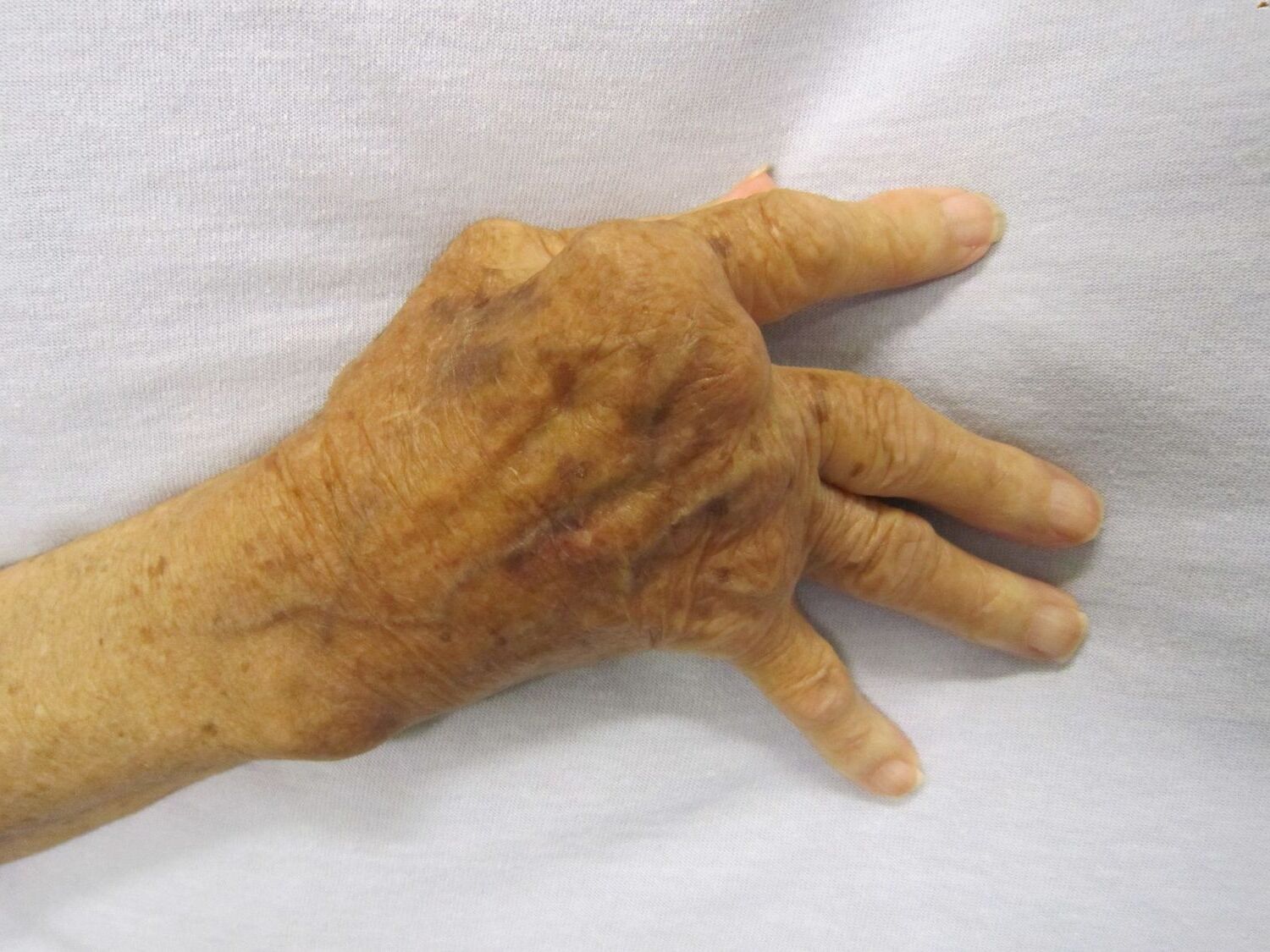
Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it doesn't have to be complicated. What is Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis? It's a type of arthritis where the rheumatoid factor, a protein often found in the blood of those with rheumatoid arthritis, is absent. This condition can still cause joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, making daily activities challenging. Unlike its counterpart, seropositive rheumatoid arthritis, this form can be trickier to diagnose since the usual blood test for rheumatoid factor comes back negative. However, other tests and symptoms help doctors identify it. Treatment often involves medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Learning about this condition can empower those affected to seek the right care and support. Understanding the basics can make a big difference in managing health effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Living with Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis requires support, adjustments, and a positive attitude. From stress management to personalized treatment plans, there are many ways to lead a fulfilling life with proper management.
