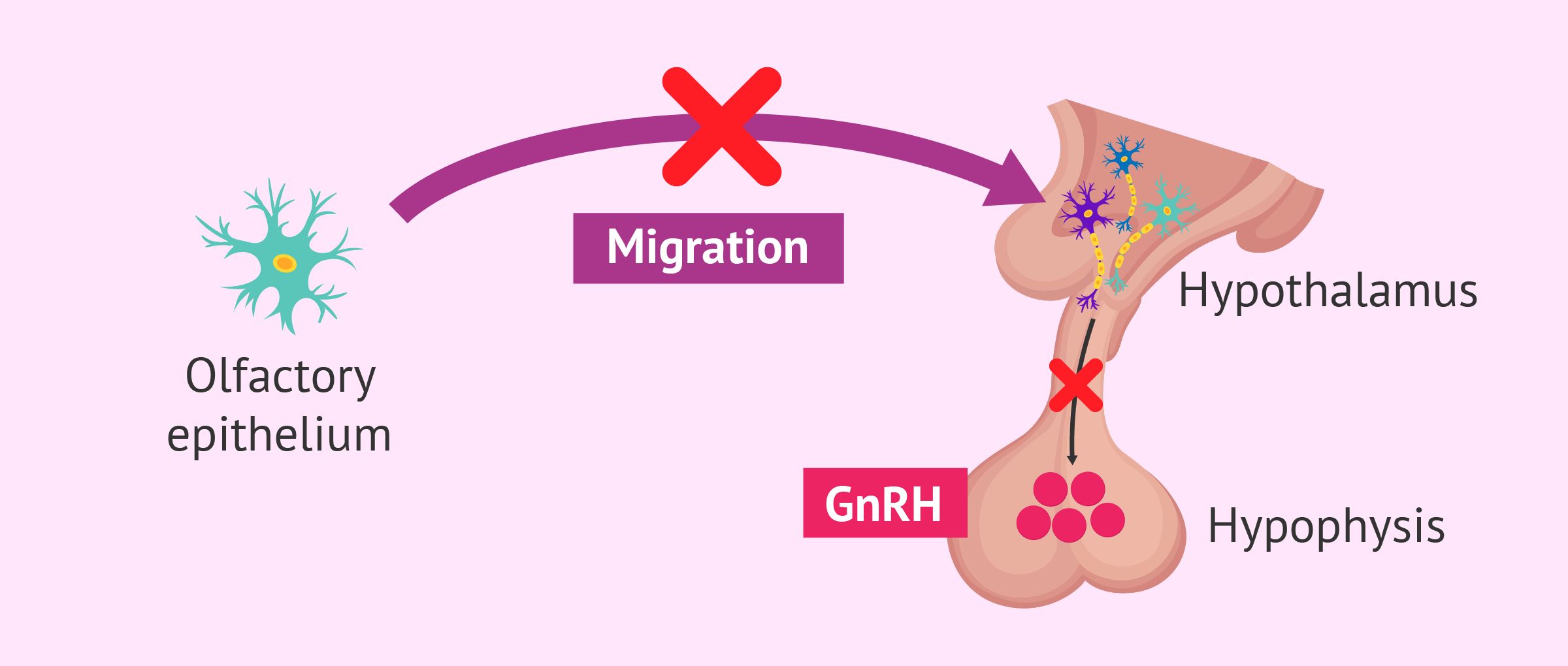
Kallmann syndrome (KS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the reproductive system and the sense of smell. Characterized by delayed or absent puberty and an impaired sense of smell (anosmia), KS can significantly impact an individual's life. This condition arises due to mutations in specific genes responsible for the migration of neurons that produce gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). Symptoms often include lack of secondary sexual characteristics, infertility, and sometimes other anomalies like hearing loss or cleft lip. Understanding KS is crucial for early diagnosis and management, which can improve quality of life. Let's dive into 25 intriguing facts about this unique condition.
