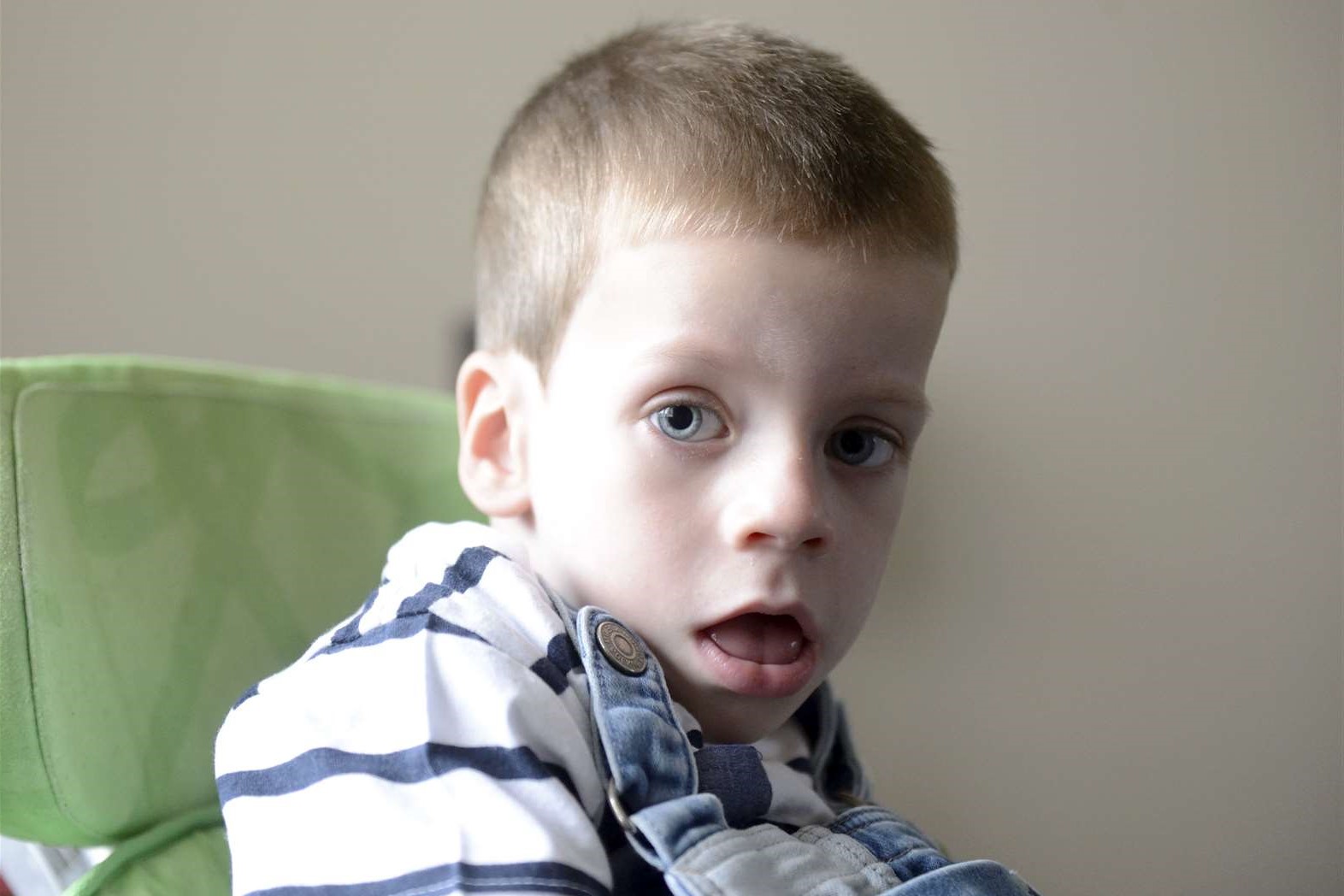
Temple–Baraitser Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. Caused by mutations in the KCNH1 gene, this condition often presents with distinctive facial features, intellectual disability, and abnormalities in the fingers and toes. Symptoms can vary widely, making it a complex condition to understand and manage. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for improving the quality of life for those affected. In this blog post, we will explore 25 facts about Temple–Baraitser Syndrome to help you better understand this rare condition. Whether you're a parent, caregiver, or just curious, these facts will provide valuable insights into the challenges and characteristics of this syndrome.
