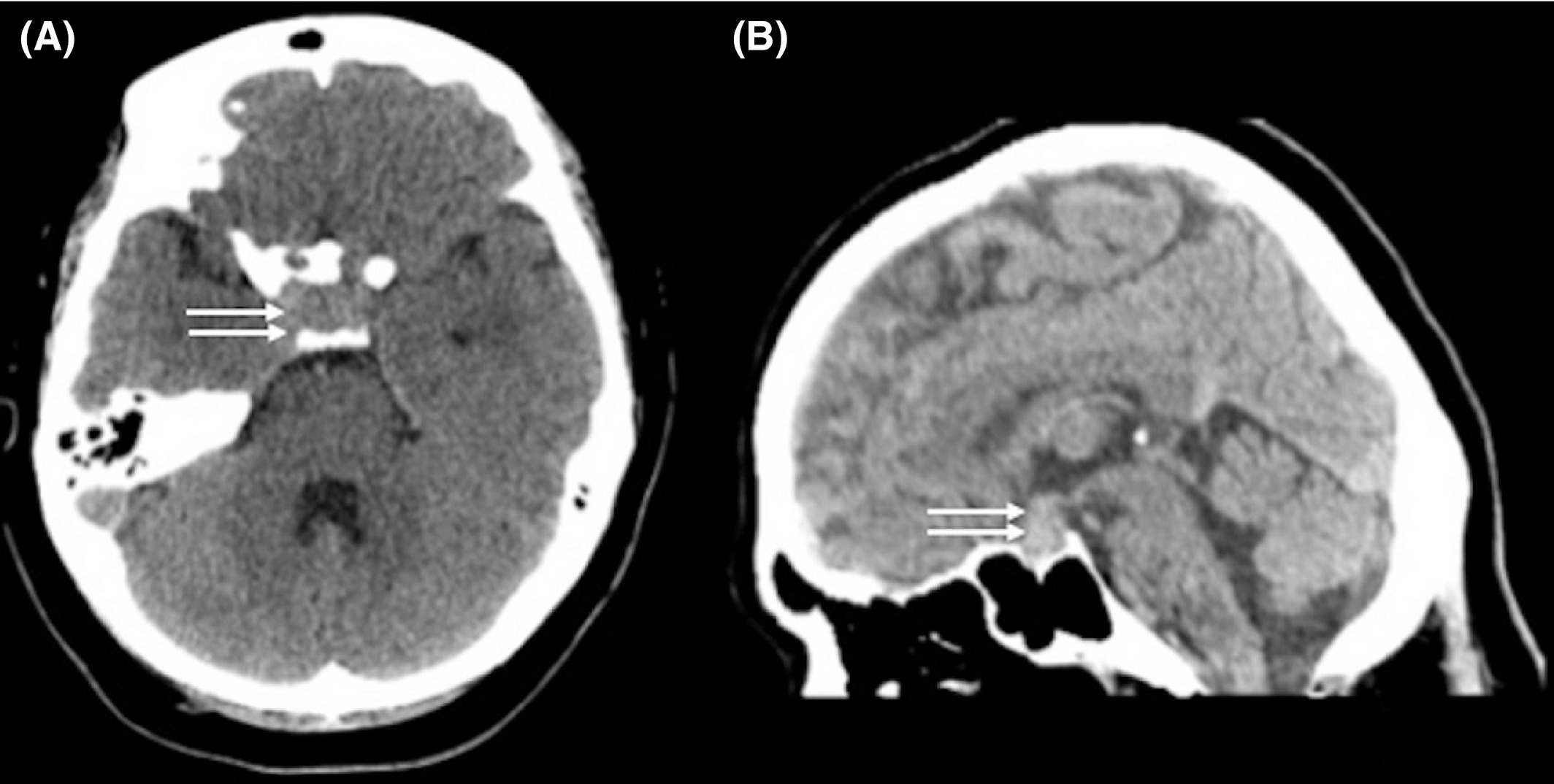
Granulomatous hypophysitis is a rare inflammatory condition affecting the pituitary gland. This disorder can cause various symptoms like headaches, vision problems, and hormonal imbalances. Often misdiagnosed due to its rarity, understanding its nuances is crucial for proper treatment. Granulomatous hypophysitis can mimic other pituitary disorders, making accurate diagnosis challenging. Treatment typically involves medications to reduce inflammation and, in some cases, surgery. Knowing the facts about this condition can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care. Let's dive into 40 essential facts about granulomatous hypophysitis to shed light on this uncommon yet significant health issue.
Key Takeaways:
- Granulomatous hypophysitis is a rare pituitary gland disorder causing hormonal imbalances and vision problems. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve prognosis and quality of life.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, joining support groups, and educating others are important for managing granulomatous hypophysitis. Awareness and understanding are crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
What is Granulomatous Hypophysitis?
