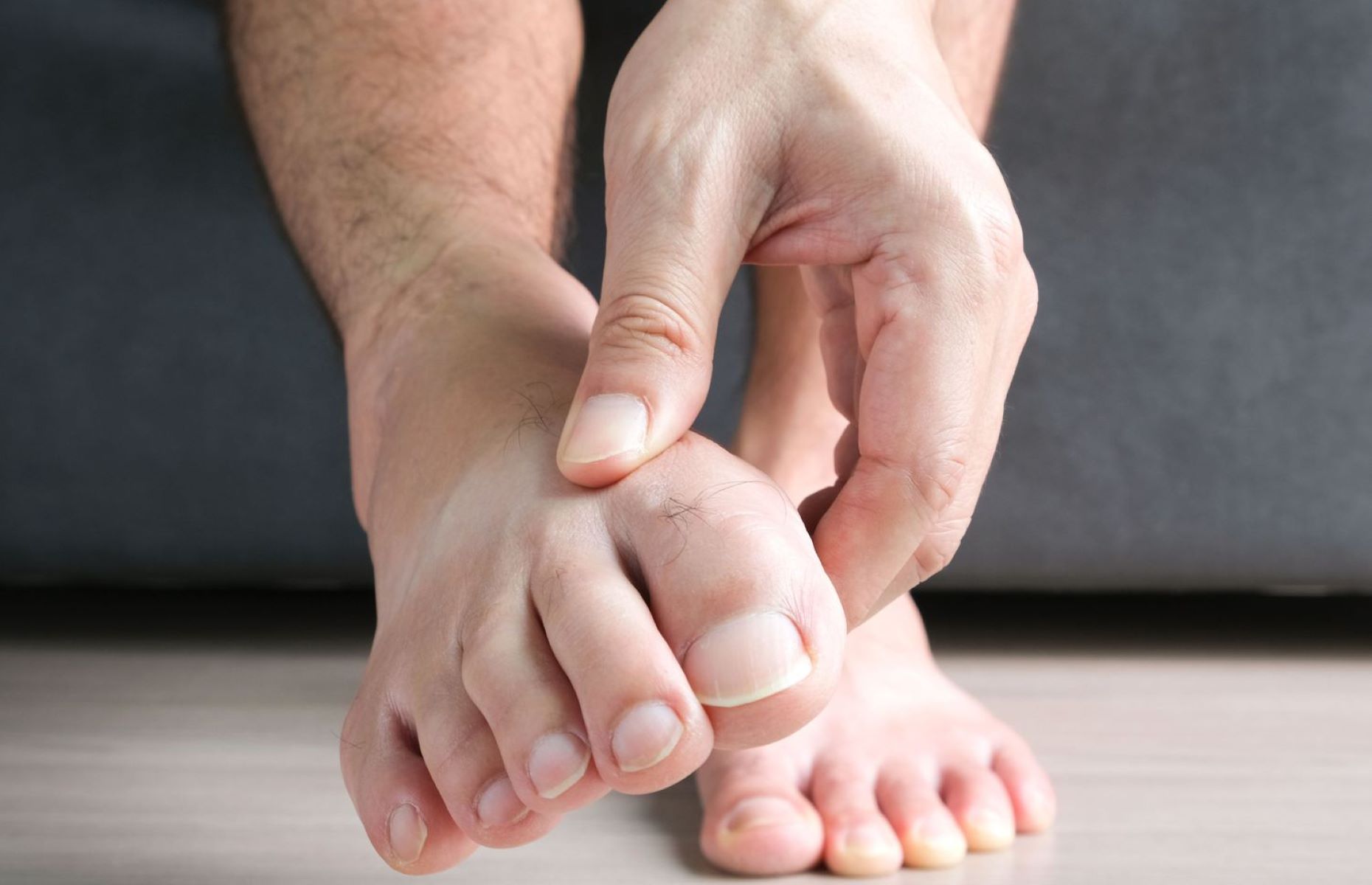
Juvenile gout might sound like a rare condition, but it’s more common than you think. Juvenile gout is a type of arthritis that affects children and teenagers, characterized by sudden and severe pain, redness, and swelling in the joints. This condition is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can form sharp crystals in the joints. While gout is often associated with adults, especially older men, kids can experience it too. Understanding the symptoms and causes can help in managing this condition effectively. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term joint damage. Lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, play a significant role in managing juvenile gout. If you suspect your child might have gout, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. Stay informed and proactive to ensure your child leads a healthy, active life.
