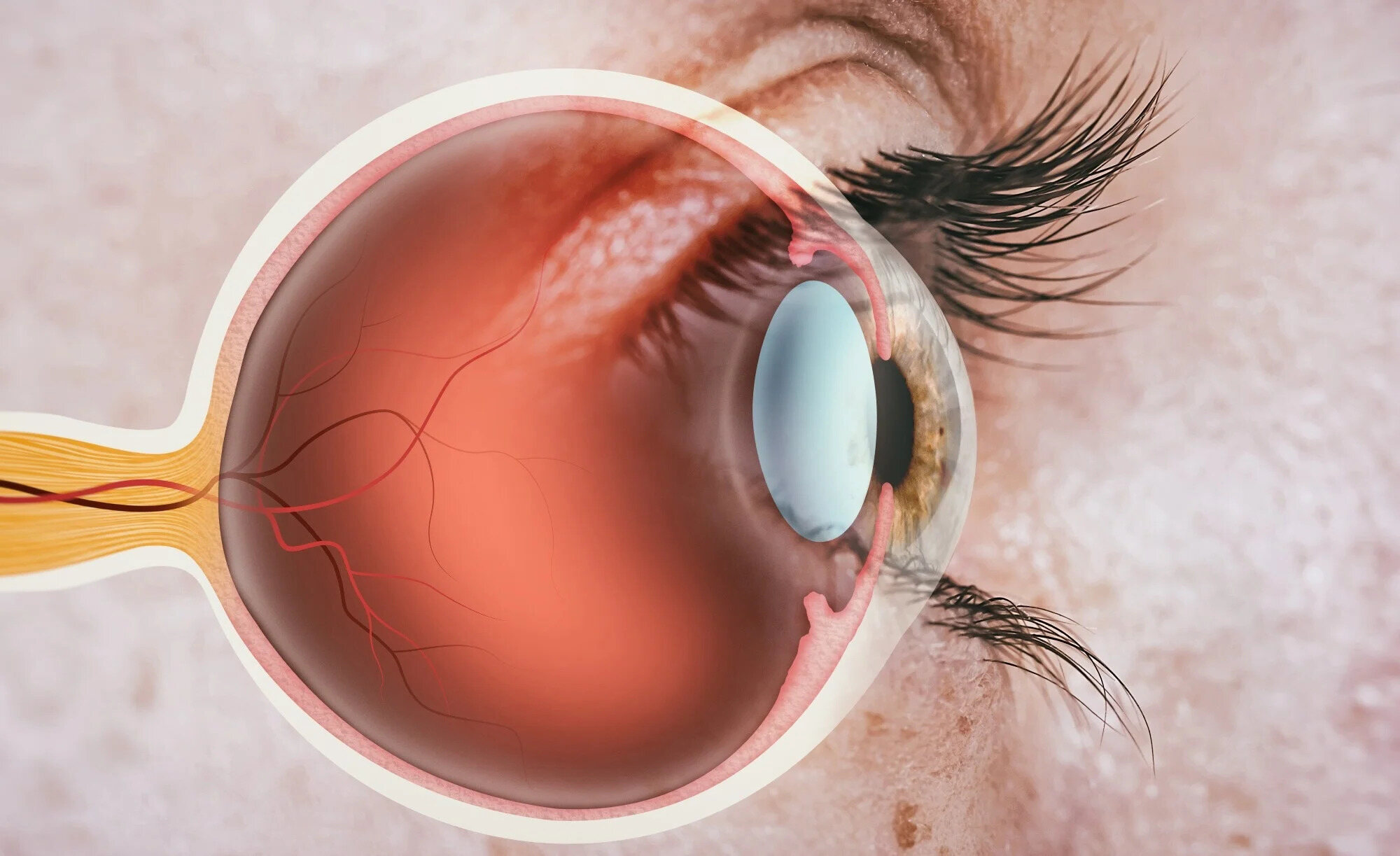
Papillitis of the optic nerve might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can be straightforward. This condition involves inflammation of the optic nerve head, which can lead to vision problems. Common symptoms include blurred vision, pain when moving the eye, and sometimes even temporary vision loss. It's often linked to infections, autoimmune diseases, or even multiple sclerosis. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term damage. Treatments typically involve steroids to reduce inflammation. Knowing the facts about this condition can help you recognize symptoms early and seek appropriate care. Ready to learn more? Let's dive into 25 essential facts about papillitis of the optic nerve.
