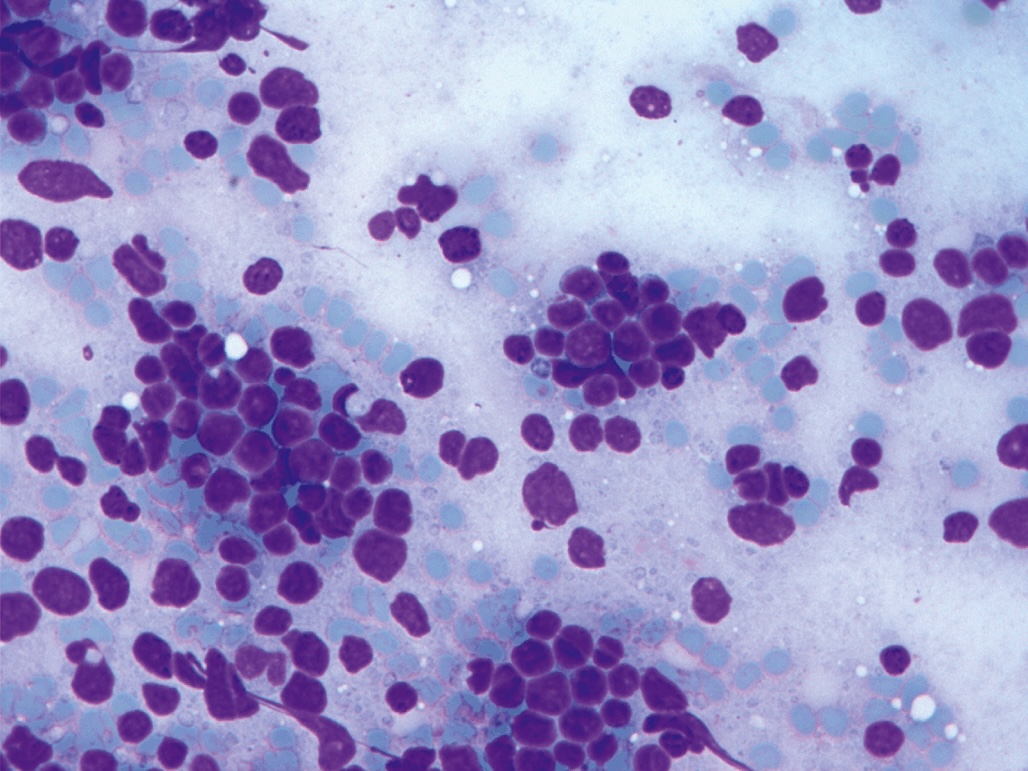
What exactly is a centrocyte? These cells play a crucial role in our immune system. Found in lymph nodes, they are part of the germinal center reaction, which helps our bodies fight off infections. Centrocytes are a type of B cell, specifically known as small cleaved cells. They undergo a process called somatic hypermutation, which allows them to adapt and improve their ability to recognize and bind to pathogens. This adaptability is vital for producing high-affinity antibodies. Understanding centrocytes can provide insights into how our immune system works and how certain diseases, like lymphomas, develop. Ready to dive deeper into the world of centrocytes? Let's explore 25 fascinating facts about these tiny but mighty cells!
Key Takeaways:
- Centrocytes, also known as small cleaved cells, are essential for producing high-affinity antibodies in the immune system. They play a crucial role in fighting off infections and providing long-lasting immunity.
- Understanding centrocytes' function can lead to new therapies and treatments for diseases like cancer and autoimmune disorders. Ongoing research holds promise for improving vaccine development and enhancing the immune response to pathogens.
What is a Centrocyte?
Centrocytes, also known as small cleaved cells, play a crucial role in the immune system. These cells are part of the germinal center reaction, which is essential for producing high-affinity antibodies. Here are some fascinating facts about centrocytes.
-
Centrocytes are B cells: These cells are a type of B lymphocyte that undergoes somatic hypermutation and selection in the germinal centers of lymph nodes.
-
Germinal center reaction: Centrocytes are formed during the germinal center reaction, a process that occurs in secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and the spleen.
