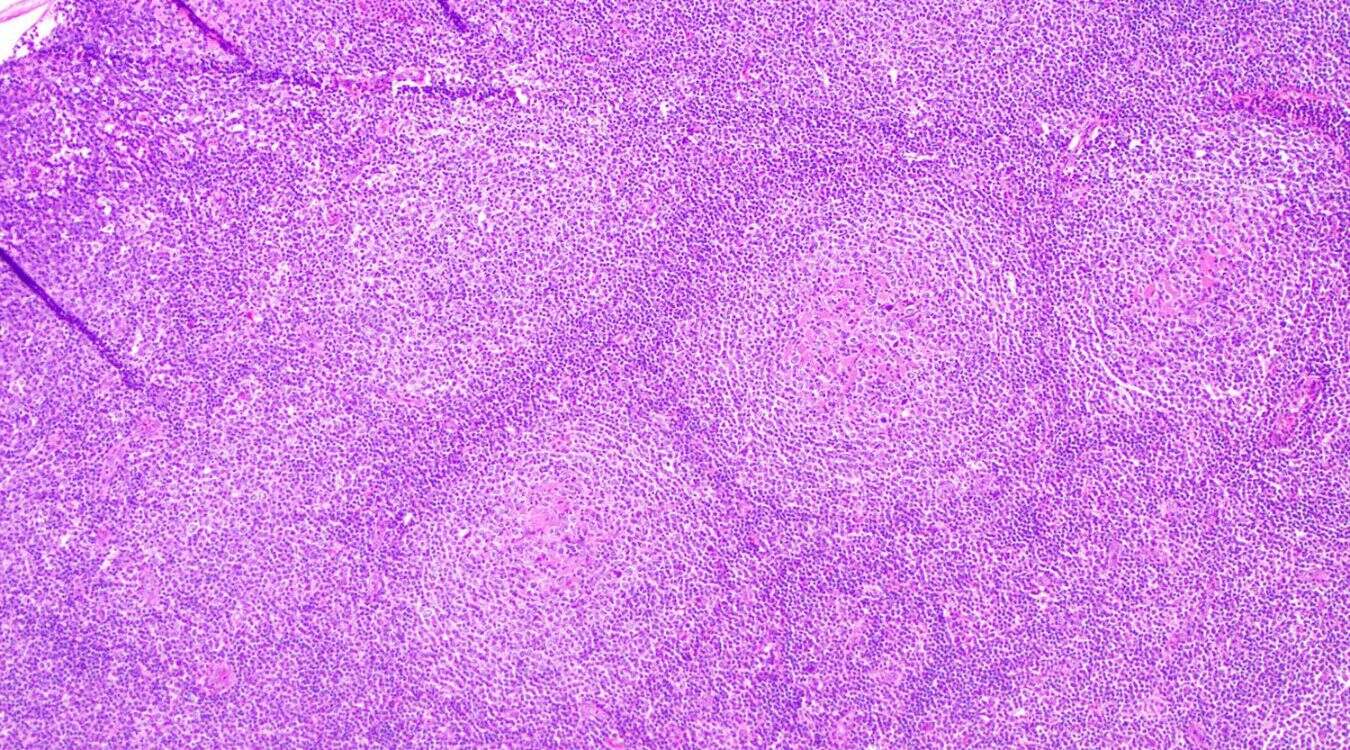
Brill–Symmers Disease, also known as Hodgkin's Lymphoma, is a type of cancer originating from white blood cells called lymphocytes. Named after pathologists Dr. Brill and Dr. Symmers, this disease primarily affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. Symptoms often include painless swelling of lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss. While the exact cause remains unknown, risk factors include a weakened immune system, family history, and certain viral infections like Epstein-Barr virus. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. Treatments typically involve chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of both. Understanding Brill–Symmers Disease can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking timely medical intervention.
Key Takeaways:
- Brill–Symmers Disease is a rare condition involving abnormal cell growth in the lymph nodes, causing symptoms like fever, fatigue, and enlarged lymph nodes. Diagnosis requires blood tests, imaging, and biopsy.
- Treatment options include corticosteroids, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, and surgery. Prognosis varies, with potential complications like increased infection risk and organ involvement. Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and develop more effective treatments.
