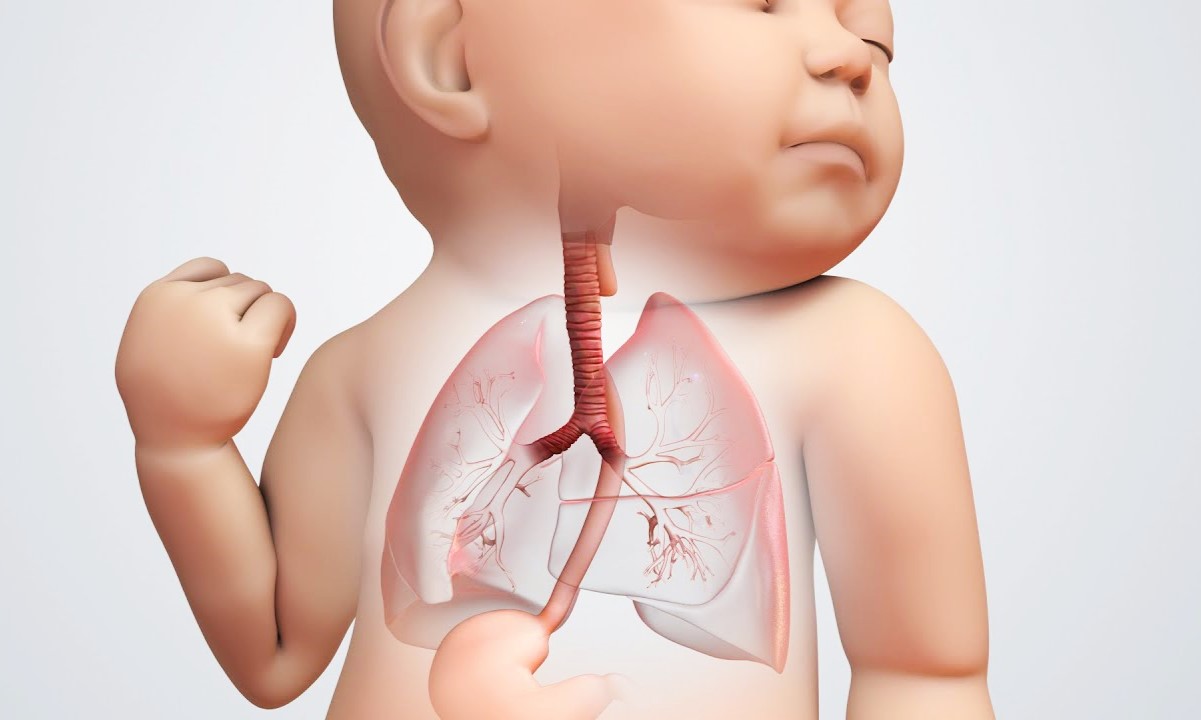
What is larynx atresia? Larynx atresia, a rare congenital condition, occurs when the larynx, or voice box, fails to develop properly, leading to a blockage. This condition can cause severe breathing difficulties at birth, making immediate medical intervention crucial. How common is larynx atresia? It's extremely rare, with only a handful of cases reported worldwide. What causes larynx atresia? The exact cause remains unknown, but it’s believed to result from genetic mutations during fetal development. How is larynx atresia diagnosed? Prenatal ultrasounds can sometimes detect it, but often, it’s diagnosed at birth due to respiratory distress. What are the treatment options? Treatment typically involves surgical procedures to create an airway, followed by long-term care to manage breathing and feeding.
Key Takeaways:
- Larynx atresia is a rare and life-threatening condition that affects newborns' ability to breathe. Early detection and immediate medical intervention are crucial for survival.
- Ongoing research and advanced medical techniques offer hope for improved diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes for individuals with larynx atresia. Support and resources are available to help affected families navigate the challenges of this condition.
What is Larynx Atresia?
Larynx atresia is a rare congenital condition where the larynx, or voice box, is completely blocked. This condition can cause severe breathing difficulties at birth and requires immediate medical attention. Here are some fascinating facts about larynx atresia.
-
Larynx atresia is a life-threatening condition that affects the airway, making it impossible for newborns to breathe normally.
-
This condition is extremely rare, occurring in approximately 1 in 50,000 births.
-
Larynx atresia is often detected during prenatal ultrasounds, allowing doctors to prepare for immediate intervention after birth.
-
The exact cause of larynx atresia is unknown, but it is believed to result from genetic mutations during fetal development.
-
Babies born with larynx atresia typically require a tracheostomy, a surgical procedure to create an opening in the neck to allow breathing.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Larynx Atresia
Recognizing the symptoms and diagnosing larynx atresia early is crucial for the survival of affected infants. Here are some key points about the symptoms and diagnosis.
-
One of the primary symptoms of larynx atresia is severe respiratory distress immediately after birth.
