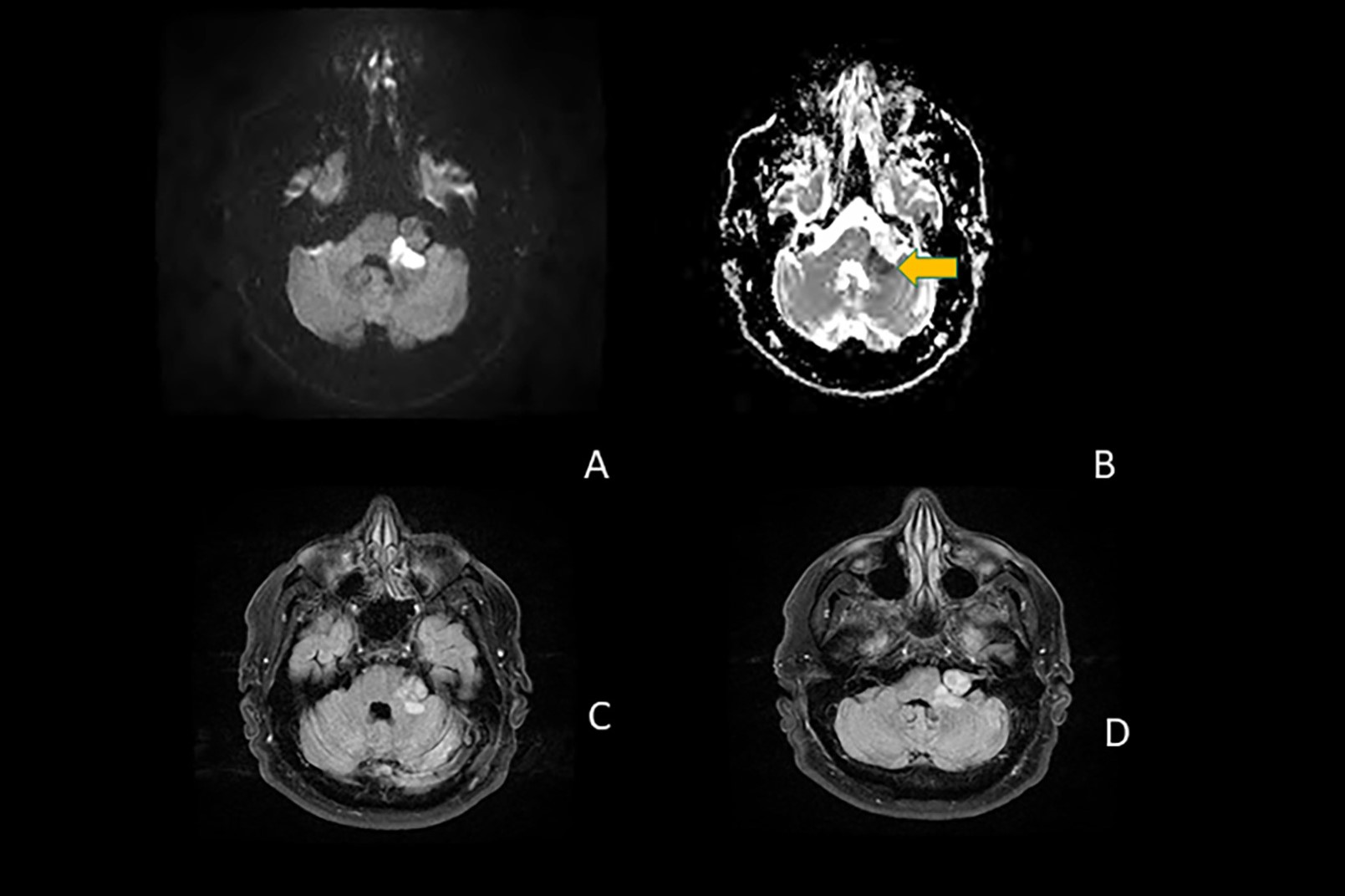
Bruns Ataxia is a rare neurological disorder that affects movement and coordination. Ever wondered what makes this condition so unique? Bruns Ataxia primarily impacts the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for balance and coordination. Symptoms often include unsteady walking, difficulty with fine motor skills, and sometimes speech problems. This condition can be caused by various factors, including genetic mutations, infections, or even tumors. Understanding Bruns Ataxia can help in recognizing its signs early and seeking appropriate medical care. Ready to learn more about this intriguing condition? Let's dive into 25 fascinating facts about Bruns Ataxia!
