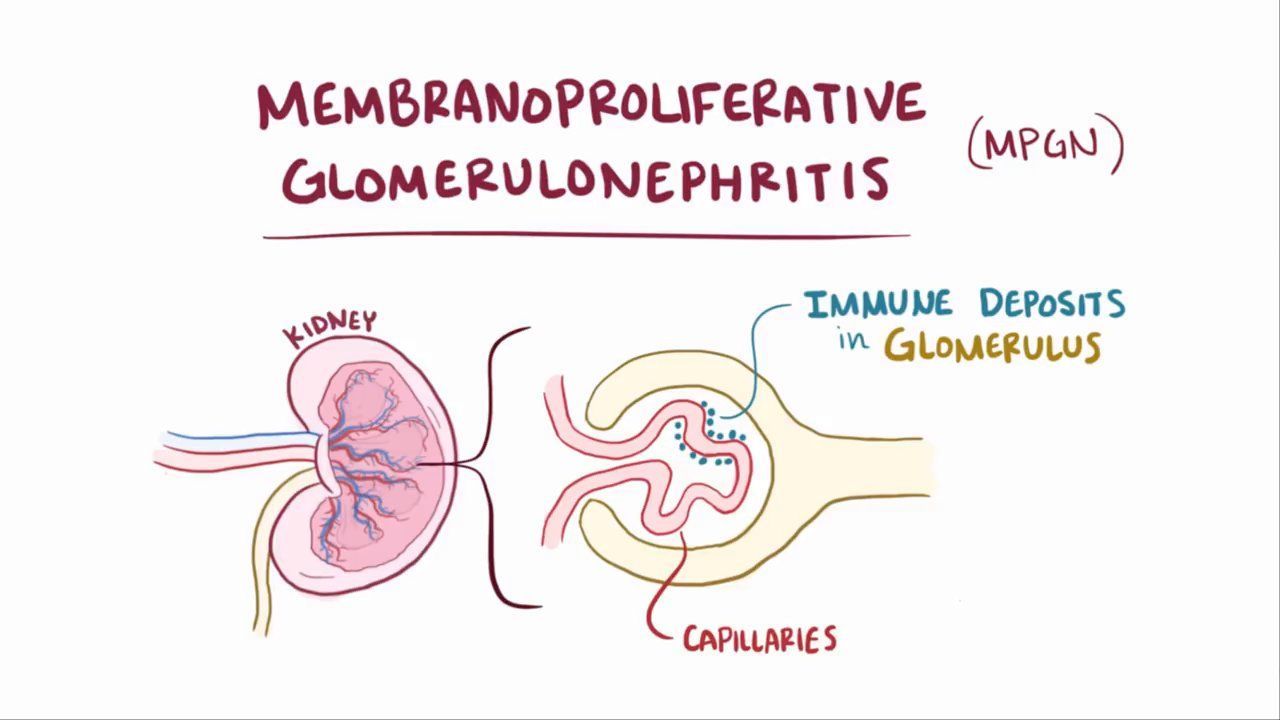
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (MPGN) Type II, also known as dense deposit disease, is a rare kidney disorder. It affects the glomeruli, which are tiny filters in the kidneys. This condition causes the immune system to deposit dense material in the glomeruli, leading to inflammation and scarring. Symptoms can include blood in the urine, swelling in various body parts, and high blood pressure. Diagnosis often involves blood tests, urine tests, and a kidney biopsy. Treatment options may range from medications to manage symptoms to more intensive therapies like plasma exchange. Understanding MPGN Type II is crucial for managing this complex condition effectively.
Key Takeaways:
- Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (Type II) is a rare kidney disease that can lead to kidney failure. It causes symptoms like blood and protein in the urine, swelling, and fatigue.
- Treatment for MPGN Type II includes medications to reduce inflammation and control the immune system, as well as managing blood pressure and making dietary changes. Regular monitoring and support are important for managing the disease.
What is Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (Type II)?
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (MPGN) Type II, also known as Dense Deposit Disease (DDD), is a rare kidney disorder. It affects the glomeruli, tiny structures in the kidneys that filter blood. Understanding this condition can help manage it better.
- MPGN Type II is a chronic kidney disease that often leads to kidney failure.
- The disease is characterized by dense deposits in the glomerular basement membrane.
- MPGN Type II is more common in children and young adults.
- Symptoms often include blood in the urine (hematuria) and protein in the urine (proteinuria).
- The exact cause of MPGN Type II is unknown, but it is believed to involve the immune system.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to a timely diagnosis and better management of the disease. Here are some key facts about the symptoms and diagnosis of MPGN Type II.
- Patients may experience swelling in the legs, ankles, or around the eyes.
- High blood pressure is a common symptom associated with MPGN Type II.
- Fatigue and weakness are often reported by patients.
- A kidney biopsy is usually required to confirm the diagnosis.
- Blood tests can reveal low levels of complement proteins, which are part of the immune system.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of MPGN Type II remains unclear, several factors are believed to contribute to its development. Understanding these can help in managing the condition.
- Genetic factors may play a role in the development of MPGN Type II.
- Infections, such as hepatitis B and C, have been linked to the disease.
- Autoimmune disorders, like lupus, can increase the risk of developing MPGN Type II.
- Certain medications may trigger the onset of the disease.
- Environmental factors, including exposure to toxins, might contribute to the condition.
Treatment Options
Managing MPGN Type II involves various treatment strategies aimed at controlling symptoms and slowing disease progression. Here are some important facts about treatment options.
- Corticosteroids are often prescribed to reduce inflammation in the kidneys.
- Immunosuppressive drugs may be used to control the immune system's activity.
- Blood pressure medications help manage hypertension associated with the disease.
- Dietary changes, such as reducing salt intake, can help manage symptoms.
- In severe cases, dialysis or kidney transplantation may be necessary.
Prognosis and Long-term Outlook
The long-term outlook for patients with MPGN Type II varies. Early diagnosis and effective management can improve the prognosis. Here are some key facts about the prognosis and long-term outlook.
- The disease often progresses slowly, but it can lead to end-stage renal disease (ESRD).
- Regular monitoring of kidney function is crucial for managing the disease.
- Some patients may experience periods of remission, where symptoms improve.
- Advances in medical research are leading to better treatment options and improved outcomes.
- Support from healthcare professionals, family, and patient support groups can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by MPGN Type II.
Final Thoughts on Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (Type II)
Understanding Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (Type II) can feel overwhelming, but knowing the facts helps. This rare kidney disorder affects the glomeruli, leading to kidney damage over time. Symptoms like blood in urine, swelling, and high blood pressure are common. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing the condition. Treatments include medications to control blood pressure and reduce protein in urine, and sometimes, immunosuppressive drugs. Regular check-ups with a nephrologist are essential for monitoring kidney function. While there's no cure, lifestyle changes like a healthy diet and avoiding smoking can help manage symptoms. Staying informed and proactive in your health care can make a significant difference. Remember, knowledge is power when dealing with any medical condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