-
Infants with this condition may also exhibit cyanosis, a bluish tint to the skin due to lack of oxygen.
-
Prenatal ultrasounds can reveal polyhydramnios, an excess of amniotic fluid, which is often associated with larynx atresia.
-
MRI and fetal echocardiography are additional diagnostic tools that can help confirm the presence of larynx atresia before birth.
-
Postnatal diagnosis involves direct laryngoscopy, where a camera is used to visualize the larynx and confirm the blockage.
Treatment Options for Larynx Atresia
Treating larynx atresia requires a multidisciplinary approach involving pediatric surgeons, neonatologists, and other specialists. Here are some treatment options.
-
The EXIT (Ex Utero Intrapartum Treatment) procedure is often used to secure the airway while the baby is still partially attached to the placenta.
-
A tracheostomy is usually performed immediately after birth to provide a stable airway for the infant.
-
Surgical reconstruction of the larynx may be necessary to restore normal breathing and vocal function.
-
Long-term care often involves speech therapy to help the child develop normal speech patterns.
-
Regular follow-up appointments with a pediatric otolaryngologist are essential to monitor the child's progress and address any complications.
Complications and Prognosis
Larynx atresia can lead to various complications, but with proper treatment, many children can lead healthy lives. Here are some facts about the complications and prognosis.
-
Without immediate intervention, larynx atresia is fatal due to the inability to breathe.
-
Complications can include infections, scarring, and difficulties with feeding and swallowing.
-
Children with larynx atresia may require multiple surgeries to address airway and vocal cord issues.
-
Early intervention and advanced medical techniques have significantly improved the survival rate for infants with larynx atresia.
-
With appropriate treatment, many children with larynx atresia can achieve normal growth and development.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Understanding the genetic and environmental factors associated with larynx atresia can help in early detection and prevention. Here are some insights.
-
Genetic mutations are believed to play a significant role in the development of larynx atresia.
-
Some cases of larynx atresia are associated with other congenital anomalies, such as heart defects and kidney abnormalities.
-
Environmental factors, such as maternal smoking and exposure to certain chemicals, may increase the risk of congenital anomalies, including larynx atresia.
-
Genetic counseling can be beneficial for families with a history of congenital anomalies to assess the risk of larynx atresia in future pregnancies.
-
Research is ongoing to identify specific genetic markers and environmental triggers associated with larynx atresia.
Support and Resources for Families
Families affected by larynx atresia need support and resources to navigate the challenges of this condition. Here are some helpful points.
-
Support groups and online communities can provide emotional support and practical advice for families dealing with larynx atresia.
-
Organizations such as the American Academy of Otolaryngology offer resources and information about congenital airway anomalies.
-
Early intervention programs can help children with larynx atresia develop essential skills and reach developmental milestones.
-
Financial assistance programs may be available to help cover the costs of medical treatments and therapies.
-
Educating family members and caregivers about larynx atresia can improve the quality of care and support for affected children.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research is crucial for improving the diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes of larynx atresia. Here are some exciting developments in this field.
-
Advances in prenatal imaging techniques are improving the early detection of larynx atresia.
-
Researchers are exploring the use of stem cell therapy to regenerate damaged laryngeal tissues.
-
Genetic studies are identifying potential targets for gene therapy to correct the underlying mutations causing larynx atresia.
-
New surgical techniques and technologies are enhancing the success rates of laryngeal reconstruction procedures.
-
Collaborative research efforts are focusing on developing standardized treatment protocols for larynx atresia.
Living with Larynx Atresia
Living with larynx atresia presents unique challenges, but with the right support, affected individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some important considerations.
-
Children with larynx atresia may require ongoing medical care and monitoring throughout their lives.
-
Speech therapy and other rehabilitative services can help improve communication skills and quality of life.
-
Participation in support groups and advocacy organizations can provide a sense of community and empowerment for affected individuals and their families.
-
Educating teachers and school staff about larynx atresia can ensure that children receive the necessary accommodations and support in educational settings.
-
Advances in medical research and treatment options continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for individuals with larynx atresia.
Final Thoughts on Larynx Atresia
Larynx atresia, a rare congenital condition, impacts the airway's development, leading to severe breathing difficulties. Early diagnosis is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Advanced imaging techniques like ultrasound and MRI play a significant role in identifying larynx atresia before birth. Treatment often involves surgical intervention to create a functional airway, which can be life-saving for affected infants.
Understanding the symptoms, such as respiratory distress and absence of crying at birth, helps in prompt medical attention. Support from specialized healthcare teams ensures better outcomes for these infants. Awareness and research continue to improve the prognosis and quality of life for those with larynx atresia.
By staying informed and advocating for early intervention, we can make a difference in the lives of families facing this challenging condition. Knowledge empowers us to support and seek the best care for those affected.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
