Ghon's Complex might sound like a mysterious term, but it's a crucial concept in understanding tuberculosis (TB). Named after Austrian pathologist Anton Ghon, this complex is a combination of a primary lung lesion and lymph node involvement. Ghon's Complex forms when the body first encounters TB bacteria, usually in childhood. The primary lesion, known as the Ghon focus, appears in the lung, while the bacteria travel to nearby lymph nodes, causing them to swell. This process is the body's way of trying to contain the infection. Understanding Ghon's Complex helps doctors diagnose and treat TB more effectively, ensuring better outcomes for patients. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 30 intriguing facts about Ghon's Complex!
Key Takeaways:
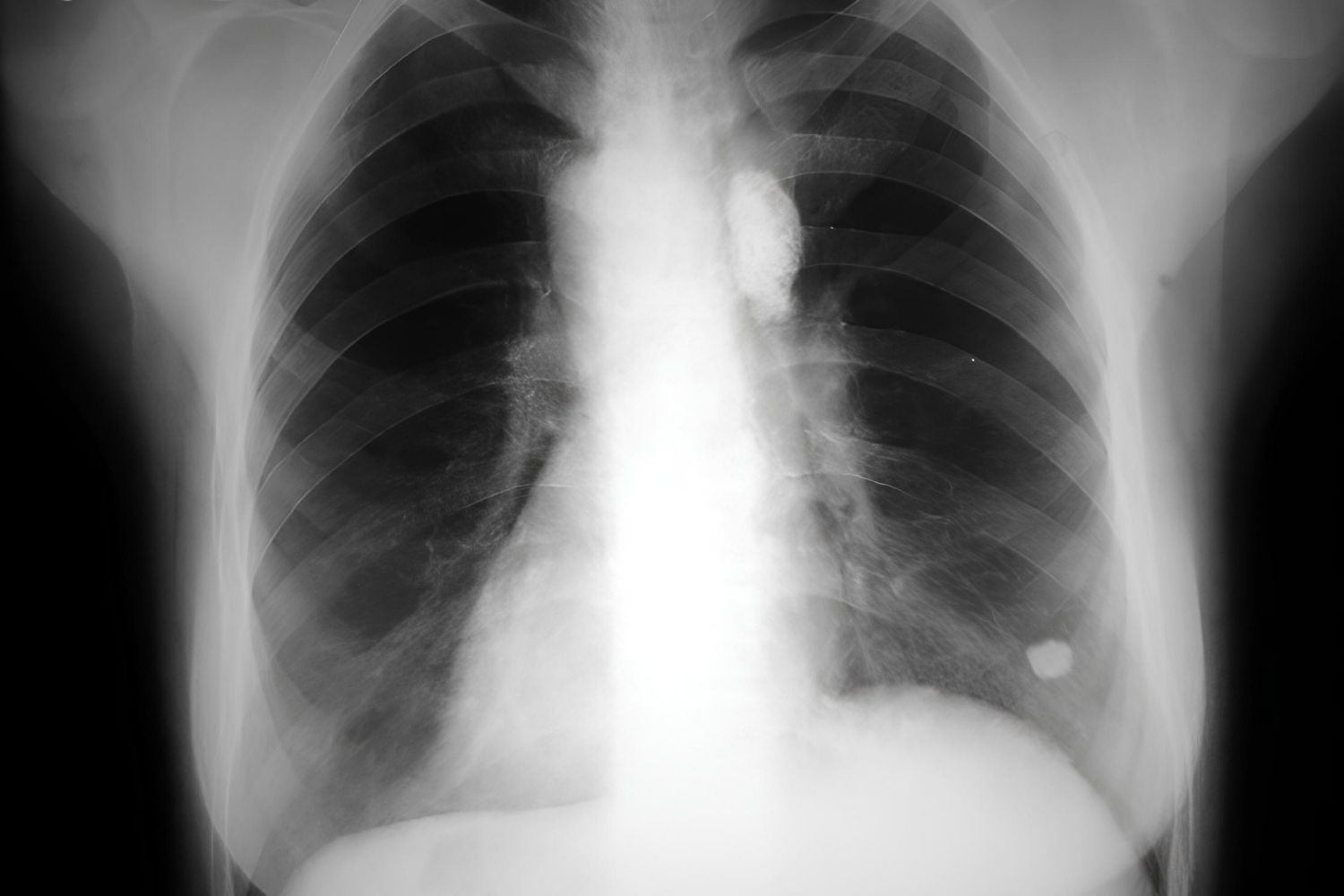
- Ghon's Complex is a lung lesion associated with tuberculosis, often seen in children. It can be detected through chest X-rays and plays a crucial role in TB diagnosis.
- Treatment involves antibiotic therapy, vaccination, and regular screening to prevent the spread of TB, a major global health issue. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help prevent TB.