- Understanding Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis involves recognizing symptoms, seeking medical support, and making lifestyle adjustments. With the right care and awareness, individuals can effectively manage this condition and lead fulfilling lives.
Understanding Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis
Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis is a type of arthritis that can be puzzling. Unlike typical rheumatoid arthritis, this condition doesn't show the usual rheumatoid factor in blood tests. Let's dive into some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis doesn't mean the absence of arthritis. It simply indicates that the rheumatoid factor, an antibody often found in rheumatoid arthritis patients, is not present in the blood.
-
Symptoms can be similar to those of rheumatoid arthritis, including joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. However, the absence of the rheumatoid factor can make diagnosis more challenging.
-
Diagnosis often relies on a combination of clinical symptoms and other blood tests, such as anti-CCP antibodies, which can be present even when the rheumatoid factor is negative.
-
Age of Onset varies widely. While rheumatoid arthritis typically begins between ages 30 and 60, negative rheumatoid factor polyarthritis can start at any age.
-
Gender Differences exist, with women being more commonly affected than men, similar to other forms of arthritis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes this condition can help in managing it better. While the exact cause remains unknown, several factors can contribute.
-
Genetic Factors play a role. A family history of arthritis can increase the likelihood of developing negative rheumatoid factor polyarthritis.
-
Environmental Triggers such as smoking and exposure to certain infections may increase the risk of developing this condition.
-
Hormonal Influences might contribute, as the condition is more prevalent in women, suggesting a possible link to hormones.
-
Immune System Malfunctions are believed to be involved, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues.
Treatment and Management
Managing negative rheumatoid factor polyarthritis involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery.
-
Medications like NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and DMARDs are commonly used to reduce inflammation and pain.
-
Physical Therapy can help maintain joint function and improve mobility, making it a crucial part of treatment.
-
Diet and Nutrition play a role in managing symptoms. Anti-inflammatory foods like fish, nuts, and leafy greens can be beneficial.
-
Exercise is important for maintaining joint flexibility and overall health. Low-impact activities like swimming and walking are often recommended.
-
Surgical Options may be considered in severe cases where joint damage is extensive and other treatments have failed.
Living with Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis
Living with this condition requires adjustments and support, but many people lead fulfilling lives with proper management.
-
Support Groups can provide emotional support and practical advice from others who understand the challenges of living with arthritis.
-
Stress Management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress, which may exacerbate symptoms.
-
Regular Check-Ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
-
Adaptive Devices like special grips and tools can make daily tasks easier and reduce strain on joints.
-
Education and Awareness about the condition can empower patients to take an active role in their treatment and management.
-
Workplace Adjustments may be necessary to accommodate physical limitations, ensuring a comfortable and productive work environment.
-
Sleep Hygiene is crucial, as quality sleep can help reduce fatigue and improve overall well-being.
-
Hydration is important, as staying well-hydrated can help maintain joint lubrication and reduce stiffness.
-
Mindfulness Practices can improve mental health and help patients cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition.
-
Family Involvement in treatment plans can provide additional support and understanding, making it easier to manage daily challenges.
-
Technology and Apps can assist in tracking symptoms, medication schedules, and appointments, helping patients stay organized.
-
Alternative Therapies like acupuncture and massage may offer additional relief from pain and stiffness for some individuals.
-
Personalized Treatment Plans are essential, as each patient's experience with the condition can vary widely.
-
Awareness of Flare-Ups is important, as recognizing early signs can help in taking prompt action to manage symptoms.
-
Positive Attitude and resilience can make a significant difference in coping with the challenges of negative rheumatoid factor polyarthritis.
-
Research and Advances in medical science continue to improve understanding and treatment options, offering hope for better management in the future.
Understanding Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis
Negative Rheumatoid Factor Polyarthritis can be a bit tricky to grasp, but knowing the facts helps. It's a form of arthritis where the rheumatoid factor test comes back negative, yet symptoms persist. This condition can affect anyone, not just the elderly. Early diagnosis is key to managing symptoms effectively. Treatments often involve a mix of medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers ensure that the condition is monitored closely. While it might seem daunting, many people lead full, active lives with the right care. Staying informed and proactive about health can make a big difference. Remember, each person's experience with this condition is unique, so personalized treatment plans are essential. Keep asking questions, stay curious, and don't hesitate to seek support from medical professionals and support groups. Knowledge is power when it comes to managing health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
