Scoliosis is a condition that affects the curvature of the spine, causing it to bend sideways. It can occur in people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence. In this article, we will explore 19 crucial facts about scoliosis, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Whether you or a loved one are living with scoliosis or simply seeking to expand your knowledge, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights and support your journey towards understanding this complex condition.
Definition and Types
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal sideways curvature of the spine. It can be categorized into different types based on the age of onset and the cause of the curvature. The most common types include adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, congenital scoliosis, and degenerative scoliosis.
Prevalence
Scoliosis affects approximately 2-3% of the population, or an estimated 6-9 million people in the United States alone. It can occur in both males and females, although females are more likely to develop severe curves that require treatment.
Age of Onset
While scoliosis can be present at birth (congenital scoliosis) or develop in adulthood (degenerative scoliosis), the most common age of onset is during adolescence. This is known as adolescent idiopathic scoliosis, and it typically appears between the ages of 10 and 18.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of scoliosis is often unknown (idiopathic scoliosis). However, various risk factors can contribute to its development. These may include genetics, family history, muscle imbalances, neuromuscular conditions (such as cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy), and certain connective tissue disorders.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of scoliosis can vary depending on the severity of the curvature. Common indications include an uneven waist or shoulders, one shoulder blade that appears more prominent than the other, an asymmetrical rib cage, and a visible sideways curvature of the spine. In some cases, scoliosis can cause back pain, difficulty breathing, and limited mobility.
Diagnosis
Scoliosis is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests such as X-rays. The degree of spinal curvature is measured using a system called Cobb angle, which helps determine the severity of the condition and guide treatment decisions.
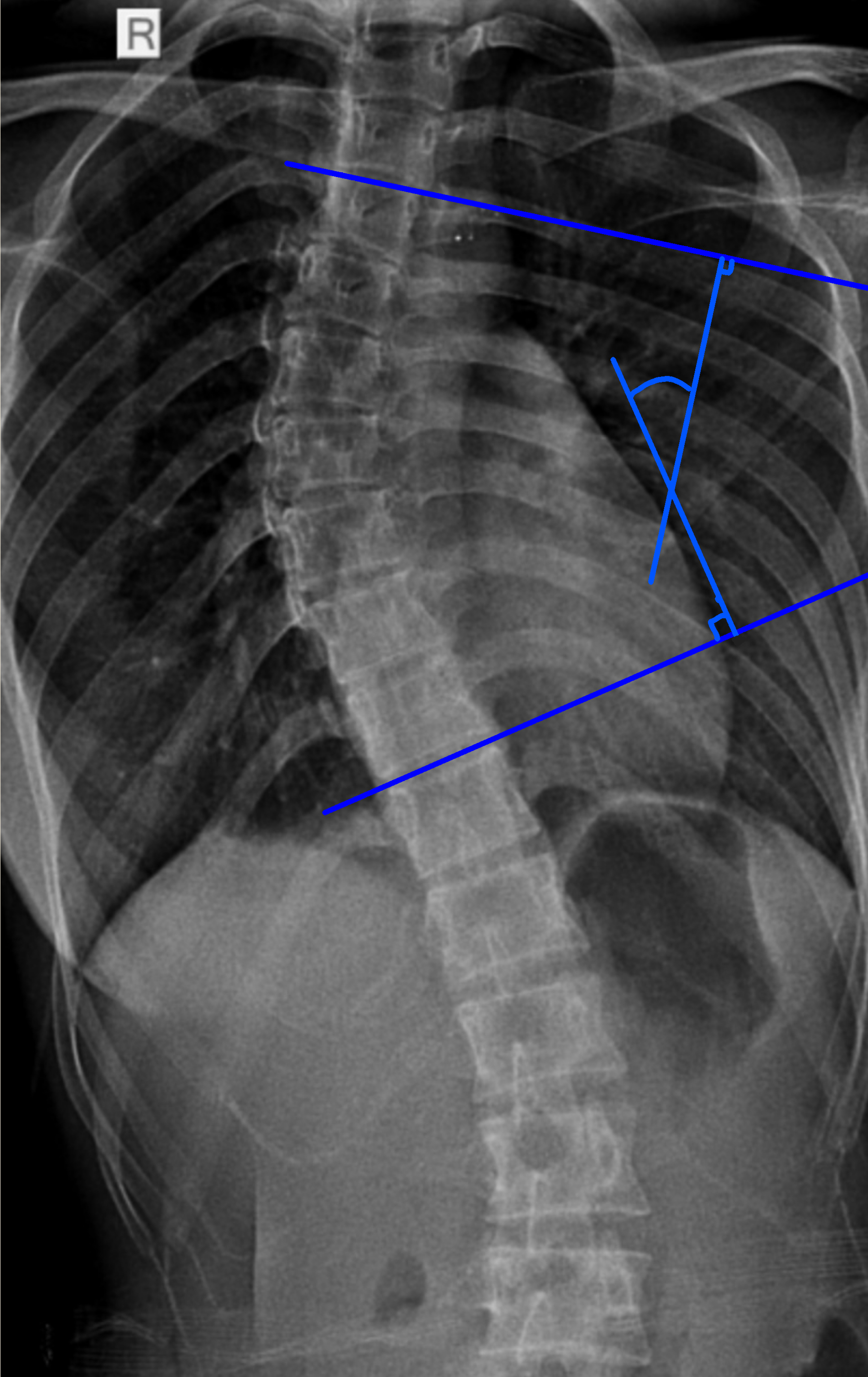
Cobb Angle Classification
The Cobb angle classification system categorizes scoliosis based on the magnitude of the spinal curve. Mild scoliosis is defined as a Cobb angle of less than 20 degrees, moderate scoliosis ranges from 20 to 45 degrees, and severe scoliosis is characterized by a Cobb angle greater than 45 degrees.