Key Takeaways:
- Papillitis, or optic neuritis, causes vision loss and color vision deficiency. It can be diagnosed through eye exams, MRI scans, and blood tests, and treated with corticosteroids and lifestyle changes.
- People at risk for papillitis include young adults, women, those with a family history of autoimmune diseases, multiple sclerosis, and infections. Diagnosis involves eye exams, MRI scans, blood tests, and VEP. Treatment includes corticosteroids, plasma exchange, immunosuppressive drugs, and lifestyle changes.
What is Papillitis of the Optic Nerve?
Papillitis, also known as optic neuritis, is an inflammation of the optic nerve head. This condition can affect vision and may be associated with various underlying health issues. Here are some intriguing facts about this eye condition.
-
Inflammation of the Optic Nerve: Papillitis involves swelling and inflammation of the optic nerve, which transmits visual information from the eye to the brain.
-
Symptoms: Common symptoms include pain with eye movement, vision loss in one eye, and color vision deficiency.
-
Causes: It can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or multiple sclerosis.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis often involves a thorough eye examination, MRI scans, and blood tests.
-
Treatment: Treatment may include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
How Does Papillitis Affect Vision?
Papillitis can significantly impact vision, making daily activities challenging. Understanding how it affects vision can help in managing the condition better.
-
Vision Loss: Vision loss can be sudden and may range from mild to severe.
-
Color Vision Deficiency: Patients often experience difficulty distinguishing colors, especially red and green.
-
Visual Field Defects: Some may notice blind spots or a reduction in their peripheral vision.
-
Temporary or Permanent: Vision changes can be temporary, but in some cases, they may become permanent.
-
Light Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to light is another common symptom.
Who is at Risk?
Certain groups of people are more susceptible to developing papillitis. Knowing the risk factors can aid in early detection and prevention.
-
Age Group: It commonly affects young adults between the ages of 20 and 40.
-
Gender: Women are more likely to develop papillitis than men.
-
Genetics: A family history of autoimmune diseases can increase the risk.
-
Multiple Sclerosis: Those with multiple sclerosis have a higher likelihood of experiencing papillitis.
-
Infections: Viral and bacterial infections can trigger the condition.
Diagnosis and Testing
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Various tests and examinations are used to diagnose papillitis.
-
Ophthalmic Examination: A detailed eye exam helps in identifying signs of inflammation.
-
MRI Scans: MRI scans of the brain and orbits can reveal abnormalities in the optic nerve.
-
Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify underlying infections or autoimmune conditions.
-
Visual Evoked Potential (VEP): This test measures the electrical activity in the brain in response to visual stimuli.
-
Lumbar Puncture: In some cases, a lumbar puncture may be performed to analyze cerebrospinal fluid.
Treatment Options
Managing papillitis involves various treatment strategies aimed at reducing inflammation and preserving vision.
-
Corticosteroids: High-dose corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment.
-
Plasma Exchange: In severe cases, plasma exchange therapy may be used.
-
Immunosuppressive Drugs: These drugs can help manage underlying autoimmune conditions.
-
Antibiotics or Antivirals: If an infection is the cause, appropriate antibiotics or antivirals are prescribed.
-
Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can support overall eye health.
Key Points on Papillitis of the Optic Nerve
Papillitis of the optic nerve, also known as optic neuritis, is a serious condition that affects vision. It involves inflammation of the optic nerve, which can lead to symptoms like blurred vision, pain with eye movement, and even temporary vision loss. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to manage the condition effectively. Treatments often include corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and speed up recovery.
Understanding the risk factors, such as autoimmune diseases and infections, can help in early detection. Regular eye check-ups and being aware of any sudden changes in vision are essential. If you experience any symptoms, consult an eye specialist immediately.
Staying informed about papillitis can make a significant difference in managing and mitigating its impact on your life. Keep an eye on your eye health, and don't hesitate to seek medical advice when needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