Granulomatous hypophysitis is a rare inflammatory condition affecting the pituitary gland. This disorder can cause a variety of symptoms due to its impact on hormone production and gland function. Here are some intriguing facts about this uncommon ailment.
-
Granulomatous hypophysitis is characterized by the formation of granulomas, which are small areas of inflammation caused by immune cells.
-
The pituitary gland, also known as the "master gland," regulates many vital body functions by releasing hormones.
-
This condition can lead to hypopituitarism, where the pituitary gland fails to produce one or more of its hormones adequately.
-
Symptoms often include headaches, vision problems, and hormonal imbalances.
-
Granulomatous hypophysitis is more common in women, particularly during pregnancy or the postpartum period.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in early diagnosis and management. Here are some key points to consider.
-
The exact cause of granulomatous hypophysitis is unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder.
-
Autoimmune diseases occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
-
Infections, such as tuberculosis or fungal infections, can sometimes trigger granulomatous hypophysitis.
-
Genetic predisposition may play a role in the development of this condition.
-
Certain medications, like immune checkpoint inhibitors used in cancer therapy, have been linked to granulomatous hypophysitis.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for effective treatment. Here are some important facts.
-
Common symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, and decreased libido.
-
Patients may experience polyuria (excessive urination) and polydipsia (excessive thirst) due to diabetes insipidus.
-
Vision problems occur when the inflammation compresses the optic chiasm, leading to visual field defects.
-
MRI scans are the primary imaging technique used to diagnose granulomatous hypophysitis.
-
Blood tests can reveal hormone deficiencies indicative of pituitary dysfunction.
Treatment Options
Treatment aims to reduce inflammation and manage hormone deficiencies. Here are some treatment facts.
-
Corticosteroids are the first line of treatment to reduce inflammation.
-
Hormone replacement therapy is often necessary to address deficiencies caused by pituitary damage.
-
Immunosuppressive drugs may be used in cases where corticosteroids are ineffective.
-
Surgery is rarely required but may be considered if there is a mass effect causing severe symptoms.
-
Regular follow-up with an endocrinologist is essential to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatments as needed.
Prognosis and Long-term Management
Living with granulomatous hypophysitis requires ongoing care and monitoring. Here are some insights into prognosis and management.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
-
Some patients may achieve complete remission with appropriate therapy.
-
Chronic cases may require long-term hormone replacement and immunosuppressive therapy.
-
Regular MRI scans are recommended to monitor the pituitary gland's condition.
-
Patients should be vigilant about new symptoms and report them to their healthcare provider promptly.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand and treat granulomatous hypophysitis. Here are some exciting developments.
-
Researchers are investigating the genetic factors that may contribute to this condition.
-
New imaging techniques are being developed to improve early diagnosis.
-
Studies are exploring the role of biologic therapies in treating autoimmune forms of granulomatous hypophysitis.
-
Clinical trials are testing novel immunosuppressive drugs for more effective treatment options.
-
Patient registries are being established to collect data and improve understanding of this rare disease.
Living with Granulomatous Hypophysitis
Managing daily life with this condition can be challenging. Here are some tips and facts to help.
-
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support overall well-being.
-
Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, may help reduce symptoms.
-
Joining a support group can provide emotional support and practical advice from others with similar experiences.
-
Keeping a symptom diary can help track changes and communicate effectively with healthcare providers.
-
Educating family and friends about the condition can foster understanding and support.
Rare but Important Facts
Granulomatous hypophysitis is rare, but these lesser-known facts highlight its significance.
-
It accounts for less than 1% of all pituitary disorders.
-
The condition can mimic other pituitary diseases, making diagnosis challenging.
-
Granulomatous hypophysitis can occur at any age but is most commonly diagnosed in middle-aged adults.
-
Some cases are idiopathic, meaning they have no identifiable cause.
-
Awareness and education about this rare condition are crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Final Thoughts on Granulomatous Hypophysitis
Granulomatous hypophysitis, a rare inflammatory condition, affects the pituitary gland, leading to various symptoms like headaches, vision problems, and hormonal imbalances. Understanding its causes, which may include autoimmune responses or infections, helps in managing the condition effectively. Diagnosis often involves MRI scans and blood tests to rule out other disorders. Treatment typically includes corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and in some cases, surgery may be necessary.
Awareness of this condition is crucial for early detection and management. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation. Staying informed about granulomatous hypophysitis can make a significant difference in managing the condition and improving quality of life. Remember, early intervention is key to better outcomes. Stay proactive about your health and seek medical advice when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
