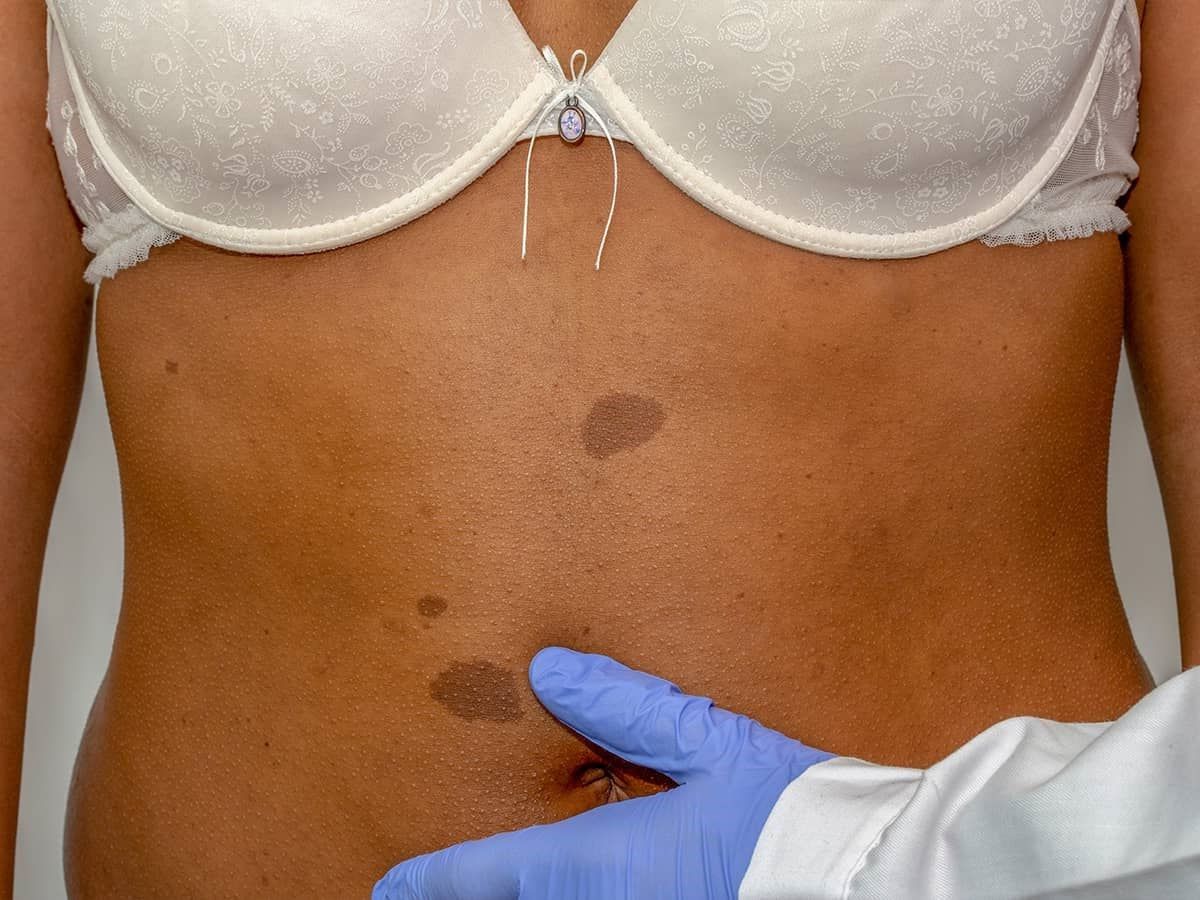
What is a neurofibroma? A neurofibroma is a type of benign tumor that grows on nerves. These tumors are made up of a mix of nerve cells and fibrous tissue. They often appear as soft bumps under the skin and can occur anywhere in the body. While they are usually not cancerous, they can cause problems if they press on nerves or other tissues. Neurofibromas are often associated with a genetic disorder called neurofibromatosis, which can lead to multiple tumors developing throughout the body. Symptoms can vary widely, from mild skin changes to significant nerve pain or dysfunction. Treatment options depend on the size and location of the tumor and may include monitoring, surgery, or other interventions. Understanding neurofibromas is crucial for managing their impact on health and quality of life.
Key Takeaways:
- Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder causing tumors on nerve tissue. It has different types, symptoms, and treatments. With support and adaptive strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite its challenges.
- Early diagnosis and proper management are crucial for living with neurofibromatosis. Support groups, technology aids, and healthy lifestyle choices play a significant role in improving the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that causes tumors to form on nerve tissue. These tumors can develop anywhere in the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Origin: Neurofibromatosis is caused by mutations in specific genes. These mutations can be inherited from a parent or occur spontaneously.
