Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy is a genetic disorder affecting the peripheral nerves, causing muscle weakness, numbness, and pain. Did you know that this condition often begins in childhood or adolescence? Symptoms can vary widely, making it tricky to diagnose. Interestingly, it’s caused by mutations in specific genes responsible for nerve function. Families with a history of this disorder should consider genetic counseling. Managing the symptoms involves physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgery. Staying informed about the latest research can help those affected lead better lives. Curious about more details? Keep reading to uncover 30 fascinating facts about this condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy is a genetic disorder that affects the nerves, causing muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and balance issues. While there is no cure, treatments and lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Research into Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy is ongoing, with potential treatments such as gene therapy and stem cell research. Participating in clinical trials and joining patient registries can provide access to new treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
What is Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy?
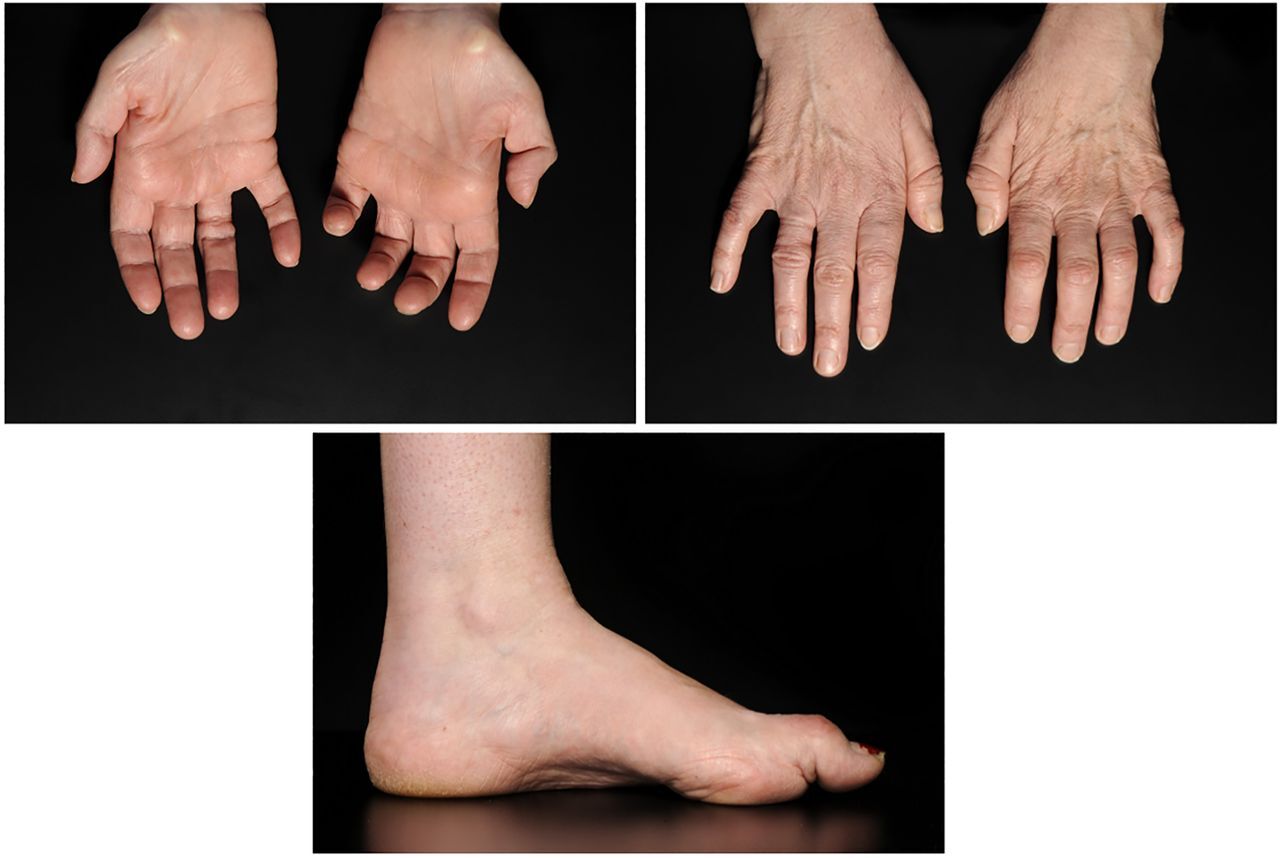
Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy (HT2N) is a genetic disorder affecting the peripheral nerves. These nerves connect the brain and spinal cord to muscles and sensory organs. Understanding this condition can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Genetic Origin: HT2N is caused by mutations in specific genes inherited from parents.
- Peripheral Nerves: It primarily impacts peripheral nerves, which control muscle movement and sensation.
- Autosomal Dominant: This condition is often autosomal dominant, meaning one copy of the mutated gene can cause the disorder.
- Late Onset: Symptoms typically appear in adolescence or adulthood, unlike other hereditary neuropathies.
- Progressive Nature: HT2N is progressive, meaning symptoms worsen over time.
Symptoms of Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management. Here are some common signs to watch for.
- Muscle Weakness: Affected individuals often experience muscle weakness, especially in the lower limbs.
- Loss of Sensation: There can be a gradual loss of sensation in the hands and feet.
- Balance Issues: Difficulty maintaining balance is a common symptom due to nerve damage.
- Foot Deformities: High arches or hammer toes may develop as a result of muscle weakness.
- Pain: Chronic pain, often described as burning or tingling, can occur in affected areas.
Diagnosis of Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Here’s how doctors identify HT2N.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic tests can confirm the presence of mutations associated with HT2N.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: These tests measure the speed of electrical signals in the nerves.
- Electromyography (EMG): EMG assesses the electrical activity of muscles to detect abnormalities.
- Family History: A detailed family history can provide clues about the hereditary nature of the condition.
- Clinical Examination: Doctors perform physical exams to check for muscle weakness and sensory loss.
Treatment Options for Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy
While there is no cure, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help maintain muscle strength and flexibility.
- Pain Management: Medications like gabapentin or pregabalin can help manage chronic pain.
- Orthopedic Devices: Braces or orthopedic shoes can assist with mobility and prevent deformities.
- Occupational Therapy: This therapy helps individuals adapt to daily activities and maintain independence.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to correct foot deformities.
Living with Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy
Managing daily life with HT2N involves various strategies to cope with symptoms and maintain well-being.
- Regular Exercise: Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can help maintain muscle strength.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports overall health and can help manage symptoms.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Assistive Devices: Using canes or walkers can improve mobility and reduce the risk of falls.
- Mental Health: Counseling or therapy can help manage the emotional impact of living with a chronic condition.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand HT2N and develop new treatments.
- Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for HT2N.
- Stem Cell Research: Stem cells may offer new ways to repair damaged nerves.
- Clinical Trials: Participating in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
- Biomarkers: Identifying biomarkers can help diagnose HT2N earlier and monitor disease progression.
- Patient Registries: Registries collect data from patients to improve understanding and treatment of HT2N.
Final Thoughts on Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy
Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy, a genetic condition, affects many people worldwide. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help manage the condition better. Early diagnosis plays a crucial role in slowing its progression. Genetic counseling offers valuable insights for families with a history of this neuropathy. Lifestyle changes, like a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve quality of life. Medications and therapies also provide relief from symptoms. Staying informed and proactive makes a significant difference. By sharing knowledge and experiences, we can support those affected and promote awareness. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. With the right approach, living with Hereditary Type 2 Neuropathy becomes more manageable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
