed in infancy. Let's explore some fascinating facts about this unique disorder.
-
Genetic Origin: Norrie Disease is caused by mutations in the NDP gene, which is located on the X chromosome. This means it is an X-linked recessive condition, primarily affecting males.
-
Eye Abnormalities: The most common symptom is blindness or severe vision impairment from birth. This happens because the retinas do not develop properly.
-
Hearing Loss: Some individuals with Norrie Disease experience progressive hearing loss, which can begin in childhood or adolescence.
-
Developmental Delays: Affected individuals may face developmental delays, including challenges with motor skills and cognitive functions.
-
Behavioral Issues: Some children with Norrie Disease may exhibit behavioral problems, such as anxiety or attention deficits.
-
Prevalence: It is extremely rare, with estimates suggesting it affects 1 in 100,000 to 1 in 500,000 newborns.
-
Family History: Since it is an inherited condition, family history plays a significant role in diagnosis. Genetic counseling is often recommended for families with a history of the disease.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves genetic testing, eye examinations, and hearing tests to confirm the presence of the disorder.
-
No Cure: Currently, there is no cure for Norrie Disease, but treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Supportive Therapies: Early intervention with therapies such as physical, occupational, and speech therapy can aid in development.
How Does Norrie Disease Affect the Eyes?
The eyes are the most significantly impacted by Norrie Disease. Understanding these effects can help in managing the condition better.
-
Retinal Detachment: The retinas may detach, leading to blindness or severe vision impairment.
-
Cataracts: Some individuals develop cataracts, which are cloudy areas in the lens of the eye.
-
Microphthalmia: This condition causes one or both eyes to be abnormally small.
-
Leukocoria: A white or grayish reflection in the pupil, often referred to as a "cat's eye reflex," is a common sign.
-
Vitreous Hemorrhage: Bleeding into the vitreous humor, the gel-like substance inside the eye, can occur.
-
Glaucoma: Increased pressure in the eye, known as glaucoma, may develop, potentially leading to further vision loss.
-
Optic Nerve Atrophy: The optic nerve, which transmits visual information from the eye to the brain, may deteriorate.
-
Persistent Hyperplastic Primary Vitreous (PHPV): This condition involves the failure of the fetal hyaloid vascular system to regress, affecting eye development.
-
Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgery may be performed to address specific eye issues, such as cataracts or retinal detachment.
-
Regular Eye Exams: Regular monitoring by an ophthalmologist is crucial for managing eye health in individuals with Norrie Disease.
What Are the Genetic Aspects of Norrie Disease?
Genetics play a crucial role in Norrie Disease. Understanding the genetic components can aid in diagnosis and family planning.
-
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance: Since it is X-linked, males are more frequently affected, while females can be carriers.
-
Carrier Females: Female carriers usually do not show symptoms but have a 50% chance of passing the mutated gene to their offspring.
-
New Mutations: In some cases, Norrie Disease results from new mutations, with no family history of the disorder.
-
Genetic Testing: Testing can identify mutations in the NDP gene, confirming the diagnosis and aiding in family planning.
-
Prenatal Testing: For families with a known history, prenatal testing can determine if the fetus has inherited the mutated gene.
-
Genetic Counseling: Counseling is recommended for affected families to understand the risks and implications of the disorder.
-
Research on Gene Therapy: Scientists are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment, aiming to correct the genetic mutation.
-
Mosaicism: Some females may exhibit mild symptoms due to mosaicism, where some cells carry the mutation while others do not.
-
Inheritance Patterns: Understanding inheritance patterns helps in predicting the likelihood of passing the disorder to future generations.
-
Genetic Variability: Different mutations in the NDP gene can result in varying degrees of severity in symptoms.
How Does Norrie Disease Impact Hearing?
Hearing can be affected in individuals with Norrie Disease, adding another layer of complexity to the condition.
-
Progressive Hearing Loss: Hearing loss may worsen over time, often starting in childhood or adolescence.
-
Sensorineural Hearing Loss: This type of hearing loss is due to damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve.
-
Hearing Aids: Devices can help manage hearing loss, improving communication and quality of life.
-
Cochlear Implants: In severe cases, cochlear implants may be considered to enhance hearing capabilities.
-
Regular Hearing Tests: Monitoring hearing regularly is important for early detection and management of hearing loss.
-
Speech Therapy: Therapy can assist in developing communication skills, especially if hearing loss is significant.
-
Auditory Training: Programs designed to improve listening skills can be beneficial for those with hearing impairments.
-
Family Support: Support from family members is crucial in managing the challenges associated with hearing loss.
-
Educational Support: Schools may provide special accommodations to support children with hearing impairments.
-
Community Resources: Access to resources and support groups can help families navigate the challenges of Norrie Disease.
Bringing It All Together
Norrie Disease, a rare genetic disorder, primarily affects males and leads to blindness from birth. This condition, caused by mutations in the NDP gene, can also result in hearing loss and developmental delays. Understanding the symptoms and genetic causes is crucial for early diagnosis and management. While there's no cure, interventions like hearing aids and special education can improve quality of life. Research continues to explore potential treatments, offering hope for future advancements. Families affected by Norrie Disease often find support through community networks and advocacy groups, which provide resources and a sense of belonging. Awareness and education about this condition can lead to better support systems and improved outcomes for those impacted. By staying informed and connected, individuals and families can navigate the challenges of Norrie Disease with resilience and optimism.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
