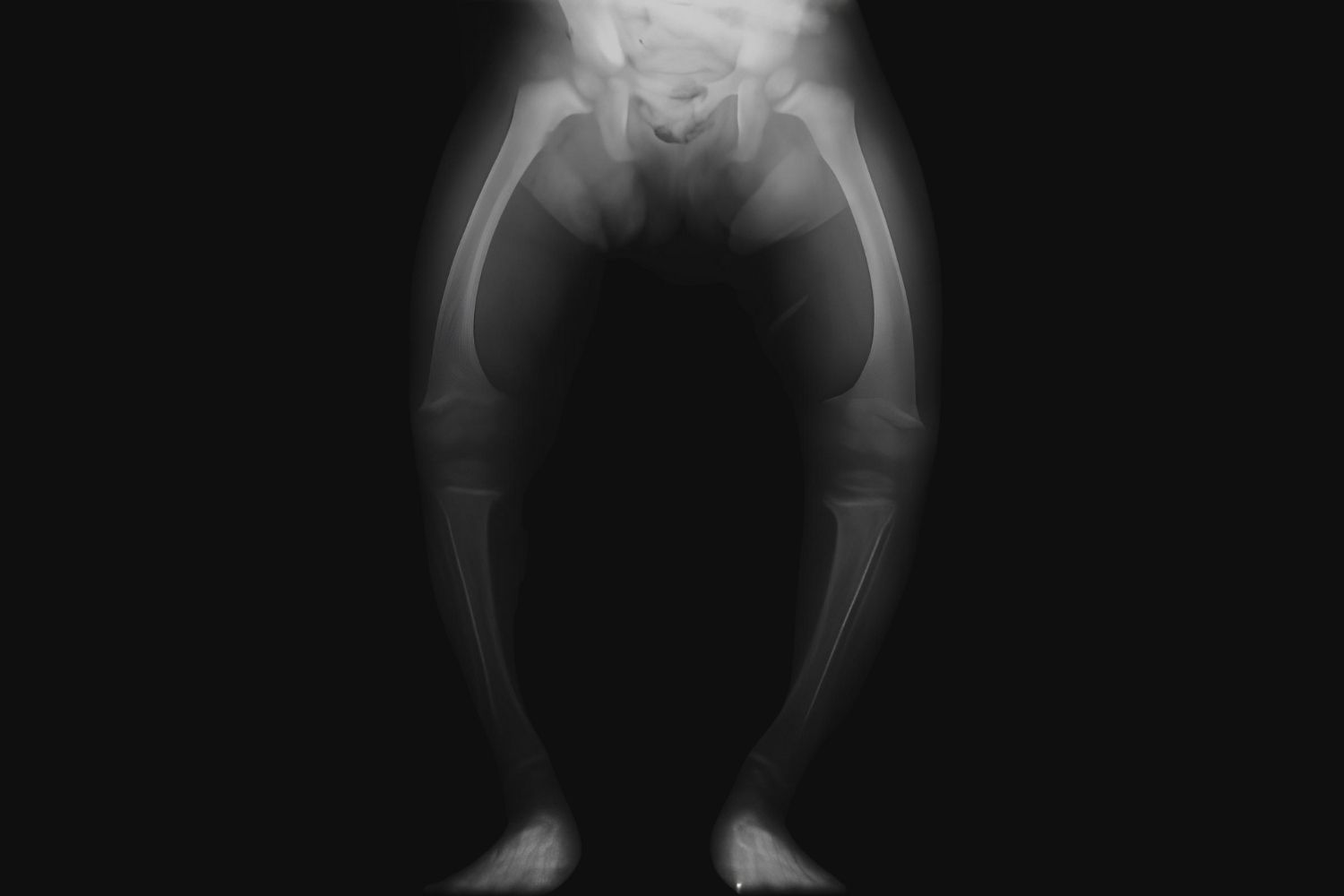
Phosphate diabetes, also known as X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH), is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to manage phosphate levels. This condition leads to low phosphate levels in the blood, causing bone pain, muscle weakness, and dental issues. Phosphate is crucial for bone health and energy production, making its regulation vital for overall well-being. Understanding the complexities of phosphate diabetes can help those affected manage symptoms and improve their quality of life. In this post, we'll explore 35 intriguing facts about phosphate diabetes, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, treatments, and the latest research. Get ready to dive into the world of phosphate diabetes and uncover the essential information you need to know!
Key Takeaways:
- Phosphate diabetes, or hypophosphatemic rickets, is a rare genetic disorder causing weak bones. It can be inherited and leads to symptoms like bone pain and dental issues in children and adults.
- Treatment involves phosphate supplements, dietary changes, and regular monitoring. Research is ongoing for gene therapy and new medications. Living well with phosphate diabetes includes regular exercise and joining support groups for emotional support.
What is Phosphate Diabetes?
