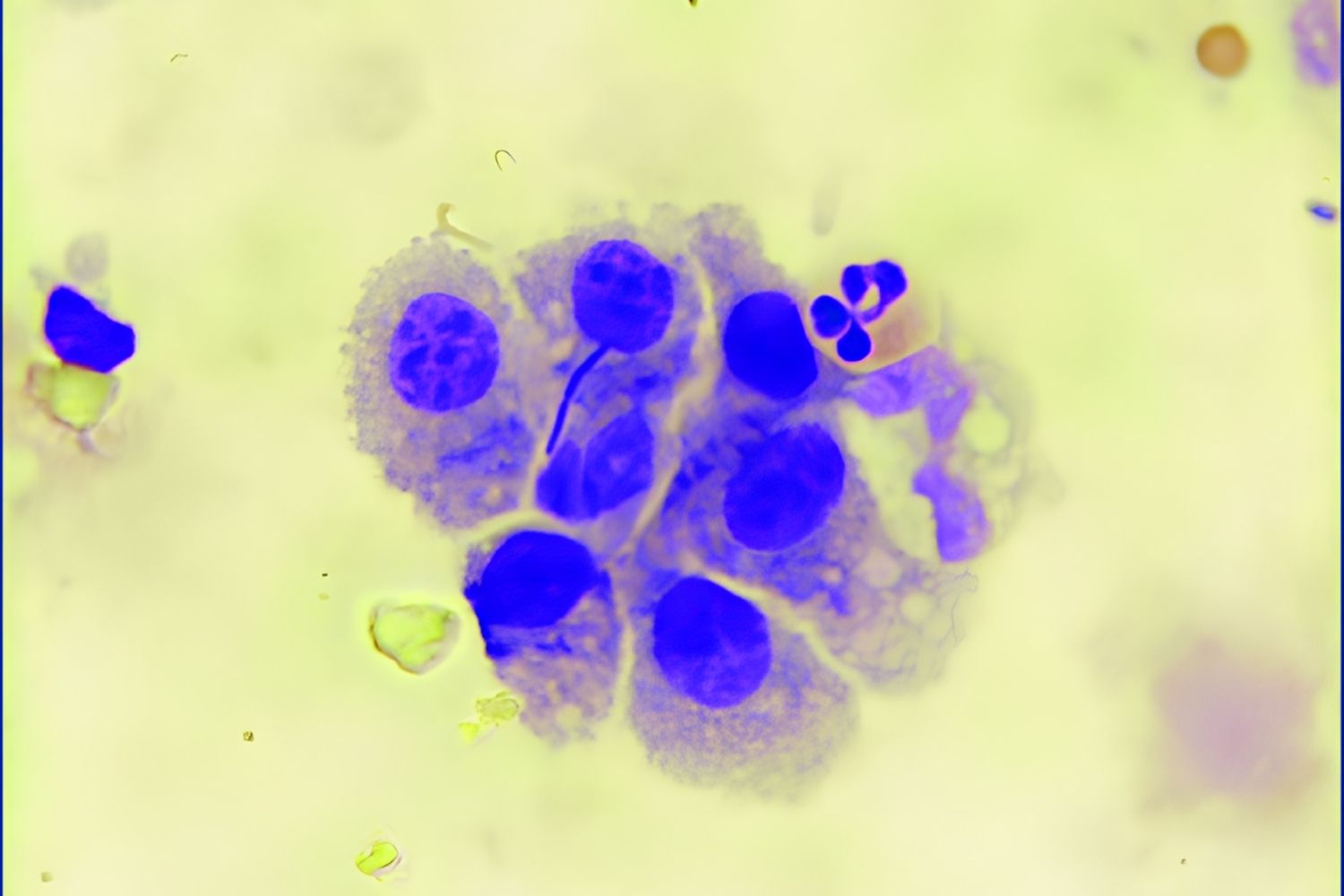
Lymphocytic pleocytosis might sound like a mouthful, but it's a term that describes an increase in lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This condition often signals an underlying issue, such as an infection, inflammation, or even certain cancers. Understanding lymphocytic pleocytosis can help in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. In this blog post, we'll dive into 30 intriguing facts about this condition, shedding light on its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. Whether you're a student, a curious reader, or someone affected by this condition, these facts will provide valuable insights into the world of lymphocytic pleocytosis.
