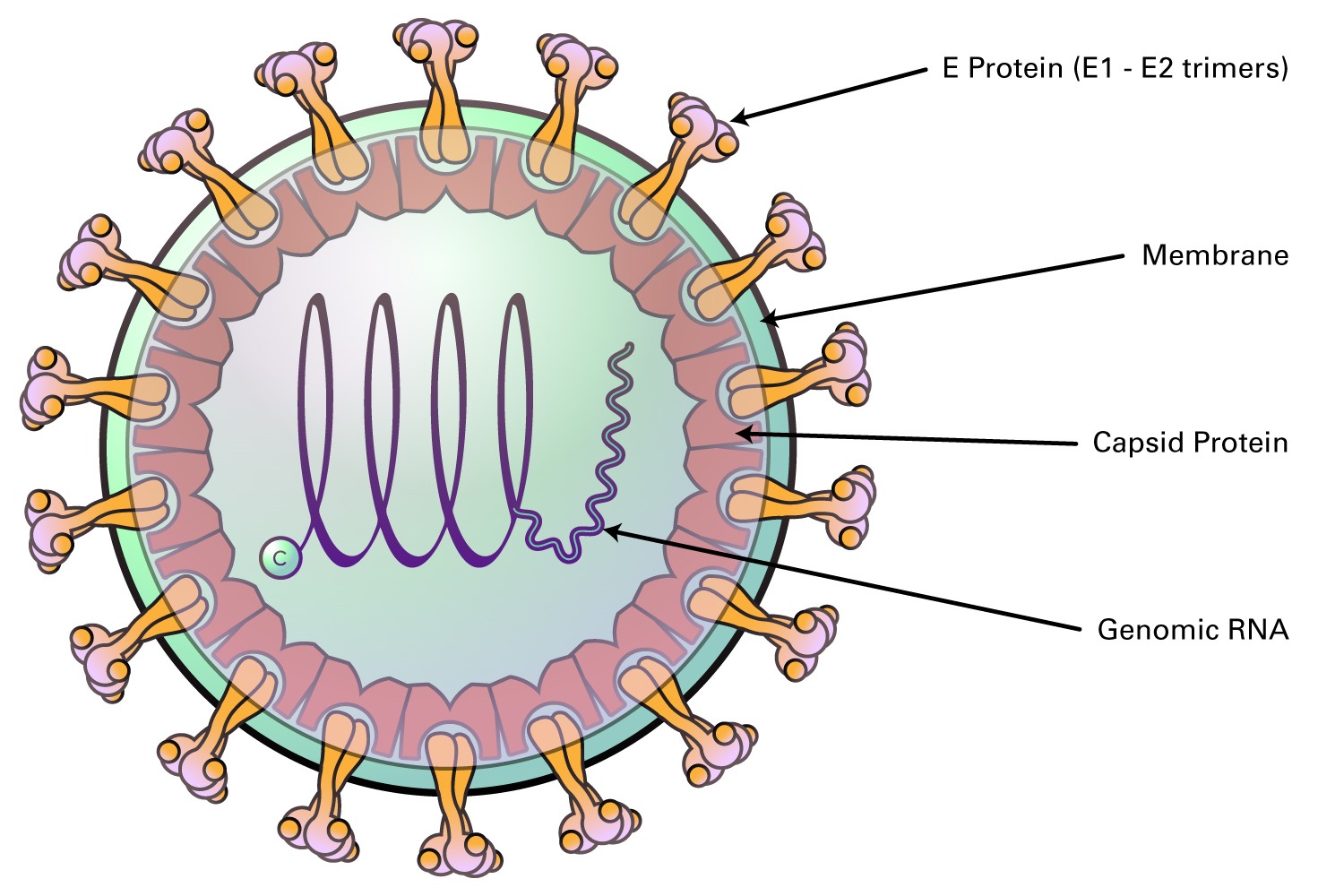
Togaviridae diseases are caused by viruses from the Togaviridae family, which includes the well-known Chikungunya and Rubella viruses. These illnesses can affect both humans and animals, leading to a range of symptoms from mild fever to severe joint pain. Chikungunya often results in debilitating joint pain that can last for months, while Rubella, also known as German measles, can cause serious complications in pregnant women. Understanding these diseases is crucial for prevention and treatment. This post will cover 20 essential facts about Togaviridae diseases, shedding light on their transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures. Stay informed and protect yourself from these viral threats.