Key Takeaways:
- Temple–Baraitser Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder with unique physical and developmental challenges, affecting fewer than 50 people worldwide. It requires early diagnosis, supportive care, and ongoing research for better treatments.
- Individuals with Temple–Baraitser Syndrome may experience intellectual disability, distinctive physical features, developmental delays, and seizures. With tailored education plans, social support, and advocacy, they can lead fulfilling lives with hope for improved outcomes.
What is Temple–Baraitser Syndrome?
Temple–Baraitser Syndrome (TBS) is a rare genetic disorder. It affects multiple parts of the body, leading to various physical and developmental challenges. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
TBS is caused by mutations in the KCNH1 gene. This gene plays a crucial role in the function of potassium channels in the brain and other tissues.
-
The syndrome was first described in 1991 by doctors Temple and Baraitser. They identified the unique combination of symptoms in several patients.
-
TBS is extremely rare, with fewer than 50 cases reported worldwide. This rarity makes it challenging to study and understand fully.
-
One of the hallmark features of TBS is intellectual disability. Most individuals with TBS have some degree of cognitive impairment.
-
Another common feature is distinctive facial features. These can include a broad nasal bridge, wide-set eyes, and a small lower jaw.
Physical Characteristics of Temple–Baraitser Syndrome
People with TBS often have unique physical traits. These characteristics can help doctors diagnose the syndrome.
-
Many individuals with TBS have broad thumbs and big toes. This trait is so common that it is considered a key diagnostic feature.
-
Some people with TBS have short stature. They may be shorter than their peers throughout their lives.
-
Joint abnormalities are also common. These can include joint stiffness or unusual joint shapes.
-
Dental issues are frequently seen in TBS patients. These can range from missing teeth to unusually shaped teeth.
-
Some individuals have skin abnormalities. These can include thickened skin or unusual skin textures.
Developmental and Neurological Aspects
TBS affects more than just physical appearance. It also impacts development and neurological function.
-
Developmental delays are common in TBS. Children may take longer to reach milestones like walking and talking.
-
Seizures are a significant concern. Many individuals with TBS experience epilepsy, which can be difficult to control.
-
Speech and language difficulties are prevalent. Some individuals may never develop the ability to speak.
-
Behavioral issues can occur. These might include hyperactivity, anxiety, or aggression.
-
Motor skills are often affected. Fine motor skills, like writing or buttoning a shirt, can be particularly challenging.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing and treating TBS requires a multidisciplinary approach. Here are some key points about how doctors manage this condition.
-
Genetic testing is essential for diagnosis. Identifying mutations in the KCNH1 gene confirms the presence of TBS.
-
Early intervention is crucial. Therapies like physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help improve outcomes.
-
Regular monitoring is necessary. Doctors need to keep an eye on growth, development, and seizure activity.
-
Medications can help manage symptoms. Anti-seizure drugs are often prescribed to control epilepsy.
-
Supportive care is vital. Families may need assistance from social workers, counselors, and other professionals.
Living with Temple–Baraitser Syndrome
Living with TBS presents unique challenges. However, with the right support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives.
-
Education plans should be tailored. Special education services can help meet the unique needs of children with TBS.
-
Social support is important. Connecting with other families facing similar challenges can provide emotional and practical support.
-
Advocacy is key. Raising awareness about TBS can help secure resources and support for affected individuals.
-
Research is ongoing. Scientists are working to better understand TBS and develop new treatments.
-
Hope is essential. Advances in medicine and technology offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those with TBS.
Final Thoughts on Temple–Baraitser Syndrome
Temple–Baraitser Syndrome, a rare genetic disorder, affects many aspects of a person's life. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can help families and caregivers provide better support. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing the condition effectively. Genetic counseling offers valuable insights for families, helping them navigate the challenges associated with this syndrome.
Raising awareness about Temple–Baraitser Syndrome can lead to more research and better resources for those affected. Support groups and online communities provide a sense of belonging and shared experiences, which can be incredibly comforting. By staying informed and connected, families can better advocate for their loved ones and contribute to a more inclusive society.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more we learn about Temple–Baraitser Syndrome, the better equipped we are to support those living with it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