Key Takeaways:
- Lymphocytic pleocytosis is a condition with increased lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid, often caused by infections or autoimmune diseases. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial for better outcomes.
- Symptoms of lymphocytic pleocytosis can include headaches, fever, neck stiffness, and confusion. Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause, including antiviral medications, antibiotics, and supportive care.
What is Lymphocytic Pleocytosis?
Lymphocytic pleocytosis is a medical condition characterized by an increased number of lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This can be a sign of various underlying health issues, often related to infections or inflammatory diseases.
-
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune system, helping the body fight off infections.
-
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounds and cushions the brain and spinal cord, providing protection and nutrient transport.
-
Normal CSF contains very few lymphocytes, typically fewer than 5 cells per microliter.
-
Lymphocytic pleocytosis is diagnosed when the lymphocyte count in CSF exceeds the normal range.
Causes of Lymphocytic Pleocytosis
Understanding the causes of lymphocytic pleocytosis can help in diagnosing the underlying condition. Here are some common causes:
-
Viral infections such as meningitis or encephalitis often lead to an increased lymphocyte count in the CSF.
-
Bacterial infections, though less common, can also cause lymphocytic pleocytosis.
-
Fungal infections like cryptococcal meningitis may result in elevated lymphocyte levels in the CSF.
-
Parasitic infections can sometimes lead to this condition, although they are rare.
-
Autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis can cause inflammation and increased lymphocytes in the CSF.
-
Certain cancers, including lymphoma and leukemia, may lead to lymphocytic pleocytosis.
Symptoms Associated with Lymphocytic Pleocytosis
Symptoms can vary depending on the underlying cause but often include signs of central nervous system involvement.
-
Headaches are a common symptom due to increased pressure in the CSF.
-
Fever often accompanies infections that cause lymphocytic pleocytosis.
-
Neck stiffness is a hallmark of meningitis, one of the conditions that can cause lymphocytic pleocytosis.
-
Nausea and vomiting may occur due to increased intracranial pressure.
-
Sensitivity to light (photophobia) is another symptom often seen in meningitis.
-
Confusion or altered mental status can be a sign of encephalitis or other serious conditions affecting the brain.
Diagnosing Lymphocytic Pleocytosis
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests.
-
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) is the primary method for obtaining CSF to analyze lymphocyte count.
-
CSF analysis includes cell count, protein levels, glucose levels, and microbiological cultures.
-
Imaging studies like MRI or CT scans may be used to identify underlying causes such as tumors or abscesses.
-
Blood tests can help identify systemic infections or autoimmune markers.
-
Electroencephalogram (EEG) may be used to assess brain function, especially if seizures are present.
Treatment Options for Lymphocytic Pleocytosis
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the condition.
-
Antiviral medications are used to treat viral infections like herpes simplex virus encephalitis.
-
Antibiotics are prescribed for bacterial infections causing lymphocytic pleocytosis.
-
Antifungal treatments are necessary for fungal infections such as cryptococcal meningitis.
-
Corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation in autoimmune conditions.
-
Chemotherapy or radiation might be required for cancers causing lymphocytic pleocytosis.
-
Supportive care including pain management and hydration is essential for patient comfort and recovery.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The prognosis for lymphocytic pleocytosis varies widely based on the underlying cause and the timeliness of treatment.
-
Early diagnosis and treatment significantly improve outcomes, especially in infectious causes.
-
Chronic conditions like multiple sclerosis may require ongoing management but can be controlled with proper treatment.
-
Severe infections or cancers may have a more guarded prognosis, but advances in medical treatments continue to improve survival rates.
Final Thoughts on Lymphocytic Pleocytosis
Lymphocytic pleocytosis, a condition marked by an increased number of lymphocytes in cerebrospinal fluid, often signals infections or inflammatory diseases. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic methods is crucial for effective treatment. Early detection can lead to better outcomes, especially in cases involving serious infections like meningitis or autoimmune disorders.
Knowledge about this condition empowers patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions. Staying aware of the latest research and advancements in medical science can help manage and treat lymphocytic pleocytosis more effectively.
Remember, if you or someone you know experiences symptoms like severe headaches, fever, or neck stiffness, seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference. Stay informed, stay healthy, and always consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
