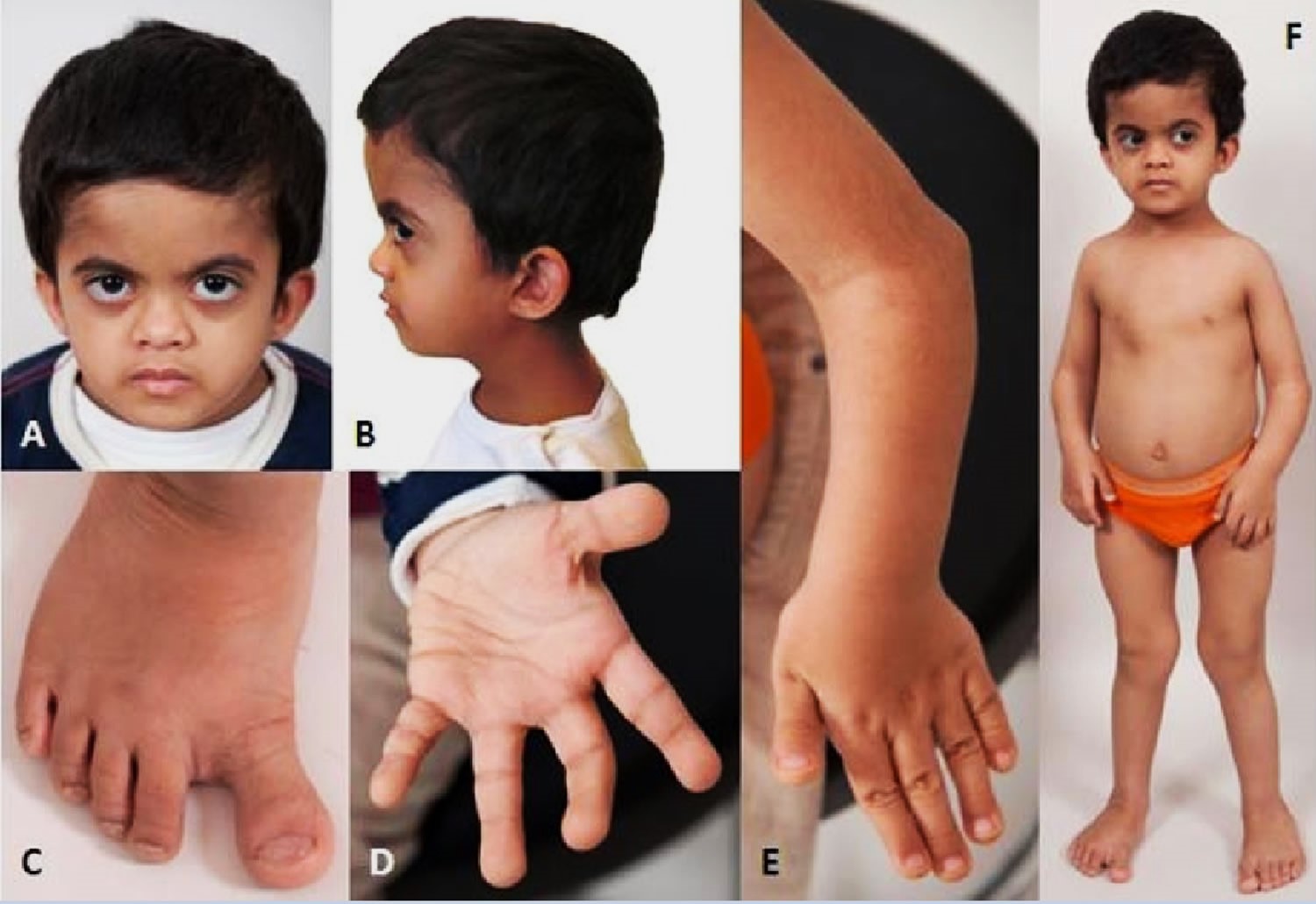
Omodysplasia Type 2 is a rare genetic disorder that affects bone development, leading to distinct physical characteristics and potential health challenges. This condition primarily impacts the long bones in the arms and legs, causing them to be shorter than average. Individuals with Omodysplasia Type 2 often have unique facial features, such as a prominent forehead and a flat nasal bridge. Caused by mutations in the GPC6 gene, this disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning both parents must carry the gene for their child to be affected. Understanding Omodysplasia Type 2 can help in recognizing symptoms early and managing the condition effectively. Here are 25 facts to give you a deeper insight into this rare genetic disorder.