Progressive Nature
In some cases, scoliosis can progress over time, particularly during periods of growth. Regular monitoring is essential to detect any changes in the curvature, as early intervention can help prevent further progression and minimize potential complications.
Treatment Options
The treatment options for scoliosis depend on various factors, including the severity of the curvature, age, and overall health of the individual. Mild cases may only require monitoring and periodic check-ups, while moderate to severe cases may necessitate bracing or surgery. Physical therapy and exercise can also play a supportive role in managing scoliosis.
Bracing
Bracing is a common non-surgical treatment option for moderate scoliosis. A brace, such as a Boston brace or a Charleston bending brace, is custom-made and worn to help halt the progression of the curvature and maintain spinal alignment during periods of growth.
Surgical Intervention
Severe cases of scoliosis, or those that continue to progress despite conservative measures, may require surgical intervention. Spinal fusion surgery is the most common procedure, where the curved portion of the spine is straightened and fused with bone grafts or implants to achieve spinal stability.
Impact on Quality of Life
Scoliosis can have a significant impact on a person’s quality of life, both physically and emotionally. Chronic pain, limited mobility, body image concerns, and potential respiratory complications can affect daily activities and overall well-being. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and peer groups can be crucial in managing these challenges.

Psychosocial Considerations
Living with scoliosis can present unique psychosocial challenges, especially for adolescents. Body image concerns, self-esteem issues, and social stigma may arise, requiring emotional support and counseling to promote self-acceptance and a positive outlook.
Posture and Exercise
Maintaining good posture and engaging in regular exercise can help manage scoliosis and improve overall spinal health. Strengthening exercises, such as core and back exercises, can support the spine and promote better alignment. Physical therapists can provide tailored exercise programs to meet individual needs.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection and diagnosis of scoliosis are crucial for effective treatment. Regular screenings in schools and awareness among parents and healthcare providers can help identify scoliosis in its early stages, allowing for timely intervention and improved outcomes.
Research and Advancements
Ongoing research in the field of scoliosis aims to enhance our understanding of its causes, progression, and treatment options. Advances in surgical techniques, bracing technology, and non-invasive interventions continue to offer hope for improved management and outcomes.
Support Networks
Support networks and organizations dedicated to scoliosis provide invaluable resources and communities for individuals and families affected by the condition. These networks offer education, emotional support, and opportunities to connect with others facing similar challenges.
Life with Scoliosis
It’s important to remember that scoliosis does not define a person’s entire life. With proper management, individuals with scoliosis can lead fulfilling lives, pursuing their passions, and achieving their goals. Adaptive techniques, accommodations, and a positive mindset can empower individuals to thrive despite the challenges they may face.
Embracing Individuality
Each person’s scoliosis journey is unique, and it’s essential to approach it with empathy, compassion, and understanding. By embracing individuality and raising awareness about scoliosis, we can create a more inclusive and supportive society for everyone affected by this condition.
Conclusion
As we conclude our exploration of these important scoliosis facts, we hope this guide has provided a comprehensive understanding of the condition. Whether you are personally affected by scoliosis or seeking knowledge to support a loved one, remember that early detection, timely intervention, and emotional support are key components in managing scoliosis. By fostering awareness and empathy, we can create a world where individuals with scoliosis can thrive and embrace their unique journeys.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.