Key Takeaways:
- Togaviridae viruses, like Chikungunya and Rubella, spread through mosquito bites and can cause fever, joint pain, and birth defects. Vaccination and mosquito control are crucial for prevention.
- Togaviridae diseases have diverse symptoms and impacts, from fever and rash to severe neurological issues. Ongoing research aims to develop vaccines and innovative methods for vector control.
What is Togaviridae?
Togaviridae is a family of viruses known to cause various diseases in humans and animals. These viruses are primarily transmitted through arthropods like mosquitoes. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about Togaviridae diseases.
Types of Togaviridae Viruses
There are several viruses within the Togaviridae family, each with unique characteristics and impacts on health.
- Alphaviruses: This group includes viruses like Chikungunya and Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE). They often cause fever, joint pain, and neurological issues.
- Rubiviruses: The most well-known member is the Rubella virus, responsible for German measles. It can lead to severe birth defects if contracted during pregnancy.
Transmission Methods
Understanding how these viruses spread is crucial for prevention and control.
- Mosquito Bites: Many Togaviridae viruses are transmitted through mosquito bites, making vector control essential.
- Vertical Transmission: Rubella can be passed from mother to fetus, leading to congenital rubella syndrome.
- Animal Reservoirs: Some alphaviruses have animal hosts, such as birds or rodents, which play a role in their life cycle.
Symptoms and Health Impacts
The symptoms of Togaviridae diseases can vary widely depending on the specific virus.
- Fever and Rash: Common symptoms include fever and rash, particularly with Rubella and Chikungunya.
- Joint Pain: Chikungunya is notorious for causing severe joint pain that can last for months.
- Neurological Issues: EEE can lead to encephalitis, causing brain inflammation, seizures, and even death.
- Congenital Defects: Rubella infection during pregnancy can result in heart defects, deafness, and intellectual disabilities in newborns.
Geographic Distribution
Togaviridae viruses are found worldwide, but their prevalence varies by region.
- Tropical Regions: Chikungunya is common in tropical and subtropical areas, including parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas.
- Temperate Zones: EEE is more prevalent in temperate regions, particularly in the eastern United States.
- Global Spread: Rubella has a global presence, but vaccination efforts have significantly reduced its incidence in many countries.
Prevention and Control
Preventing Togaviridae diseases involves a combination of strategies.
- Vaccination: The MMR vaccine protects against Rubella, reducing the risk of congenital rubella syndrome.
- Mosquito Control: Reducing mosquito populations through insecticides, larvicides, and eliminating standing water helps prevent alphavirus transmission.
- Personal Protection: Using insect repellent, wearing long sleeves, and sleeping under mosquito nets can reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
Treatment Options
While there are no specific antiviral treatments for most Togaviridae diseases, supportive care can alleviate symptoms.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help manage joint pain and fever.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial, especially when dealing with fever and joint pain.
- Hospital Care: Severe cases, such as encephalitis caused by EEE, may require hospitalization and intensive care.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to better understand Togaviridae viruses and develop new treatments and vaccines.
- Vaccine Development: Scientists are working on vaccines for alphaviruses like Chikungunya to prevent outbreaks.
- Vector Control Innovations: New methods, such as genetically modified mosquitoes, are being explored to reduce mosquito populations and disease transmission.
Final Thoughts on Togaviridae Diseases
Understanding Togaviridae diseases helps in preventing and managing these viral infections. These viruses, including Chikungunya and Rubella, spread through mosquito bites or respiratory droplets. Symptoms range from mild fever to severe joint pain. Vaccination and mosquito control are key in reducing their impact.
Staying informed about Togaviridae can protect communities from outbreaks. Simple actions like using insect repellent, wearing long sleeves, and ensuring vaccinations are up-to-date make a big difference.
Knowledge empowers us to take proactive steps in safeguarding health. By staying vigilant and adopting preventive measures, we can minimize the risks associated with these viruses.
Remember, awareness and prevention go hand in hand. Stay safe, stay informed, and take action to protect yourself and your loved ones from Togaviridae diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
