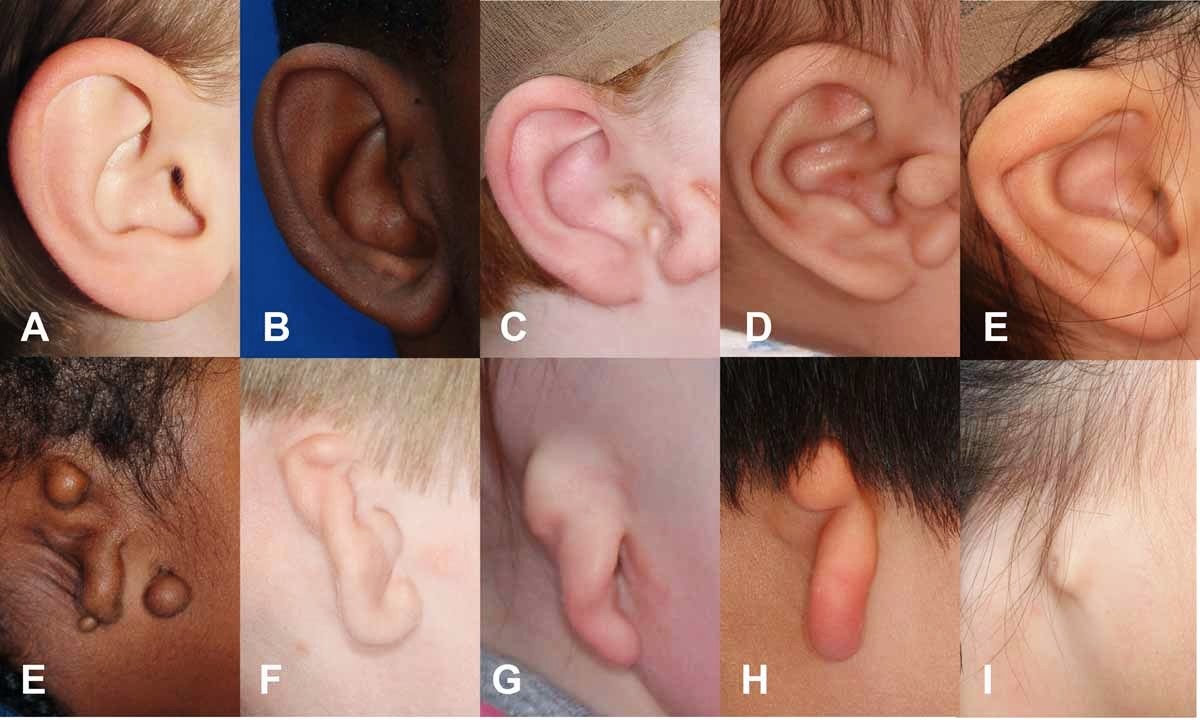
Meatal atresia is a rare condition that affects the ear canal, leading to hearing issues. But what exactly is it? Meatal atresia occurs when the ear canal is either underdeveloped or completely closed. This can happen in one or both ears and often comes with other ear abnormalities. Symptoms can range from mild hearing loss to complete deafness in the affected ear. Causes include genetic factors, infections during pregnancy, or exposure to certain medications. Treatment options vary, including surgery to open the ear canal or hearing aids to improve hearing. Understanding meatal atresia is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Key Takeaways:
- Meatal atresia is a rare condition where the urethral opening is narrow or missing, causing urinary issues. Surgery and regular check-ups can improve quality of life and manage complications.
- Early detection and treatment of meatal atresia can lead to a healthier life. Surgery, antibiotics, and support networks play a crucial role in managing this condition.
What is Meatal Atresia?
Meatal atresia is a medical condition where the external opening of the urethra is either absent or abnormally narrow. This can lead to various complications, especially related to urination. Here are some fascinating facts about meatal atresia.
-
Congenital Condition: Meatal atresia is often present at birth, meaning it is a congenital condition. It can be detected early in life through routine medical examinations.
