Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome, also known as Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), is a rare genetic disorder that affects blood vessels. This condition can lead to abnormal blood vessel formation, causing frequent nosebleeds, skin discolorations, and even serious complications like internal bleeding. HHT is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a single copy of the altered gene can cause the disorder. People with this syndrome often experience symptoms from childhood, but the severity can vary widely. Understanding Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome is crucial for managing its symptoms and improving quality of life. Here are 30 facts to help you get a better grasp of this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome, or HHT, is a rare genetic disorder causing abnormal blood vessel formation. It leads to symptoms like nosebleeds, skin lesions, and internal bleeding, requiring careful management and support.
- Genetic and environmental factors influence the severity of HHT. Lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and support networks are crucial for managing the condition effectively and improving outcomes.
What is Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome?
Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome, also known as Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), is a genetic disorder affecting blood vessels. It can lead to various complications, primarily due to abnormal blood vessel formation. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Basis: HHT is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a single copy of the altered gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the disorder.
-
Prevalence: Approximately 1 in 5,000 people worldwide are affected by HHT, making it relatively rare.
-
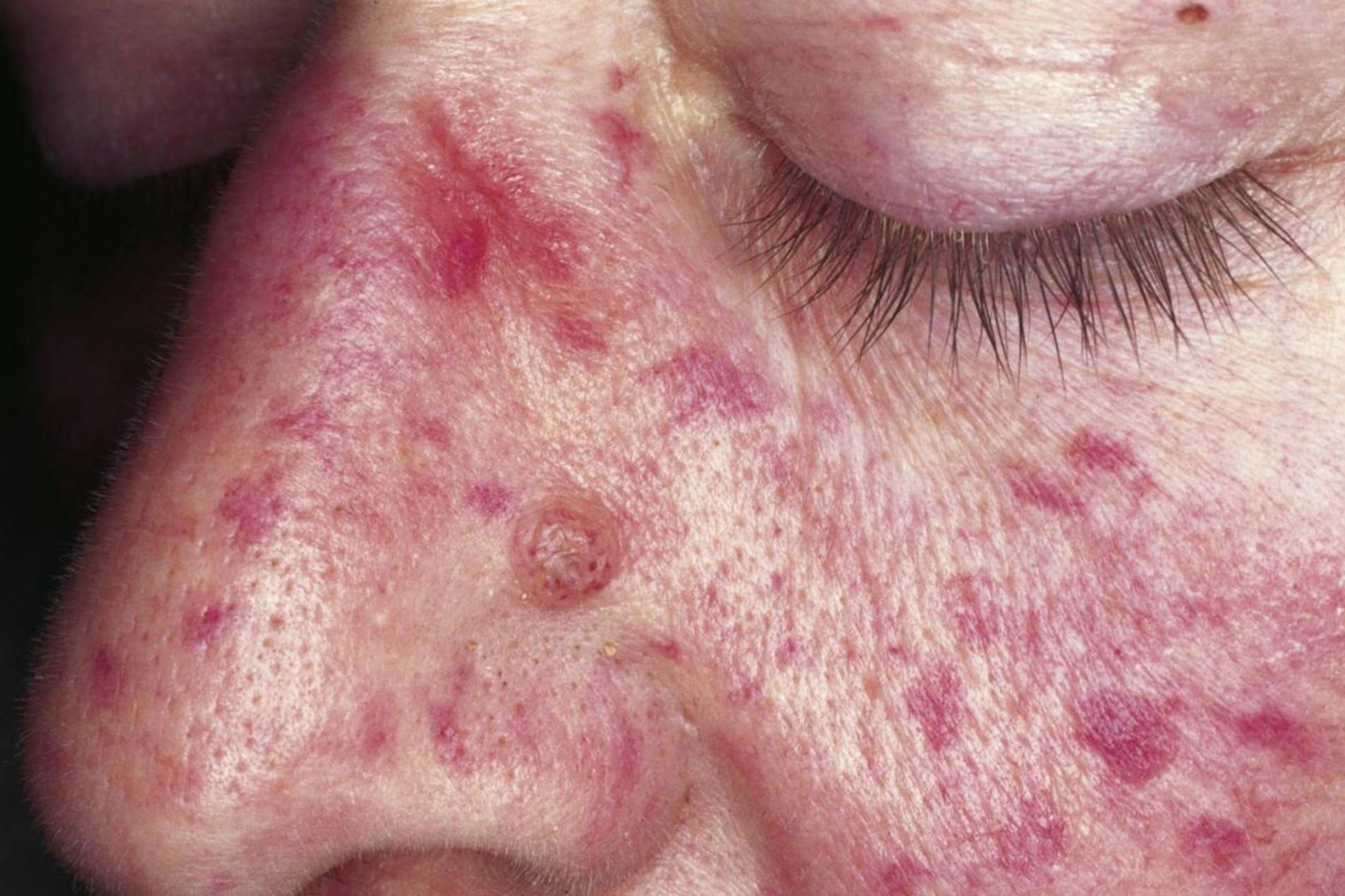
Telangiectasias: Small, dilated blood vessels called telangiectasias are a hallmark of HHT. They often appear on the skin and mucous membranes.
