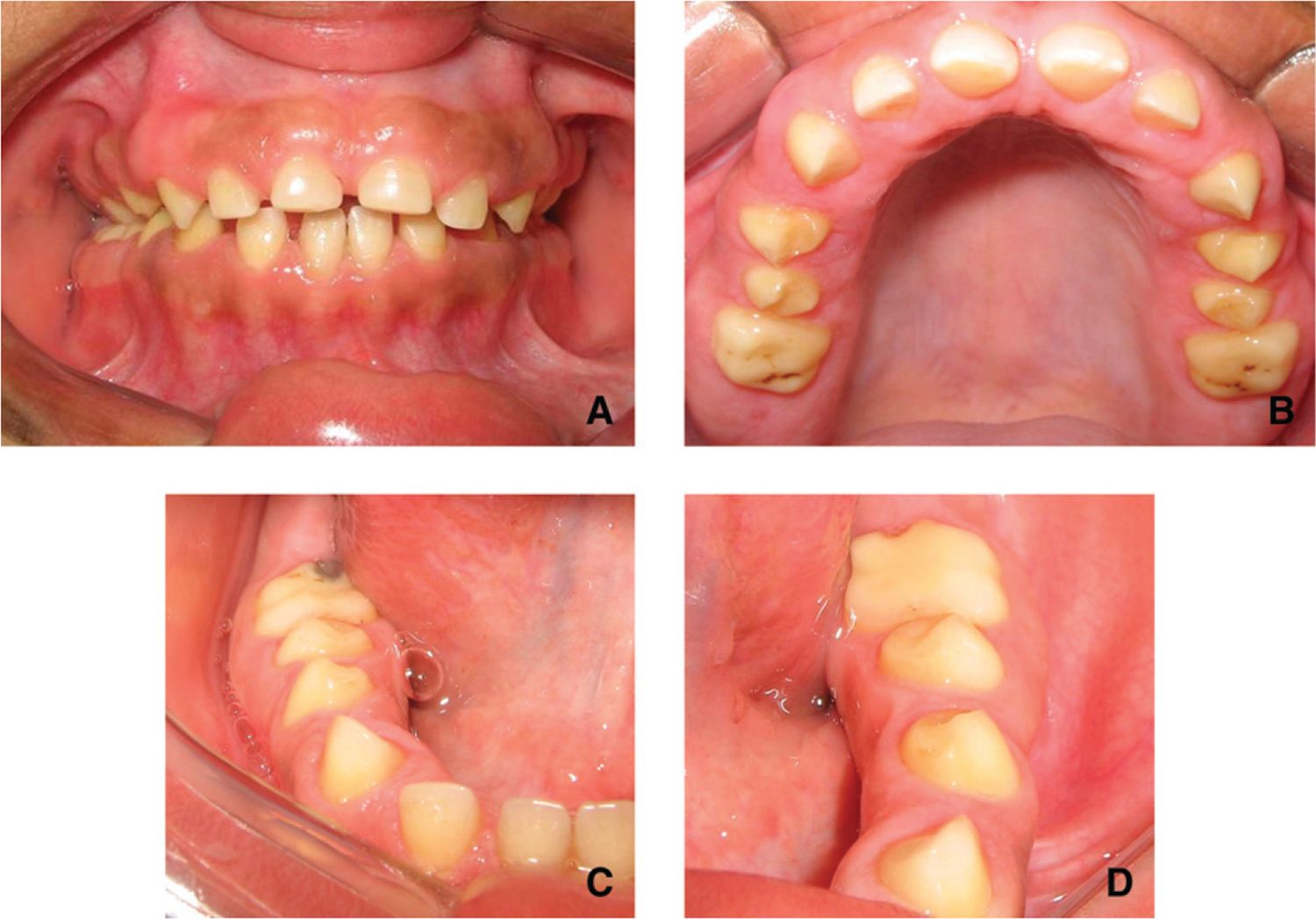
What is Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant? Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant is a rare genetic condition that causes an overgrowth of gum tissue. This condition can lead to swollen gums, making it difficult to chew or speak. Often, it's inherited, meaning it runs in families. The gums become thick and fibrous, sometimes covering teeth completely. This can cause dental problems, like misaligned teeth or difficulty maintaining oral hygiene. Treatment usually involves surgery to remove excess tissue, but it might need repeating if the tissue grows back. Understanding this condition helps in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. If you or someone you know has symptoms, consulting a dental professional is crucial.