Key Takeaways:
- Juvenile gout is a rare condition in young people, caused by uric acid buildup. It can be managed with medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring to prevent complications.
- Recognizing symptoms and early diagnosis are crucial for effective management of juvenile gout. Lifestyle changes, hydration, and avoiding trigger foods can help prevent gout attacks.
Understanding Juvenile Gout
Juvenile gout is a rare condition that affects young people, typically under the age of 18. It involves the buildup of uric acid in the blood, leading to painful joint inflammation. While gout is more common in adults, understanding its occurrence in children is crucial for early diagnosis and management.
-
Juvenile gout is rare. Unlike adult gout, which is relatively common, juvenile gout is quite rare. It affects a small percentage of children, making it a unique condition that requires special attention.
-
Uric acid buildup causes gout. The condition occurs when uric acid, a waste product in the blood, accumulates and forms crystals in the joints. This leads to inflammation and intense pain.
-
Genetics play a role. Family history can increase the risk of developing juvenile gout. If a parent or close relative has gout, a child may be more susceptible to the condition.
-
Diet influences uric acid levels. Foods high in purines, like red meat and shellfish, can raise uric acid levels. Children with a diet rich in these foods may have a higher risk of developing gout.
-
Obesity is a risk factor. Being overweight can contribute to higher uric acid levels, increasing the likelihood of gout in children. Maintaining a healthy weight is important for prevention.
Symptoms of Juvenile Gout
Recognizing the symptoms of juvenile gout is essential for timely treatment. The condition can cause significant discomfort and impact a child's daily life.
-
Sudden joint pain is common. Gout attacks often start with sudden, severe pain in one or more joints. The big toe is a common site, but other joints can be affected too.
-
Swelling and redness occur. The affected joint may become swollen, red, and warm to the touch. This inflammation is a hallmark of gout.
-
Limited joint movement. Pain and swelling can restrict movement in the affected joint, making it difficult for children to perform everyday activities.
-
Fever may accompany attacks. Some children experience a mild fever during a gout attack, adding to their discomfort.
-
Attacks can last days. Gout attacks can persist for several days, with pain gradually subsiding. However, without treatment, attacks may become more frequent.
Diagnosing Juvenile Gout
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for managing juvenile gout effectively. Healthcare professionals use various methods to identify the condition.
-
Blood tests measure uric acid. Doctors often perform blood tests to check uric acid levels. Elevated levels can indicate gout.
-
Joint fluid analysis confirms diagnosis. Extracting fluid from the affected joint and examining it under a microscope can reveal uric acid crystals, confirming gout.
-
X-rays rule out other conditions. Imaging tests like X-rays help rule out other joint issues and assess any damage caused by gout.
-
Family history is considered. A thorough family history can provide clues about the likelihood of juvenile gout, aiding in diagnosis.
-
Symptoms guide diagnosis. Doctors rely on the characteristic symptoms of gout, such as sudden joint pain and swelling, to make an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options for Juvenile Gout
Managing juvenile gout involves a combination of lifestyle changes and medication to control symptoms and prevent future attacks.
-
Medications reduce inflammation. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks.
-
Colchicine prevents attacks. This medication can help prevent future gout attacks by reducing inflammation and lowering uric acid levels.