Key Takeaways:
- Kallmann Syndrome (KS) is a rare genetic disorder affecting puberty and smell. It can cause infertility and requires hormone replacement therapy for management.
- Ongoing research on KS aims to develop new treatments using gene therapy and stem cell research. Patient registries and advocacy organizations support individuals with KS.
What is Kallmann Syndrome?
Kallmann syndrome (KS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the reproductive system and the sense of smell. It is a form of hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, meaning the body produces insufficient sex hormones due to a problem with the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
-
Kallmann syndrome is named after Franz Josef Kallmann, a German-American psychiatrist who first described the condition in 1944.
-
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism means the body has low levels of sex hormones because the hypothalamus or pituitary gland isn't working properly.
-
Anosmia, or the inability to smell, is a hallmark symptom of KS. Most individuals with KS have a reduced or absent sense of smell.
-
Genetic mutations in several different genes can cause KS, including KAL1, FGFR1, PROKR2, and PROK2.
Symptoms of Kallmann Syndrome
KS presents a variety of symptoms, primarily related to delayed or absent puberty and reproductive issues. Here are some key symptoms to look out for:
-
Delayed puberty is often the first noticeable symptom. Individuals with KS may not develop secondary sexual characteristics like facial hair or breast development.
-
Infertility is common due to the lack of sex hormone production, affecting both males and females with KS.
-
Micropenis and undescended testes can be symptoms in males with KS.
-
Amenorrhea, or the absence of menstrual periods, is a symptom in females with KS.
Diagnosis of Kallmann Syndrome
Diagnosing KS involves a combination of clinical evaluations, genetic testing, and imaging studies. Early diagnosis can help manage symptoms more effectively.
-
Genetic testing can identify mutations in genes known to cause KS, aiding in diagnosis.
-
MRI scans of the brain can reveal abnormalities in the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
-
Hormone tests measure levels of sex hormones, which are typically low in individuals with KS.
-
Olfactory testing can assess the sense of smell, which is often reduced or absent in KS patients.
Treatment Options for Kallmann Syndrome
While there is no cure for KS, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Hormone replacement therapy is a common approach.
-
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) helps induce puberty and maintain secondary sexual characteristics.
-
Gonadotropin injections can stimulate the production of sex hormones and support fertility.
-
Testosterone therapy is often used for males to promote the development of male secondary sexual characteristics.
-
Estrogen and progesterone therapy is used for females to induce menstrual cycles and develop female secondary sexual characteristics.
Living with Kallmann Syndrome
Living with KS involves ongoing medical care and support. Understanding the condition can help individuals manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives.
-
Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor hormone levels and adjust treatments as needed.
-
Psychological support can help individuals cope with the emotional and social challenges of KS.
-
Support groups provide a community for individuals with KS to share experiences and advice.
-
Education and awareness about KS can help reduce stigma and improve understanding among peers and family members.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand KS and develop new treatments. Advances in genetics and endocrinology hold promise for the future.
-
Gene therapy is being explored as a potential treatment to correct genetic mutations causing KS.
-
Stem cell research may offer new ways to regenerate damaged tissues and restore hormone production.
-
Clinical trials are testing new medications and therapies to improve symptoms and quality of life for KS patients.
-
Patient registries help researchers gather data on KS, leading to better understanding and treatment options.
-
Advocacy organizations work to raise awareness, fund research, and support individuals with KS and their families.
Understanding Kallmann Syndrome
Kallmann syndrome (KS) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the development of the hypothalamus, leading to delayed or absent puberty and an impaired sense of smell. Knowing the facts about KS can help in early diagnosis and treatment, improving the quality of life for those affected. Symptoms vary widely, but common signs include delayed puberty, infertility, and anosmia. Genetic testing and hormone replacement therapy are key components of managing KS. Support from healthcare professionals and patient communities can make a significant difference. Awareness and education about KS are crucial for better outcomes. If you or someone you know shows symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and care. Understanding KS empowers individuals and families to navigate this condition with knowledge and confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