Key Takeaways:
- Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant causes excessive gum tissue growth, leading to dental issues. It's genetic, with symptoms appearing in childhood. Treatment includes surgery and regular dental visits for effective management.
- Living with Gingival Fibromatosis requires dietary adjustments, emotional support, and awareness. Ongoing research aims to improve treatment through gene therapy and innovative surgical techniques.
Understanding Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant
Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant is a rare condition affecting the gums. It causes an overgrowth of gum tissue, which can lead to various dental issues. Let's explore some intriguing facts about this condition.
-
Genetic Roots
Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. This means if one parent carries the gene, there's a 50% chance of passing it to their children. -
Gum Overgrowth
The condition is characterized by excessive growth of the gum tissue. This overgrowth can cover teeth partially or completely, affecting oral hygiene and appearance. -
Not Just Cosmetic
While it might seem like a cosmetic issue, gingival fibromatosis can lead to serious dental problems. It can cause difficulty in chewing, speaking, and maintaining oral hygiene. -
Early Onset
Symptoms often appear in childhood or adolescence. The gum overgrowth tends to progress with age, requiring early intervention. -
Variable Severity
The severity of gum overgrowth varies among individuals. Some may experience mild enlargement, while others face significant overgrowth that requires surgical intervention.
Causes and Symptoms
Understanding the causes and symptoms can help in early detection and management of the condition.
-
Genetic Mutations
Mutations in specific genes are responsible for this condition. These mutations affect the normal regulation of gum tissue growth. -
Thickened Gums
One of the primary symptoms is the thickening of the gums. This can lead to a bulky appearance and discomfort. -
Delayed Tooth Eruption
In some cases, the overgrown gums can delay the eruption of teeth, leading to misalignment and other dental issues. -
Bleeding Gums
The excessive gum tissue can be prone to bleeding, especially during brushing or flossing. -
Bad Breath
Due to difficulty in maintaining oral hygiene, individuals may experience bad breath, also known as halitosis.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Proper diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing gingival fibromatosis effectively.
-
Clinical Examination
Diagnosis typically involves a thorough clinical examination by a dentist or periodontist. They assess the extent of gum overgrowth and its impact on oral health. -
Genetic Testing
In some cases, genetic testing may be recommended to confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific gene mutation. -
Surgical Intervention
Surgical removal of excess gum tissue, known as gingivectomy, is a common treatment. This helps restore normal gum contour and improve oral function. -
Regular Dental Visits
Frequent dental check-ups are essential for monitoring the condition and preventing complications. -
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and using antiseptic mouthwash to prevent infections.
Living with Gingival Fibromatosis
Living with this condition requires adjustments and awareness to manage symptoms effectively.
-
Dietary Considerations
Soft foods may be recommended to avoid irritating the gums. A balanced diet also supports overall oral health. -
Psychological Impact
The condition can affect self-esteem and confidence due to its impact on appearance. Support from family and counseling can be beneficial. -
Speech Therapy
In cases where speech is affected, therapy may help improve communication skills. -
Support Groups
Connecting with others who have similar experiences can provide emotional support and practical advice. -
Awareness and Education
Raising awareness about gingival fibromatosis can help in early detection and reduce stigma associated with the condition.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of gingival fibromatosis.
-
Gene Therapy Potential
Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment. This could target the underlying genetic cause and prevent gum overgrowth. -
Innovative Surgical Techniques
Advancements in surgical techniques aim to provide better outcomes with minimal discomfort and faster recovery. -
Pharmacological Approaches
Studies are investigating medications that could help regulate gum tissue growth and reduce the need for surgery. -
Patient Registries
Establishing patient registries can help gather data on the condition, leading to improved treatment strategies and patient care. -
Collaboration Among Experts
Collaboration between geneticists, dentists, and researchers is crucial for advancing knowledge and developing effective treatments for gingival fibromatosis.
Final Thoughts on Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant
Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant might sound like a mouthful, but understanding it can make a big difference. This genetic condition causes the gums to grow excessively, which can lead to discomfort and dental issues. It's not just about having a big smile; it's about maintaining oral health. Regular dental check-ups are crucial for managing this condition. Treatments like surgery or medications can help, but they depend on the severity and individual needs. Genetics play a huge role, so if it runs in the family, staying informed is key. While it might seem daunting, with the right care and attention, those affected can lead healthy lives. Awareness and education are powerful tools in managing Gingival Fibromatosis Dominant. Keep learning, stay proactive, and remember, a healthy smile is always worth the effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
