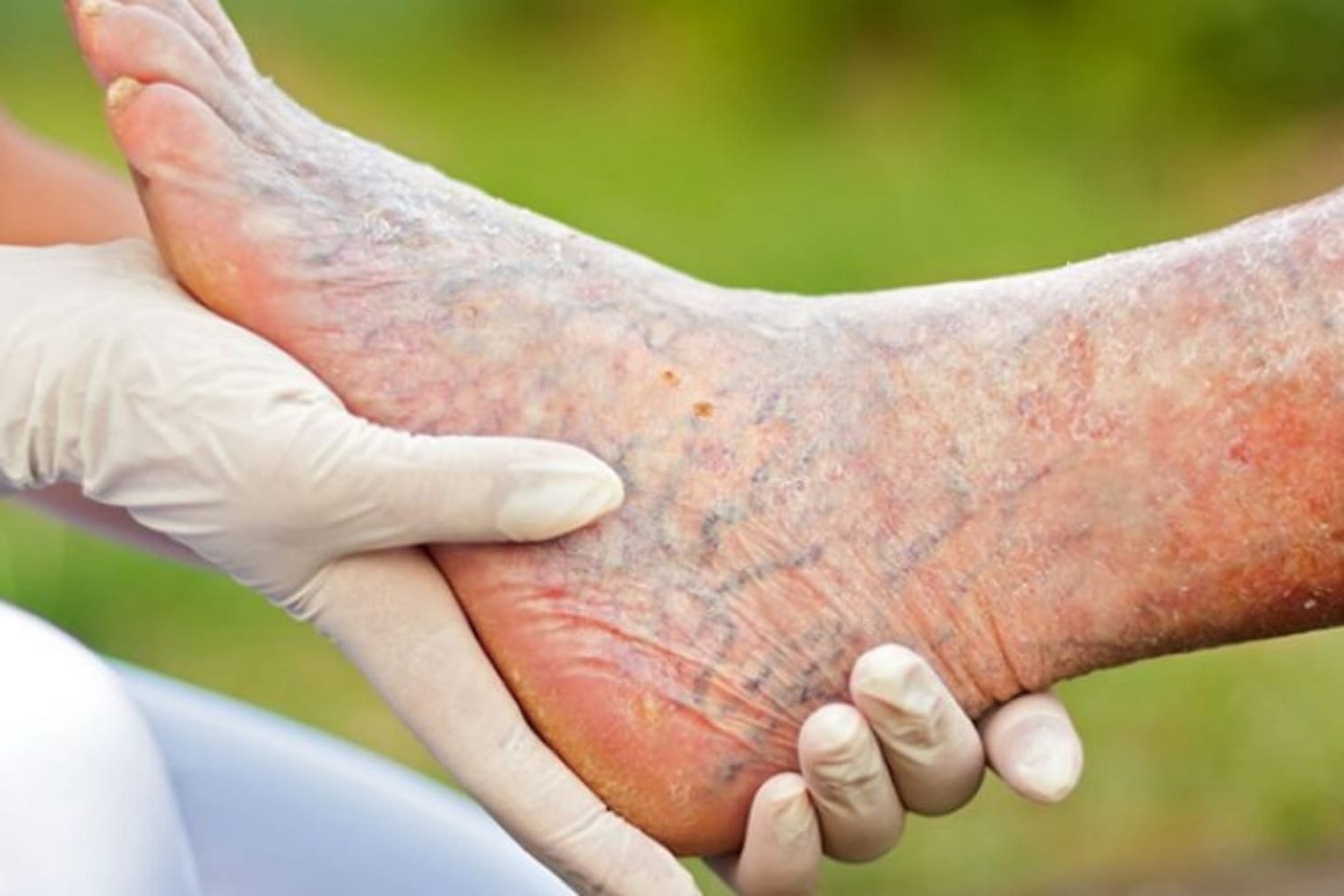
Ischemia is a condition where blood flow (and thus oxygen) is restricted or reduced in a part of the body. This can happen in various organs, but it's most commonly associated with the heart, leading to ischemic heart disease. Why is ischemia dangerous? Because it can cause tissue damage and even tissue death due to lack of oxygen. Symptoms can vary depending on the affected area but often include pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Understanding ischemia is crucial for early detection and treatment, which can significantly improve outcomes. In this article, we'll explore 40 essential facts about ischemia, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventive measures.
Key Takeaways:
- Ischemia can affect any part of the body, not just the heart. Recognizing symptoms and managing risk factors through healthy habits can help prevent serious complications like heart attacks and strokes.
- Early diagnosis and treatment of ischemia are crucial. Tests like ECG and imaging, along with lifestyle changes and medications, can help restore blood flow and prevent tissue damage.
What is Ischemia?
Ischemia happens when blood flow to a part of the body is reduced, preventing oxygen and nutrients from reaching tissues. This can cause damage or dysfunction in the affected area. Here are some interesting facts about ischemia.
-
Ischemia can affect any part of the body. While most people think of heart attacks, ischemia can occur in the brain, limbs, or intestines.