Phosphate diabetes, also known as hypophosphatemic rickets, is a rare genetic disorder affecting phosphate metabolism. This condition leads to low levels of phosphate in the blood, causing weak bones and other health issues. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Roots: Phosphate diabetes is often inherited in an X-linked dominant pattern, meaning it can be passed down from one generation to the next through the X chromosome.
-
Phosphate Role: Phosphate is crucial for bone health and energy production. Low phosphate levels can lead to rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
-
Symptoms in Children: Kids with phosphate diabetes may experience bone pain, delayed growth, and dental problems due to weak bones.
-
Adult Symptoms: Adults might suffer from bone pain, muscle weakness, and frequent fractures.
-
Diagnosis: Blood tests measuring phosphate, calcium, and vitamin D levels help diagnose this condition. Genetic testing can confirm the diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in managing phosphate diabetes better. Here are some key points:
-
PHEX Gene Mutation: Mutations in the PHEX gene are the most common cause of phosphate diabetes. This gene plays a role in regulating phosphate levels in the body.
-
Other Genetic Mutations: Mutations in other genes like FGF23, DMP1, and ENPP1 can also lead to phosphate diabetes.
-
Family History: A family history of the condition increases the risk of inheriting phosphate diabetes.
-
Gender Differences: Males are more severely affected due to the X-linked inheritance pattern, while females may have milder symptoms.
-
Environmental Factors: Although primarily genetic, environmental factors like diet and overall health can influence the severity of symptoms.
Treatment Options
Managing phosphate diabetes involves a combination of treatments to maintain phosphate levels and bone health. Here are some treatment facts:
-
Phosphate Supplements: Oral phosphate supplements help increase phosphate levels in the blood.
-
Vitamin D Therapy: Active forms of vitamin D, like calcitriol, are often prescribed to enhance phosphate absorption.
-
Dietary Changes: A diet rich in phosphate, including dairy products, nuts, and seeds, can support treatment.
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent blood tests are necessary to monitor phosphate and calcium levels during treatment.
-
Growth Hormone Therapy: In some cases, growth hormone therapy may be recommended to support growth in children.
Complications and Challenges
Living with phosphate diabetes can present several challenges and complications. Here are some important considerations:
-
Bone Deformities: Untreated phosphate diabetes can lead to bone deformities, especially in children.
-
Dental Issues: Weak enamel and frequent cavities are common dental problems associated with this condition.
-
Hearing Loss: Some individuals may experience hearing loss due to abnormalities in the bones of the middle ear.
-
Kidney Stones: High doses of phosphate supplements can increase the risk of kidney stones.
-
Psychosocial Impact: Chronic pain and physical limitations can affect mental health and quality of life.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve the understanding and treatment of phosphate diabetes. Here are some exciting developments:
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment to correct genetic mutations causing phosphate diabetes.
-
New Medications: New drugs targeting the underlying genetic causes are being developed and tested.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries help collect data on the condition, aiding research and improving patient care.
-
International Collaboration: Global research collaborations are essential for advancing the understanding and treatment of rare diseases like phosphate diabetes.
Living with Phosphate Diabetes
Managing daily life with phosphate diabetes requires a proactive approach. Here are some tips for living well with this condition:
-
Regular Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises can help strengthen bones and improve overall health.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others with similar experiences.
-
Education: Educating yourself and your family about the condition can empower you to manage it effectively.
-
Medical Team: Working with a multidisciplinary medical team, including endocrinologists, nephrologists, and dietitians, ensures comprehensive care.
-
Mental Health: Addressing mental health needs through counseling or therapy can improve quality of life.
Interesting Facts
Here are some additional interesting facts about phosphate diabetes that you might find intriguing:
-
Historical Cases: The first cases of phosphate diabetes were described in the early 20th century, highlighting its long-standing recognition.
-
Rare Condition: Phosphate diabetes is considered a rare disease, affecting approximately 1 in 20,000 people.
-
Animal Models: Animal models, like mice with similar genetic mutations, are used in research to study the condition and test new treatments.
-
Public Awareness: Increased public awareness and advocacy efforts are helping to improve diagnosis and treatment options.
-
Personal Stories: Many individuals with phosphate diabetes share their personal stories online, offering inspiration and support to others.
Final Thoughts on Phosphate Diabetes
Phosphate diabetes, also known as hypophosphatemic rickets, is a rare but significant condition. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options can make a big difference in managing it effectively. Early diagnosis and proper medical care are crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected.
Genetic factors play a major role, so family history should be considered. Treatment often involves phosphate supplements and vitamin D to help manage symptoms and improve bone health. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure that the condition is monitored and managed well.
Awareness and education about phosphate diabetes can lead to better outcomes and support for those living with this condition. By staying informed and proactive, individuals and families can navigate the challenges of phosphate diabetes more effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
