Antibacterial properties are like tiny superheroes fighting off germs and keeping us healthy. But what exactly makes something antibacterial? Antibacterial substances are agents that kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. These can be found in everyday items like soaps, hand sanitizers, and even some fabrics. They work by targeting the bacteria's cell walls, proteins, or DNA, effectively stopping them in their tracks. This is crucial in preventing infections and maintaining hygiene. However, overuse can lead to resistant strains, making it important to use them wisely. Nature also offers its own antibacterial wonders, such as honey and garlic, which have been used for centuries. Understanding these properties helps us make informed choices about our health and environment. So, next time you wash your hands or use a sanitizer, remember the tiny warriors at work!
Key Takeaways:
- Antibacterial properties are found in natural sources like garlic and honey, and are crucial in preventing infections and promoting overall health and hygiene.
- Understanding how antibacterial agents work, such as disrupting cell walls and inhibiting protein synthesis, helps us appreciate their importance in healthcare, food safety, and agriculture.
What Are Antibacterial Properties?
Antibacterial properties refer to the ability of a substance to inhibit the growth of or destroy bacteria. These properties are crucial in medicine, food preservation, and personal hygiene. Let's explore some fascinating facts about these properties.
-
Natural Sources: Many plants and herbs, like garlic and ginger, naturally possess antibacterial properties. These have been used in traditional medicine for centuries to treat infections.
-
Honey's Power: Honey, especially Manuka honey, is known for its strong antibacterial effects. It can help heal wounds and prevent infections due to its natural hydrogen peroxide content.
-
Silver's Role: Silver has been used for its antibacterial properties since ancient times. Silver nanoparticles are now used in medical devices and wound dressings to prevent bacterial growth.
-
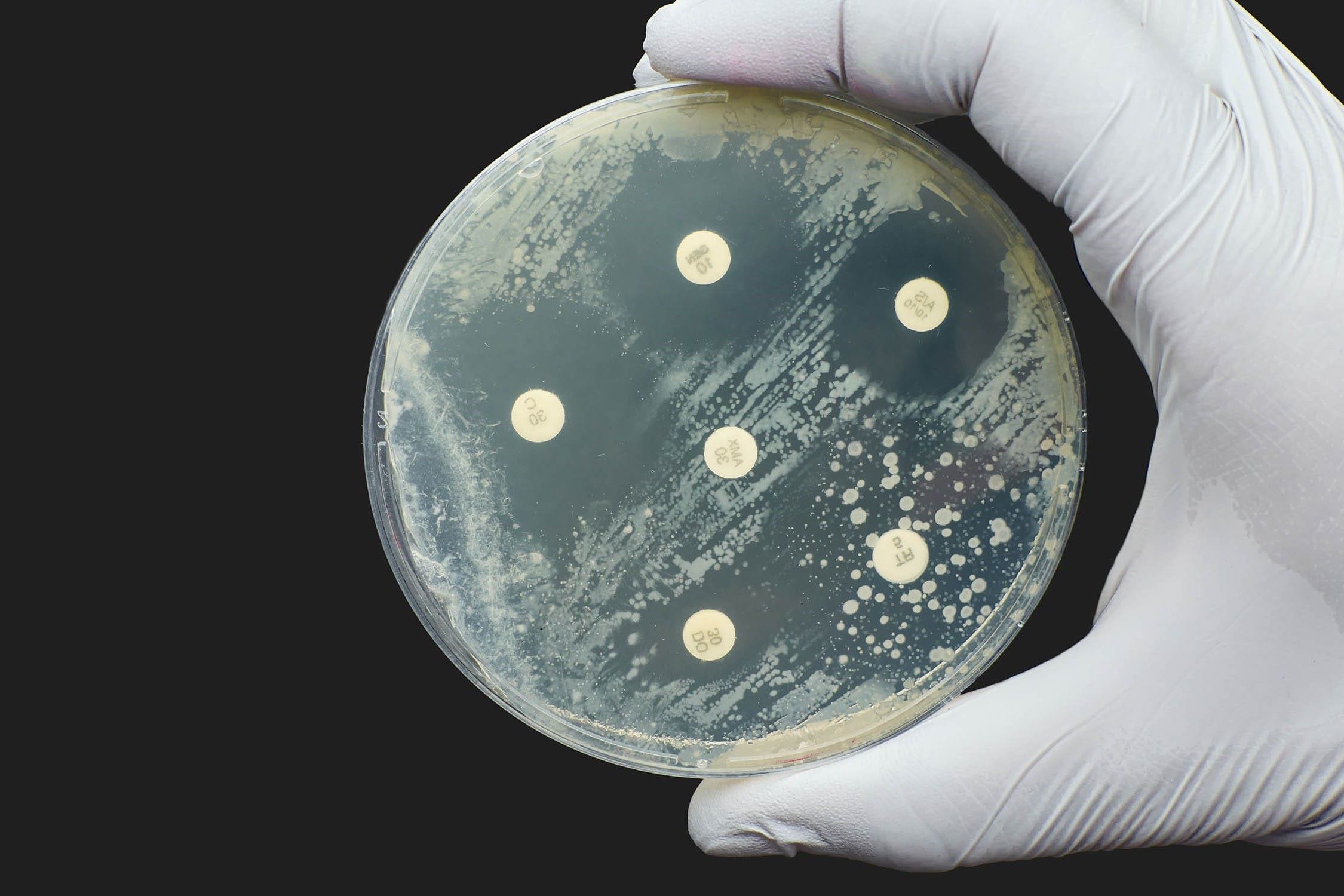
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are drugs specifically designed to combat bacterial infections. They work by killing bacteria or stopping their reproduction, allowing the body's immune system to eliminate them.