-
Somatic hypermutation: This process involves the introduction of mutations into the variable region of the antibody genes, allowing centrocytes to produce antibodies with higher affinity for antigens.
-
Affinity maturation: Centrocytes undergo selection based on the affinity of their antibodies for the antigen, leading to the production of high-affinity antibodies.
-
Class switch recombination: Centrocytes can undergo class switch recombination, changing the antibody isotype they produce, such as switching from IgM to IgG.
Role in the Immune System
Centrocytes are integral to the adaptive immune response. They help the body fight off infections by producing specific antibodies. Let's dive into their role in more detail.
-
Antigen presentation: Centrocytes present antigens to T cells, which helps in the activation and differentiation of T cells.
-
Memory B cells: Some centrocytes differentiate into memory B cells, which provide long-lasting immunity by remembering past infections.
-
Plasma cells: Other centrocytes become plasma cells, which are responsible for producing large quantities of antibodies.
-
Interaction with follicular dendritic cells: Centrocytes interact with follicular dendritic cells in the germinal center, which present antigens and provide survival signals.
-
Cytokine signaling: Centrocytes respond to cytokines, which are signaling molecules that influence their differentiation and function.
Centrocytes in Health and Disease
Centrocytes play a role in both health and disease. Understanding their function can provide insights into various medical conditions.
-
Autoimmune diseases: Dysregulation of centrocytes can lead to autoimmune diseases, where the immune system attacks the body's own tissues.
-
Lymphomas: Centrocytes can give rise to certain types of lymphomas, such as follicular lymphoma, which is a cancer of the lymphatic system.
-
Immunodeficiencies: Defects in centrocyte function can result in immunodeficiencies, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
-
Vaccination: Effective vaccines rely on the generation of high-affinity antibodies by centrocytes, providing long-term protection against diseases.
-
Allergies: Centrocytes can contribute to allergic reactions by producing antibodies that recognize harmless substances as threats.
Research and Therapeutic Potential
Ongoing research on centrocytes holds promise for developing new therapies and improving existing treatments.
-
Monoclonal antibodies: Understanding centrocyte biology can aid in the development of monoclonal antibodies, which are used to treat various diseases, including cancer and autoimmune disorders.
-
Gene therapy: Advances in gene therapy may allow for the correction of genetic defects in centrocytes, potentially curing certain immunodeficiencies.
-
Targeted therapies: Researchers are exploring targeted therapies that specifically modulate centrocyte function, offering new treatment options for lymphomas and other diseases.
-
Vaccine development: Insights into centrocyte function can inform the design of more effective vaccines, enhancing the immune response to pathogens.
-
Immunotherapy: Centrocytes are a focus of immunotherapy research, which aims to harness the immune system to fight cancer and other diseases.
Interesting Facts About Centrocytes
Here are some additional intriguing facts about these vital immune cells.
-
Morphology: Centrocytes have a distinctive appearance, with a small, cleaved nucleus and scant cytoplasm.
-
Life span: The life span of centrocytes is relatively short, typically lasting only a few days unless they differentiate into memory B cells or plasma cells.
-
Migration: Centrocytes migrate within the germinal center, moving between the dark zone, where they proliferate, and the light zone, where they undergo selection.
-
Surface markers: Centrocytes express specific surface markers, such as CD19 and CD20, which help identify them among other B cells.
-
Evolutionary significance: The ability of centrocytes to produce high-affinity antibodies has been crucial for the evolution of adaptive immunity, allowing organisms to effectively combat a wide range of pathogens.
The Final Word on Centrocytes
Centrocytes, or small cleaved cells, play a crucial role in the immune system. These cells are essential for producing antibodies and fighting infections. Found in the germinal centers of lymph nodes and spleen, they undergo a process called somatic hypermutation, which helps create diverse antibodies. This diversity is vital for the body to recognize and combat various pathogens.
Understanding centrocytes can aid in diagnosing and treating lymphomas, a type of cancer affecting lymphatic cells. Research continues to uncover more about these cells, offering hope for better treatments and outcomes for patients.
In summary, centrocytes are small but mighty players in our immune defense. Their ability to adapt and respond to threats makes them indispensable. As science progresses, so will our knowledge and ability to harness the power of these remarkable cells.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