-
Types of Neurofibromatosis: There are three main types: NF1, NF2, and Schwannomatosis. Each type has distinct characteristics and symptoms.
-
NF1 Prevalence: NF1 is the most common form, affecting about 1 in 3,000 people worldwide.
-
NF2 Rarity: NF2 is less common, with an occurrence of about 1 in 25,000 people.
-
Schwannomatosis Rarity: Schwannomatosis is the rarest form, affecting approximately 1 in 40,000 individuals.
-
Tumor Growth: Tumors in neurofibromatosis are usually benign, but they can sometimes become cancerous.
-
Skin Manifestations: People with NF1 often have café-au-lait spots, which are light brown skin patches.
-
Lisch Nodules: These are tiny, benign growths on the iris of the eye, commonly found in individuals with NF1.
-
Hearing Loss: NF2 often leads to hearing loss due to tumors on the auditory nerves.
-
Pain in Schwannomatosis: This type is characterized by chronic pain due to tumors on peripheral nerves.
Diagnosis and Symptoms
Diagnosing neurofibromatosis involves a combination of physical exams, genetic testing, and imaging studies. Here are some key facts about its diagnosis and symptoms.
-
Early Diagnosis: NF1 can often be diagnosed in childhood based on physical symptoms like café-au-lait spots.
-
Genetic Testing: Genetic tests can confirm a diagnosis of neurofibromatosis by identifying mutations in the relevant genes.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans are crucial for detecting tumors in the brain and spinal cord.
-
Symptom Variability: Symptoms can vary widely even among individuals with the same type of neurofibromatosis.
-
Learning Disabilities: Many children with NF1 experience learning disabilities or ADHD.
-
Bone Deformities: NF1 can cause bone deformities, such as scoliosis or bowing of the legs.
-
Vision Problems: Tumors on the optic nerve can lead to vision problems in NF1.
-
Balance Issues: NF2 can cause balance problems due to vestibular schwannomas affecting the inner ear.
-
Skin Tumors: Neurofibromas, or skin tumors, are common in NF1 and can vary in size and number.
-
Headaches: Frequent headaches are a common symptom in individuals with NF2.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for neurofibromatosis, various treatments can help manage symptoms and complications. Let's look at some facts about treatment options.
-
Surgical Removal: Surgery can remove tumors that cause pain or other complications.
-
Radiation Therapy: This may be used to shrink tumors that cannot be surgically removed.
-
Chemotherapy: In cases where tumors become cancerous, chemotherapy might be necessary.
-
Pain Management: Medications and therapies can help manage chronic pain, especially in Schwannomatosis.
-
Hearing Aids: Hearing aids or cochlear implants can assist individuals with NF2-related hearing loss.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can improve mobility and balance in affected individuals.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups and imaging tests are essential for monitoring tumor growth.
-
Genetic Counseling: Genetic counseling can help families understand the risks of passing the condition to offspring.
-
Support Groups: Support groups provide emotional support and resources for individuals and families affected by neurofibromatosis.
-
Research and Trials: Ongoing research and clinical trials aim to find better treatments and, eventually, a cure.
Living with Neurofibromatosis
Living with neurofibromatosis can be challenging, but many individuals lead fulfilling lives with proper management and support. Here are some insights into daily life with this condition.
-
Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about neurofibromatosis can help reduce stigma and improve understanding.
-
Adaptive Strategies: Individuals often develop adaptive strategies to cope with physical and cognitive challenges.
-
Mental Health Support: Psychological support is crucial for managing anxiety and depression related to the condition.
-
Family Impact: The condition can affect family dynamics, requiring open communication and support.
-
Employment Considerations: Some individuals may need workplace accommodations to manage symptoms effectively.
-
Social Connections: Maintaining social connections and friendships is important for emotional well-being.
-
Advocacy and Rights: Advocacy groups work to protect the rights and improve the quality of life for those with neurofibromatosis.
-
Technological Aids: Technology, such as apps and devices, can assist with daily tasks and symptom management.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Healthy lifestyle choices, including diet and exercise, can improve overall health.
-
Hope for the Future: Advances in research and treatment continue to offer hope for better management and potential cures.
Bringing It All Together
Neurofibromas are more than just a medical term. They're a part of the complex world of genetic disorders. These tumors, often linked with Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1), can vary greatly in size and impact. While some remain small and harmless, others might require medical attention. Understanding the symptoms and treatment options is crucial for those affected. Early diagnosis can make a big difference in managing the condition. Advances in genetic research offer hope for better treatments and possibly a cure in the future. Awareness and education are key in supporting individuals with neurofibromas. By staying informed, we can help reduce the stigma and improve the quality of life for those living with this condition. Remember, knowledge is power, and sharing it can lead to a more compassionate and understanding world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