Key Takeaways:
- Omodysplasia Type 2 is a rare genetic disorder causing short limbs and unique facial features. It presents challenges in mobility, growth, and respiratory health, but treatments and support groups offer hope for affected individuals and families.
- Genetic counseling and ongoing research play crucial roles in understanding and managing Omodysplasia Type 2. Families can make informed decisions about family planning, while researchers explore gene therapy and clinical trials for potential treatments.
What is Omodysplasia Type 2?
Omodysplasia Type 2 is a rare genetic disorder affecting bone development. It primarily impacts the long bones in the arms and legs, leading to short stature and other skeletal abnormalities. Here are some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Mutation: Omodysplasia Type 2 is caused by mutations in the GPC6 gene. This gene plays a crucial role in bone growth and development.
-
Inheritance Pattern: The disorder follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. Both parents must carry the mutated gene for their child to be affected.
-
Prevalence: Omodysplasia Type 2 is extremely rare, with only a few documented cases worldwide. Its rarity makes it a subject of interest for genetic researchers.
-
Symptoms: Individuals with this condition often exhibit short limbs, a small chest, and distinctive facial features such as a flat nasal bridge and a prominent forehead.
-
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves genetic testing to identify mutations in the GPC6 gene. Radiographic imaging can also reveal characteristic bone abnormalities.
How Does Omodysplasia Type 2 Affect Daily Life?
Living with Omodysplasia Type 2 presents unique challenges. Understanding these can help in managing the condition better.
-
Mobility Issues: Short limbs can lead to difficulties in walking and other physical activities. Assistive devices may be necessary for mobility.
-
Growth Delays: Children with Omodysplasia Type 2 often experience delayed growth and development compared to their peers.
-
Respiratory Problems: A small chest can lead to respiratory issues, requiring regular monitoring and medical intervention.
-
Physical Therapy: Regular physical therapy can help improve mobility and muscle strength, enhancing the quality of life.
-
Social Impact: Short stature and physical differences can affect social interactions and self-esteem, especially during childhood and adolescence.
Medical Management and Treatment
While there is no cure for Omodysplasia Type 2, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Orthopedic Interventions: Surgery may be necessary to correct bone deformities and improve function.
-
Respiratory Support: In severe cases, respiratory support such as ventilators may be required to assist with breathing.
-
Growth Hormone Therapy: Some patients may benefit from growth hormone therapy to promote bone growth and increase height.
-
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition is essential for overall health and can support bone development.
-
Regular Monitoring: Frequent medical check-ups are crucial to monitor growth, respiratory function, and other health parameters.
Genetic Counseling and Family Planning
Genetic counseling can provide valuable information for families affected by Omodysplasia Type 2.
-
Carrier Testing: Parents can undergo genetic testing to determine if they are carriers of the GPC6 mutation.
-
Prenatal Diagnosis: Prenatal genetic testing can identify if a fetus is affected by Omodysplasia Type 2, allowing for early intervention and planning.
-
Family Planning: Genetic counseling can help families make informed decisions about having more children.
-
Support Groups: Connecting with support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition.
-
Educational Resources: Access to educational materials can help families understand the disorder and navigate the challenges it presents.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Omodysplasia Type 2 and develop new treatments.
-
Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment to correct the underlying genetic mutation.
-
Clinical Trials: Participation in clinical trials can provide access to new treatments and contribute to scientific knowledge.
-
Animal Models: Animal models of Omodysplasia Type 2 are being used to study the disease and test new therapies.
-
Patient Registries: Patient registries collect data on individuals with Omodysplasia Type 2, helping researchers track the natural history of the disease.
-
Collaborative Research: International collaborations among researchers, clinicians, and patient organizations are crucial for advancing our understanding of this rare disorder.
Understanding Omodysplasia Type 2
Omodysplasia Type 2, a rare genetic disorder, affects bone development, leading to distinct physical characteristics. Recognizing its signs early can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Genetic counseling plays a crucial role for families, offering insights into inheritance patterns and potential risks for future generations.
Medical advancements continue to provide hope for better treatments. While there's no cure yet, supportive care and therapies can make a significant difference. Staying informed and connected with healthcare professionals ensures the best possible outcomes.
Raising awareness about Omodysplasia Type 2 helps foster a supportive community. Sharing knowledge and experiences can empower those affected and their families. Remember, every bit of information contributes to a broader understanding and better support for individuals living with this condition. Keep learning, stay connected, and support each other in this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