Key Takeaways:
- Bruns Ataxia is a rare neurological disorder affecting balance and movement, often caused by genetic mutations. Early recognition and therapy can improve quality of life for those affected.
- Ongoing research into Bruns Ataxia aims to uncover better treatments, including gene therapy and new medications. Understanding genetic and environmental factors is crucial for prevention and management.
What is Bruns Ataxia?
Bruns Ataxia is a rare neurological disorder affecting balance, coordination, and movement. Understanding this condition can help those affected and their families navigate the challenges it presents.
- Bruns Ataxia is named after Ludwig Bruns, a German neurologist who first described the condition in the late 19th century.
- This disorder primarily affects the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for coordinating voluntary movements.
- Symptoms often include unsteady gait, difficulty with fine motor skills, and frequent falls.
- Bruns Ataxia can be caused by various factors, including genetic mutations, infections, and brain injuries.
- Diagnosis typically involves a combination of neurological exams, imaging tests like MRI, and genetic testing.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to better management of Bruns Ataxia. Here are some key facts about its symptoms and diagnosis process.
- Early signs may include clumsiness, difficulty walking, and slurred speech.
- As the disease progresses, individuals might experience tremors, muscle stiffness, and involuntary eye movements.
- Cognitive impairments, such as difficulty with concentration and memory, can also occur.
- A thorough neurological examination is crucial for diagnosing Bruns Ataxia.
- MRI scans can reveal abnormalities in the cerebellum and other parts of the brain.
- Genetic testing can identify specific mutations linked to the disorder, aiding in diagnosis and family planning.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for Bruns Ataxia, various treatments and management strategies can improve quality of life.
- Physical therapy can help maintain mobility and improve balance.
- Occupational therapy assists individuals in performing daily activities more effectively.
- Speech therapy can address communication difficulties and swallowing problems.
- Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms like muscle stiffness and tremors.
- Assistive devices, such as walkers and wheelchairs, can enhance mobility and independence.
- Regular follow-ups with a neurologist are essential for monitoring the progression of the disease.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Understanding the genetic and environmental factors involved in Bruns Ataxia can provide insights into its causes and potential preventive measures.
- Some cases of Bruns Ataxia are inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to develop the disorder.
- Other cases may result from autosomal recessive inheritance, requiring two copies of the mutated gene.
- Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or infections, can also contribute to the development of Bruns Ataxia.
- Prenatal exposure to certain substances, like alcohol, may increase the risk of developing the disorder.
- Family history plays a significant role in assessing the risk of Bruns Ataxia.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to uncover more about Bruns Ataxia and develop better treatments.
- Scientists are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for genetic forms of Bruns Ataxia.
- Advances in neuroimaging techniques are helping researchers understand the brain changes associated with the disorder.
- Clinical trials are testing new medications and therapies to improve symptoms and slow disease progression.
Final Thoughts on Bruns Ataxia
Bruns Ataxia, a rare neurological disorder, affects coordination and balance, making daily activities challenging. Understanding Bruns Ataxia helps in recognizing its symptoms early, leading to better management. This condition, often linked to genetic factors, requires a multidisciplinary approach for treatment. Physical therapy, medications, and lifestyle adjustments play crucial roles in improving quality of life for those affected.
Raising awareness about Bruns Ataxia can lead to more research and support for patients and their families. Knowledge empowers individuals to seek appropriate care and advocate for advancements in treatment. While living with Bruns Ataxia presents challenges, a supportive community and informed medical care can make a significant difference.
Stay informed, support research, and spread awareness to help those battling this condition. Every effort counts in making life better for individuals with Bruns Ataxia.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