-
Coronary artery disease is a common cause. When arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, it leads to ischemic heart disease.
-
Transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) are mini-strokes. These temporary blockages in blood flow to the brain can be warning signs of a future stroke.
-
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) causes leg ischemia. Reduced blood flow to the legs can lead to pain, ulcers, or even gangrene.
-
Ischemic colitis affects the intestines. This condition occurs when blood flow to the colon is reduced, causing pain and digestive issues.
Symptoms of Ischemia
Recognizing the symptoms of ischemia can be crucial for early intervention and treatment. Here are some signs to watch for.
-
Chest pain or angina. This is a common symptom of heart-related ischemia, often triggered by physical activity or stress.
-
Shortness of breath. Reduced blood flow to the heart can make it difficult to breathe, especially during exertion.
-
Numbness or weakness. Ischemia in the brain or limbs can cause sudden numbness, weakness, or paralysis.
-
Abdominal pain. Ischemic colitis can cause severe abdominal pain, often after eating.
-
Cold or pale skin. Reduced blood flow to the limbs can make the skin feel cold or look pale.
Causes of Ischemia
Understanding what causes ischemia can help in preventing it. Here are some common causes.
-
Atherosclerosis. This condition involves the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow.
-
Blood clots. Clots can block arteries, leading to ischemia in various parts of the body.
-
Vasospasm. Sudden constriction of blood vessels can reduce blood flow, causing ischemia.
-
Low blood pressure. Severely low blood pressure can reduce blood flow to organs and tissues.
-
Embolism. A piece of debris or clot traveling through the bloodstream can lodge in an artery, causing ischemia.
Risk Factors for Ischemia
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing ischemia. Here are some key risk factors.
-
Smoking. Tobacco use damages blood vessels and increases the risk of atherosclerosis.
-
High blood pressure. Hypertension can damage arteries and lead to ischemia.
-
High cholesterol. Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to the buildup of fatty deposits in arteries.
-
Diabetes. This condition increases the risk of atherosclerosis and ischemia.
-
Obesity. Excess weight strains the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of ischemia.
Diagnosing Ischemia
Early diagnosis of ischemia is essential for effective treatment. Here are some methods used to diagnose ischemia.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG). This test measures the electrical activity of the heart and can detect ischemia.
-
Stress tests. These tests evaluate how the heart performs under physical stress, revealing potential ischemia.
-
Imaging tests. Techniques like MRI, CT scans, and angiography can visualize blood flow and detect blockages.
-
Blood tests. Certain markers in the blood can indicate ischemia or related conditions.
-
Ankle-brachial index (ABI). This test compares blood pressure in the ankle and arm to detect peripheral artery disease.
Treating Ischemia
Treatment for ischemia aims to restore blood flow and prevent further damage. Here are some common treatments.
-
Medications. Drugs like blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering medications, and vasodilators can help manage ischemia.
-
Lifestyle changes. Quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly can improve blood flow and reduce risk.
-
Angioplasty. This procedure involves inflating a small balloon inside a blocked artery to restore blood flow.
-
Stenting. A stent, or small mesh tube, can be placed in an artery to keep it open and maintain blood flow.
-
Bypass surgery. Surgeons can create a new pathway for blood to flow around a blocked artery.
Complications of Ischemia
If left untreated, ischemia can lead to serious complications. Here are some potential issues.
-
Heart attack. Prolonged ischemia in the heart can cause a heart attack, damaging heart muscle.
-
Stroke. Ischemia in the brain can lead to a stroke, causing permanent damage or disability.
-
Tissue death. Severe ischemia can cause tissues to die, leading to gangrene or organ failure.
-
Chronic pain. Reduced blood flow can cause ongoing pain, especially in the legs.
-
Digestive problems. Ischemic colitis can lead to chronic digestive issues and malnutrition.
Preventing Ischemia
Taking steps to prevent ischemia can improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications. Here are some prevention tips.
-
Maintain a healthy diet. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve blood vessel health.
-
Exercise regularly. Physical activity helps keep blood vessels flexible and reduces the risk of atherosclerosis.
-
Manage stress. Chronic stress can contribute to high blood pressure and ischemia.
-
Monitor health conditions. Regular check-ups and managing conditions like diabetes and hypertension can reduce risk.
-
Avoid smoking. Quitting smoking can significantly improve blood vessel health and reduce the risk of ischemia.
The Final Word on Ischemia
Ischemia, a condition marked by reduced blood flow, can affect various parts of the body, leading to serious health issues. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for managing and preventing complications. From coronary artery disease to peripheral artery disease, ischemia manifests in different forms, each requiring specific medical attention.
Early detection and lifestyle changes, like a balanced diet and regular exercise, play a significant role in managing ischemia. Medical interventions, including medications and surgeries, offer additional support for those affected. Staying informed and proactive can make a world of difference in maintaining heart and overall health.
Remember, knowledge is power. By staying aware of ischemia and its impacts, you can take steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment options. Stay healthy, stay informed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