What is Brill–Symmers Disease?
Brill–Symmers Disease, also known as idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease (iMCD), is a rare disorder involving an overgrowth of cells in the body's lymph nodes. This condition can affect multiple lymph node regions and has various symptoms and complications.
-
Rare Condition: Brill–Symmers Disease is extremely rare, with only a few hundred cases reported worldwide.
-
Named After Doctors: The disease is named after Dr. Brill and Dr. Symmers, who first described it in the 1950s.
-
Lymph Node Overgrowth: It involves the abnormal growth of cells in the lymph nodes, leading to enlarged lymph nodes.
-
Multicentric: The term "multicentric" means that the disease affects multiple lymph node regions simultaneously.
-
Idiopathic: The word "idiopathic" indicates that the cause of the disease is unknown.
Symptoms of Brill–Symmers Disease
Symptoms can vary widely among patients, making diagnosis challenging. Here are some common symptoms associated with this condition.
-
Fever: Many patients experience recurrent fevers without any apparent infection.
-
Fatigue: Chronic fatigue is a common symptom, often making daily activities difficult.
-
Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss can occur due to the body's increased metabolic demands.
-
Night Sweats: Patients often report severe night sweats, disrupting sleep.
-
Enlarged Lymph Nodes: Swollen lymph nodes, particularly in the neck, armpits, and groin, are a hallmark of the disease.
Diagnosis of Brill–Symmers Disease
Diagnosing this rare condition can be complex and often requires multiple tests and evaluations.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can reveal elevated levels of inflammatory markers.
-
Imaging Studies: CT scans and MRIs help identify enlarged lymph nodes and other affected areas.
-
Lymph Node Biopsy: A biopsy of an enlarged lymph node is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Exclusion of Other Diseases: Doctors must rule out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as lymphoma or autoimmune diseases.
-
Histopathological Examination: Examining tissue samples under a microscope helps identify characteristic cell patterns.
Treatment Options for Brill–Symmers Disease
Treatment varies depending on the severity of the disease and the patient's overall health. Here are some common treatment approaches.
-
Corticosteroids: These drugs help reduce inflammation and control symptoms.
-
Immunotherapy: Medications that modulate the immune system can be effective in managing the disease.
-
Chemotherapy: In severe cases, chemotherapy may be used to control cell overgrowth.
-
Surgery: Surgical removal of enlarged lymph nodes may be necessary in some cases.
-
Supportive Care: Managing symptoms like pain and fatigue is crucial for improving the patient's quality of life.
Prognosis and Complications
The prognosis for Brill–Symmers Disease varies widely, and complications can arise if the disease is not managed effectively.
-
Variable Prognosis: Some patients respond well to treatment, while others may have a more challenging course.
-
Increased Infection Risk: The disease and its treatments can weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of infections.
-
Organ Involvement: In some cases, the disease can affect organs like the liver, spleen, and kidneys.
-
Secondary Cancers: There is a risk of developing secondary cancers, such as lymphoma, in patients with Brill–Symmers Disease.
-
Chronic Pain: Persistent pain, particularly in the lymph node regions, can be a long-term issue.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Brill–Symmers Disease and develop more effective treatments.
-
Genetic Studies: Researchers are investigating potential genetic factors that may contribute to the disease.
-
New Therapies: Clinical trials are exploring new medications and treatment approaches.
-
Biomarkers: Identifying biomarkers could help in early diagnosis and monitoring disease progression.
-
Patient Registries: Collecting data from patients worldwide helps researchers identify patterns and improve treatment strategies.
-
Awareness and Education: Increasing awareness among healthcare providers and the public is essential for early diagnosis and effective management.
Final Thoughts on Brill–Symmers Disease
Brill–Symmers Disease, also known as Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system. Named after pathologists Dr. Brill and Dr. Symmers, this disease has unique characteristics that set it apart from other lymphomas. Early detection and treatment are crucial for better outcomes. Symptoms like swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and unexplained weight loss should not be ignored. Treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and sometimes stem cell transplants. Advances in medical research continue to improve survival rates and quality of life for patients. Understanding the facts about Brill–Symmers Disease can help in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate medical care. Stay informed and consult healthcare professionals for any concerns. Knowledge is power when it comes to managing health conditions like this.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