-
Affects Both Genders: While it is more commonly diagnosed in males, females can also be affected by meatal atresia. The condition can present differently based on gender.
-
Urinary Issues: One of the primary symptoms is difficulty urinating. This can range from a weak urine stream to complete urinary obstruction.
-
Associated Syndromes: Meatal atresia can be part of a broader syndrome, such as hypospadias or other congenital anomalies. These syndromes often involve multiple organ systems.
-
Surgical Intervention: Treatment usually involves surgery to create or widen the urethral opening. This procedure is known as a meatotomy or meatoplasty.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Understanding the symptoms and how meatal atresia is diagnosed can help in early detection and treatment.
-
Painful Urination: Patients often experience pain during urination due to the restricted flow of urine.
-
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Frequent UTIs are common in individuals with meatal atresia because of incomplete bladder emptying.
-
Physical Examination: A simple physical examination by a healthcare provider can often diagnose meatal atresia. The external genitalia are inspected for abnormalities.
-
Imaging Tests: In some cases, imaging tests like ultrasounds or voiding cystourethrograms (VCUG) are used to assess the extent of the condition.
-
Urodynamic Studies: These tests measure how well the bladder and urethra are storing and releasing urine, helping to diagnose functional issues.
Treatment Options
Various treatment options are available to manage meatal atresia, ranging from non-invasive methods to surgical procedures.
-
Meatotomy: This is a minor surgical procedure where a small incision is made to widen the urethral opening.
-
Meatoplasty: A more extensive surgical procedure that reconstructs the urethral opening to ensure proper urine flow.
-
Catheterization: Temporary catheterization may be used to relieve urinary obstruction until surgery can be performed.
-
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are often prescribed to treat or prevent UTIs associated with meatal atresia.
-
Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the success of the treatment and to check for any complications.
Complications and Prognosis
While treatment is generally effective, there can be complications and varying prognoses for individuals with meatal atresia.
-
Scar Tissue Formation: Post-surgical scar tissue can sometimes cause re-narrowing of the urethral opening, requiring additional procedures.
-
Incontinence: Some patients may experience urinary incontinence after surgery, although this is relatively rare.
-
Long-Term Monitoring: Lifelong monitoring may be necessary to ensure that the urethral opening remains functional and to manage any recurring issues.
-
Quality of Life: Successful treatment can significantly improve the quality of life, allowing individuals to lead normal, healthy lives.
-
Psychological Impact: The condition and its treatment can have psychological effects, especially in children. Counseling and support groups can be beneficial.
Prevalence and Research
Understanding the prevalence and ongoing research can provide insights into future treatments and management strategies.
-
Rare Condition: Meatal atresia is relatively rare, affecting a small percentage of the population.
-
Genetic Factors: Research suggests that genetic factors may play a role in the development of meatal atresia, although more studies are needed.
-
Environmental Factors: Some environmental factors during pregnancy may increase the risk of congenital anomalies like meatal atresia.
-
Innovative Treatments: Ongoing research is exploring less invasive treatments and better surgical techniques to improve outcomes.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries and databases are being developed to collect data and improve understanding of the condition.
Living with Meatal Atresia
Living with meatal atresia involves managing symptoms and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
-
Hydration: Staying well-hydrated can help reduce the risk of UTIs and other complications.
-
Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor the condition and catch any issues early.
-
Healthy Diet: A balanced diet can support overall health and reduce the risk of infections.
-
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can improve bladder function and overall well-being.
-
Support Networks: Joining support groups or networks can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition.
Final Thoughts on Meatal Atresia
Meatal atresia, a condition affecting the ear canal, can lead to hearing loss and other complications. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. Treatments range from hearing aids to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the condition. Regular check-ups with an ENT specialist can help monitor and manage symptoms. Awareness and education about meatal atresia can empower individuals and families to seek timely medical advice. By staying informed, you can take proactive steps to address any hearing issues and ensure better outcomes. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to health. Stay curious, stay informed, and take charge of your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