What is Ghon's Complex?
Ghon's Complex is a term used in medical science, specifically in the context of tuberculosis (TB). It refers to a specific lesion seen in the lungs of individuals infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Understanding Ghon's Complex can provide insights into how TB affects the body.
-
Named After Anton Ghon: The term comes from Anton Ghon, an Austrian pathologist who first described it in the early 20th century.
-
Primary Infection Indicator: Ghon's Complex typically indicates a primary TB infection, meaning it's often seen in people who have been recently infected.
-
Consists of Two Parts: It includes a Ghon focus, which is the initial site of infection in the lung, and a lymph node involvement.
-
Calcification Over Time: Over time, the lesions can calcify, becoming visible on chest X-rays as a sign of past infection.
-
Common in Children: More frequently observed in children than adults, as their immune systems are still developing.
How Does Ghon's Complex Form?
The formation of Ghon's Complex involves a series of steps that begin with the inhalation of TB bacteria. Here are the key stages:
-
Inhalation of Bacteria: The process starts when TB bacteria are inhaled into the lungs.
-
Initial Infection Site: The bacteria settle in the alveoli, the tiny air sacs in the lungs, forming the Ghon focus.
-
Immune Response: The body's immune system responds, sending white blood cells to the infection site.
-
Lymphatic Spread: The bacteria can spread to nearby lymph nodes, causing them to swell.
-
Granuloma Formation: The immune system forms granulomas, which are clusters of immune cells that wall off the bacteria.
Symptoms and Detection
Ghon's Complex itself might not cause noticeable symptoms, but it plays a crucial role in the diagnosis of TB. Here’s what you need to know:
-
Often Asymptomatic: Many people with Ghon's Complex do not show symptoms, especially in the early stages.
-
Chest X-Rays: It can be detected through chest X-rays, where calcified lesions appear as white spots.
-
Tuberculin Skin Test: A positive tuberculin skin test can indicate TB infection, prompting further investigation for Ghon's Complex.
-
Sputum Test: Sputum samples can be tested for TB bacteria to confirm the presence of an active infection.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can also help detect TB infection and assess the immune response.
Complications and Risks
While Ghon's Complex itself is not usually harmful, it can lead to complications if the TB infection progresses. Here are some potential risks:
-
Reactivation of TB: In some cases, the bacteria can become active again, leading to secondary TB.
-
Spread to Other Organs: TB can spread from the lungs to other parts of the body, such as the kidneys or spine.
-
Scarring and Fibrosis: The lesions can cause scarring in the lungs, leading to reduced lung function.
-
Pleural Effusion: Fluid can accumulate around the lungs, causing difficulty breathing.
-
Miliary TB: In severe cases, TB can spread throughout the body, causing tiny lesions in multiple organs.
Treatment and Prevention
Managing Ghon's Complex involves treating the underlying TB infection and preventing its spread. Here are some key points:
-
Antibiotic Therapy: TB is treated with a combination of antibiotics over several months.
-
Directly Observed Therapy (DOT): Health workers may supervise patients to ensure they complete their treatment.
-
Vaccination: The BCG vaccine can help prevent TB, especially in children.
-
Regular Screening: High-risk individuals, such as healthcare workers, should undergo regular TB screening.
-
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy immune system through proper nutrition and exercise can help prevent TB.
Historical and Global Context
Understanding the historical and global context of Ghon's Complex can provide a broader perspective on TB. Here are some interesting facts:
-
Ancient Disease: TB has been affecting humans for thousands of years, with evidence found in ancient Egyptian mummies.
-
Global Health Issue: TB remains a major global health issue, with millions of new cases each year.
-
High-Risk Areas: Certain regions, such as sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia, have higher rates of TB.
-
Drug-Resistant TB: The emergence of drug-resistant TB strains poses a significant challenge to treatment.
-
World TB Day: March 24th is World TB Day, aimed at raising awareness and promoting efforts to combat TB.
Final Thoughts on Ghon's Complex
Ghon's Complex, a key indicator of tuberculosis, plays a crucial role in diagnosing this infectious disease. Named after Anton Ghon, it consists of a primary lesion in the lung and lymph nodes. Understanding its formation helps medical professionals detect TB early, improving treatment outcomes.
Recognizing symptoms like persistent cough, fever, and weight loss can prompt timely medical attention. Early detection and treatment are vital in managing TB and preventing its spread. Ghon's Complex highlights the importance of awareness and proactive healthcare.
By staying informed about TB and its indicators, individuals can contribute to better public health. Knowledge empowers us to take action, seek medical advice, and support those affected. Ghon's Complex serves as a reminder of the ongoing battle against tuberculosis and the need for vigilance in safeguarding our health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