-
Lifestyle changes are crucial. Encouraging a healthy diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can help manage gout and reduce the risk of attacks.
-
Hydration is important. Drinking plenty of water helps flush uric acid from the body, reducing the likelihood of crystal formation.
-
Avoiding trigger foods helps. Limiting foods high in purines, such as red meat and sugary drinks, can prevent uric acid buildup and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
Long-term Management of Juvenile Gout
Effective long-term management of juvenile gout is essential to prevent complications and improve quality of life for affected children.
-
Regular check-ups are necessary. Routine medical appointments help monitor uric acid levels and adjust treatment plans as needed.
-
Education empowers families. Teaching families about gout and its management empowers them to make informed decisions and support their child's health.
-
Support groups offer assistance. Joining support groups can provide families with valuable resources and emotional support from others facing similar challenges.
-
Monitoring uric acid levels is key. Regular blood tests to monitor uric acid levels help ensure that treatment is effective and adjustments are made when necessary.
-
Adherence to treatment is vital. Consistently following prescribed treatment plans, including medication and lifestyle changes, is crucial for managing juvenile gout effectively.
Complications of Untreated Juvenile Gout
Ignoring juvenile gout can lead to serious complications that affect a child's health and well-being.
-
Joint damage can occur. Repeated gout attacks can cause permanent joint damage, leading to chronic pain and reduced mobility.
-
Kidney stones may develop. High uric acid levels can lead to the formation of kidney stones, causing additional pain and complications.
-
Chronic gout is a risk. Without proper management, juvenile gout can progress to chronic gout, characterized by frequent attacks and persistent symptoms.
-
Increased risk of other conditions. Untreated gout can increase the risk of developing other health issues, such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease.
-
Impact on quality of life. Chronic pain and mobility issues can significantly impact a child's quality of life, affecting their ability to participate in activities and enjoy daily life.
Prevention Strategies for Juvenile Gout
Preventing juvenile gout involves proactive measures to reduce risk factors and promote overall health.
-
Healthy diet is essential. Encouraging a balanced diet low in purines can help prevent uric acid buildup and reduce the risk of gout.
-
Regular exercise is beneficial. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and supports overall health, reducing the risk of gout.
-
Weight management is crucial. Maintaining a healthy weight can lower uric acid levels and decrease the likelihood of gout attacks.
-
Hydration supports kidney function. Drinking enough water helps the kidneys flush out uric acid, reducing the risk of crystal formation.
-
Avoiding sugary drinks helps. Limiting sugary beverages can prevent uric acid spikes and reduce the risk of gout attacks.
Myths and Misconceptions about Juvenile Gout
Understanding the facts about juvenile gout helps dispel common myths and misconceptions surrounding the condition.
-
Gout is not just an adult issue. While more common in adults, gout can affect children, making awareness and understanding important.
-
Diet alone doesn't cause gout. While diet plays a role, genetics and other factors also contribute to the development of gout.
-
Gout is not always preventable. Some risk factors, like genetics, cannot be controlled, but lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk.
-
Juvenile gout is not always severe. With proper management, many children with gout can lead healthy, active lives without severe symptoms.
-
Medication is not the only solution. A combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring is often the most effective approach to managing juvenile gout.
Final Thoughts on Juvenile Gout
Juvenile gout, though rare, is a condition that demands attention. Understanding its symptoms and causes can lead to early diagnosis and better management. Kids with gout often experience joint pain and swelling, which can be mistaken for other ailments. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for effective treatment. Lifestyle changes, like a balanced diet and regular exercise, play a significant role in managing this condition. Encouraging kids to avoid foods high in purines, such as red meat and certain seafood, can help reduce flare-ups. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals ensure that any changes in symptoms are monitored closely. With the right approach, kids can lead active, healthy lives despite this condition. Parents and caregivers should stay informed and proactive, providing the support needed for their children's well-being. Knowledge and vigilance are key in navigating the challenges of juvenile gout.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