-
Soap and Water: Regular soap and water are effective at removing bacteria from the skin. The mechanical action of washing helps dislodge bacteria, while soap breaks down oils that trap germs.
How Do Antibacterial Agents Work?
Antibacterial agents work through various mechanisms to combat bacteria. Understanding these mechanisms can help us appreciate their importance in health and hygiene.
-
Cell Wall Disruption: Some antibacterial agents work by disrupting the bacterial cell wall, causing the bacteria to burst and die. Penicillin is a classic example of this mechanism.
-
Protein Synthesis Inhibition: Certain antibiotics, like tetracycline, prevent bacteria from producing proteins necessary for their growth and reproduction, effectively stopping their spread.
-
DNA Interference: Some agents, such as quinolones, interfere with bacterial DNA replication, preventing bacteria from multiplying and spreading.
-
Metabolic Pathway Blockage: Sulfonamides block essential metabolic pathways in bacteria, starving them of nutrients and leading to their death.
-
Biofilm Disruption: Biofilms are protective layers that bacteria form to shield themselves. Some antibacterial agents can penetrate and disrupt these biofilms, making bacteria more vulnerable.
Why Are Antibacterial Properties Important?
Antibacterial properties play a vital role in various aspects of life, from healthcare to food safety. Here are some reasons why they are essential.
-
Infection Control: Antibacterial properties help prevent and control infections, reducing the spread of diseases in hospitals and communities.
-
Food Preservation: These properties are used in food preservation to prevent spoilage and extend shelf life, ensuring food safety.
-
Hygiene Products: Many personal care products, like hand sanitizers and toothpaste, contain antibacterial agents to maintain hygiene and prevent infections.
-
Medical Devices: Antibacterial coatings on medical devices, such as catheters and implants, reduce the risk of infections during medical procedures.
-
Agriculture: In agriculture, antibacterial agents help protect crops from bacterial diseases, ensuring healthy and abundant yields.
Challenges and Considerations
While antibacterial properties are beneficial, they also present challenges and considerations that need to be addressed.
-
Antibiotic Resistance: Overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to antibiotic resistance, where bacteria evolve to resist the effects of drugs, making infections harder to treat.
-
Environmental Impact: The widespread use of antibacterial agents can impact the environment, affecting ecosystems and contributing to resistance.
-
Balance and Moderation: It's crucial to use antibacterial products judiciously, balancing their benefits with potential risks to health and the environment.
Wrapping Our Thoughts on Antibacterial Properties
Antibacterial properties play a crucial role in keeping our world healthier. From natural remedies like honey and garlic to modern medicines such as antibiotics, these properties help fight off harmful bacteria. They’re essential in preventing infections and promoting healing. However, overuse of antibiotics can lead to antibiotic resistance, a growing concern worldwide. This makes it important to use them wisely and explore alternative solutions when possible. Natural antibacterial agents offer a promising path, providing effective options without contributing to resistance. Understanding how these properties work can empower us to make informed choices about our health. Whether it’s choosing the right cleaning products or considering natural remedies, knowledge is power. As we continue to learn and adapt, antibacterial properties will remain a key ally in our quest for a healthier, safer environment. Stay informed, stay healthy, and let’s keep those germs at bay!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
