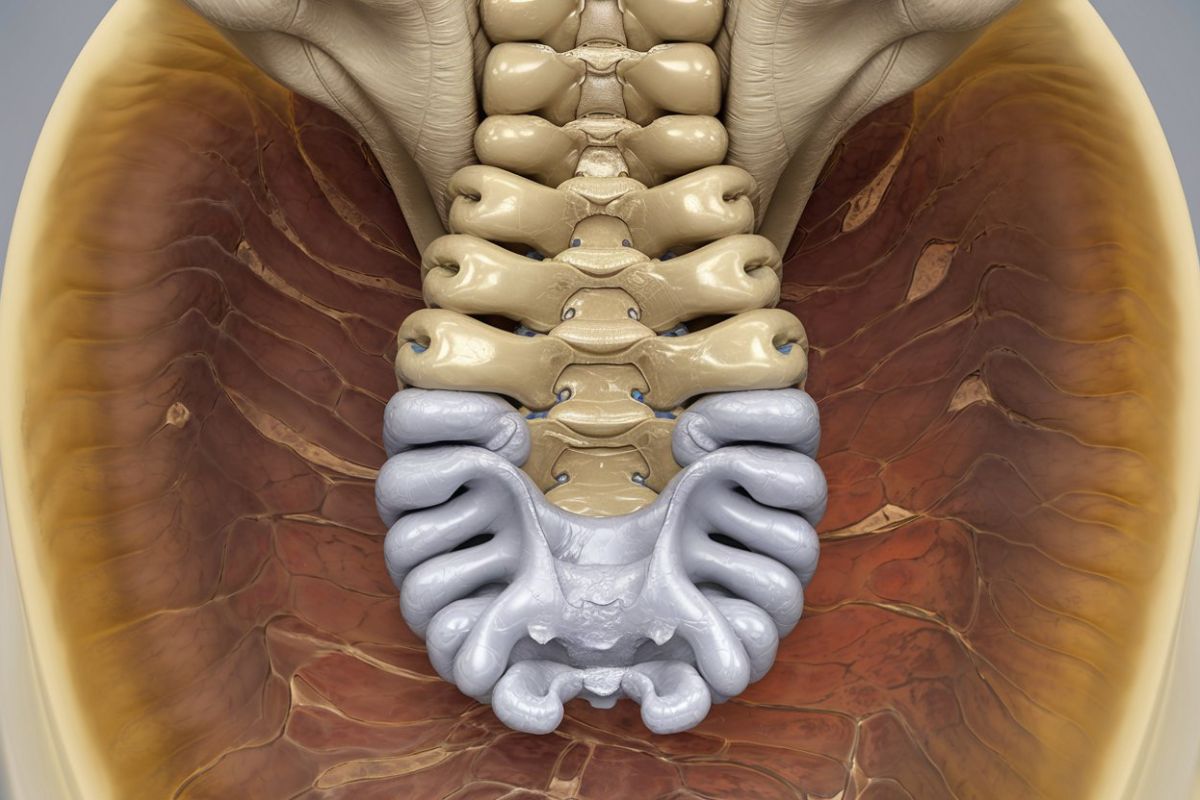
What is a sacral meningocele? A sacral meningocele is a rare type of spinal defect where a sac filled with cerebrospinal fluid protrudes through an opening in the sacrum, the lower part of the spine. This condition can be present at birth and may cause various symptoms, including lower back pain, bladder issues, and leg weakness. Understanding sacral meningocele is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve quality of life. In this blog post, we'll explore 30 intriguing facts about sacral meningocele, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Get ready to learn more about this unique medical condition!
Key Takeaways:
- Sacral meningocele is a rare condition involving a sac filled with cerebrospinal fluid that protrudes through a defect in the sacrum. It can cause symptoms like lower back pain, bowel and bladder dysfunction, and leg weakness.
- Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing sacral meningocele effectively. Surgery is often required to repair the defect and prevent complications, while non-surgical options like physical therapy and pain management may be sufficient in mild cases.
What is Sacral Meningocele?
Sacral meningocele is a rare condition involving a sac filled with cerebrospinal fluid that protrudes through a defect in the sacrum. This condition can affect the nervous system and other bodily functions. Here are some intriguing facts about sacral meningocele.
-
Rare Condition: Sacral meningocele is an uncommon congenital disorder, affecting approximately 1 in 5,000 live births.
-
Neural Tube Defect: It is classified as a neural tube defect, which occurs when the neural tube fails to close completely during embryonic development.
-
Types: There are two main types: anterior sacral meningocele and posterior sacral meningocele. The anterior type is more common.
-
Symptoms Vary: Symptoms can range from mild to severe, including lower back pain, bowel and bladder dysfunction, and leg weakness.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis often involves imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans to visualize the sac and its contents.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors can help in early detection and management of sacral meningocele.
-
Genetic Factors: Genetic mutations can play a role in the development of sacral meningocele.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors during pregnancy, such as lack of folic acid, can increase the risk.
-
Family History: A family history of neural tube defects can elevate the risk of sacral meningocele in newborns.
-
Maternal Health: Conditions like diabetes and obesity in the mother can contribute to the risk.
-
Medications: Certain medications taken during pregnancy, such as anti-seizure drugs, may increase the likelihood of neural tube defects.
Symptoms and Complications
The symptoms and complications associated with sacral meningocele can significantly impact a person's quality of life.
-
Lower Back Pain: Persistent lower back pain is a common symptom.
-
Neurological Issues: Neurological symptoms may include leg weakness or numbness.
-
Bowel Dysfunction: Many individuals experience bowel dysfunction, leading to constipation or incontinence.
-
Bladder Issues: Bladder dysfunction is also common, causing urinary incontinence or retention.
-
Infections: The sac can become infected, leading to serious complications such as meningitis.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing sacral meningocele effectively.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: In some cases, sacral meningocele can be detected during prenatal ultrasounds.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans provide detailed images of the sac and surrounding structures, aiding in diagnosis.
-
CT Scans: CT scans can also be used to diagnose sacral meningocele, especially in emergency situations.
-
Surgical Treatment: Surgery is often required to repair the defect and prevent complications.
-
Non-Surgical Options: In mild cases, non-surgical treatments such as physical therapy and pain management may be sufficient.
Living with Sacral Meningocele
Living with sacral meningocele involves managing symptoms and preventing complications through various strategies.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor the condition and detect any changes early.
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve mobility and reduce pain.
-
Bladder Training: Bladder training techniques can help manage urinary incontinence.
-
Bowel Management: Dietary changes and medications can assist in managing bowel dysfunction.
-
Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for individuals and families affected by sacral meningocele.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve the understanding and treatment of sacral meningocele.
-
Genetic Research: Studies are being conducted to identify specific genetic mutations associated with sacral meningocele.
-
Folic Acid: Research highlights the importance of folic acid supplementation during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
-
Advanced Imaging: Advances in imaging technology are improving the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment planning.
-
Stem Cell Therapy: Experimental treatments like stem cell therapy are being explored as potential options for repairing neural tube defects.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries are being established to collect data and improve understanding of the condition, leading to better treatment outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Sacral Meningocele
Understanding sacral meningocele can be overwhelming, but knowing the facts helps. This condition involves a sac-like protrusion at the base of the spine, often present at birth. It can lead to various complications, including neurological issues and mobility problems. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Regular check-ups, physical therapy, and sometimes surgery are part of the treatment plan.
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in supporting children with this condition. Staying informed and working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best care possible. Remember, while sacral meningocele presents challenges, many individuals lead fulfilling lives with the right support and medical care. Stay proactive, seek support, and focus on the positives. Knowledge truly empowers those affected by this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