-
Nosebleeds: Frequent nosebleeds, or epistaxis, are a common symptom. They occur due to fragile blood vessels in the nasal lining.
-
Internal Bleeding: HHT can cause bleeding in internal organs, such as the lungs, liver, and brain, leading to serious health issues.
-
AVMs: Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are abnormal connections between arteries and veins. They can occur in various organs and pose significant risks.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis often involves genetic testing, imaging studies, and clinical evaluation of symptoms.
-
Screening: Family members of individuals with HHT are often screened for the disorder due to its hereditary nature.
-
Treatment: While there is no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and preventing complications. This may include medications, laser therapy, or surgery.
-
Iron Deficiency: Chronic bleeding can lead to iron deficiency anemia, requiring iron supplements or blood transfusions.
Symptoms and Complications
Understanding the symptoms and potential complications of HHT is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Here are some key points to consider.
-
Skin Lesions: Telangiectasias can appear as red or purple spots on the skin, particularly on the face, lips, and fingers.
-
Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Telangiectasias in the digestive tract can cause gastrointestinal bleeding, leading to anemia and other complications.
-
Pulmonary AVMs: AVMs in the lungs can cause shortness of breath, fatigue, and an increased risk of stroke or brain abscess.
-
Cerebral AVMs: AVMs in the brain can lead to headaches, seizures, or even hemorrhagic stroke.
-
Liver Involvement: Liver AVMs can cause high-output heart failure, portal hypertension, and other liver-related issues.
-
Fatigue: Chronic bleeding and anemia can result in persistent fatigue and weakness.
-
Vision Problems: Rarely, telangiectasias can affect the eyes, leading to vision problems.
-
Heart Issues: High-output heart failure can occur due to the increased blood flow through AVMs.
-
Pregnancy Risks: Pregnant women with HHT are at higher risk for complications, including severe bleeding and preeclampsia.
-
Infections: AVMs in the lungs can increase the risk of infections, such as brain abscesses.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Both genetic and environmental factors play a role in the manifestation and severity of HHT. Here are some insights into these influences.
-
Gene Mutations: Mutations in the ENG, ACVRL1, and SMAD4 genes are commonly associated with HHT.
-
Variable Expression: The severity of symptoms can vary widely, even among family members with the same genetic mutation.
-
Environmental Triggers: Factors like trauma, surgery, or certain medications can exacerbate symptoms or trigger bleeding episodes.
-
Age of Onset: Symptoms can appear at any age, but nosebleeds often start in childhood, while other complications may develop later in life.
-
Gender Differences: Some studies suggest that women may experience more severe symptoms than men, particularly during pregnancy.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Avoiding activities that increase the risk of bleeding, such as contact sports, can help manage the condition.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups and monitoring of symptoms are essential for early detection and management of complications.
-
Support Networks: Joining support groups and connecting with others who have HHT can provide valuable emotional and practical support.
-
Research Advances: Ongoing research aims to better understand the genetic basis of HHT and develop more effective treatments.
-
Awareness: Raising awareness about HHT among healthcare providers and the general public can lead to earlier diagnosis and improved outcomes.
Final Thoughts on Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome
Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome, also known as Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT), is a rare genetic disorder that affects blood vessels. It can lead to frequent nosebleeds, skin abnormalities, and complications in organs like the lungs, liver, and brain. Understanding the symptoms and seeking early medical advice can help manage the condition effectively. Genetic counseling is crucial for families with a history of HHT to understand their risks. While there's no cure, treatments like laser therapy for nosebleeds and medications to control bleeding can improve quality of life. Awareness and education about this condition are key to better management and support for those affected. Stay informed, consult healthcare professionals, and connect with support groups to navigate life with Osler–Weber–Rendu Syndrome.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
