Eggs are one of nature’s tastiest and healthy power foods. Can you believe that one small egg contains all the essential vitamins and minerals we need for a healthy diet?
Not only do eggs give us the strength we need for our day to day lives, but it also keeps our brains active. Eggs are amazing, and to prove that, here are more egg facts that will get you egg-cited!
- You can peel hard-boiled eggs by blowing it out of its shell from one end of the egg.
- Blood can be used as an egg substitute in baking and making ice cream.
- Eggs have about 6 grams of high-quality protein in them.
- Eggs are also rich in choline which helps promote normal cell activity.
- It takes 24 to 26 hours for a hen to develop an egg.
- Chickens are capable of laying an egg inside another egg.
- Concerning their body size, kiwis lay the largest eggs.
- Hens turn their eggs over 50 times a day to keep the yolk from sticking to the side.
- Only fertilized bumblebee eggs turn into females and queens.
- British eggs are illegal in the U.S. because they are unwashed.
- U.S. eggs are illegal in British supermarkets because they are washed.
- Eggs contain about 9 essential amino acids.
- Eggs are the least expensive source of protein.
- Eggs are also gluten-free.
- Chickens do not produce one egg at a time.
- Eggs contain zero carbs and no sugar which won’t make you feel rounded after eating them.
- The hats that chefs wear traditionally have pleats that are equal to the number of ways you can cook an egg.
- The color of the eggshell has nothing to do with the egg’s nutritional value or its flavor. Instead, they indicate the breed of the hen that laid the egg.
- The diet of the hen will determine the color of the yolk.
- Brighter yolks are due to the marigold petals farmers put in the hens feed.
Egg Facts Infographics

Yolk means yellow.
The word means yolk was derived from an old English word. This would mean that it is technically egg white and egg yellow.
The Araucana chicken can lay different colored eggs.
That’s why it is also referred to as the Easter Egg Chicken. It is capable of laying eggs in a natural blue, green, brown, and pink eggs.
This breed of chicken is native in Chile and its name originates from where the breed is believed to have first been bred in.
There is a marketing organization called the American Egg Board.
This organization focuses on the promotion and marketing of, you guessed it, eggs. They are best known for their long-running slogan – The Incredible, Edible Egg.
Your breakfast McMuffin isn't served all day for a reason.
This is mainly due to the cooking temperature used for the grill. Their eggs need to be cooked at a lower temperature compared to cooking their hamburger patties.
Having to constantly change the grill’s temperature could alter the quality of the ingredients and even make some people sick.
1 in every 20,000 eggs may contain bacteria.
This means that there is a .0005% chance that the egg you are eating could contain salmonella. If you are a regular consumer of eggs, you might encounter a contaminated egg once every 84 years.

Three men once set out to Antarctica to recover penguin eggs.
In 1912, three men from the United Kingdom wanted to examine the embryonic contents of emperor penguin eggs. During their expedition, one man broke his teeth from his violent shaking from the cold.
In the end, when the three men had returned, a museum refused to accept the eggs for display.
A breed of Catfish lays its eggs with the eggs of the Cichlid fish.
This fish carries its young inside its mouth. When the eggs hatch first inside the adoptive mother’s mouth, it will eat its unborn children that are present inside.
Before the Cichlid fish notices this, the children of the catfish have already eaten every youngling.
Fake chicken eggs are a problem in China.
In China, these fake eggs are made to look like the real thing. It is made from a mixture of resin, coagulant, and starch with a counterfeit shell. It has been reported that 1 person can make around 1500 fake eggs a day.
There is more protein in a cooked egg than raw eggs.
This means that you should probably stop drinking those eggs raw, Rocky.
The ostrich egg globe was made from real ostrich eggs.
This is one of the oldest globes ever made. It originated in the year 1504 and was made to depict the New World.
This globe is engraved with immaculate details on two conjoined halves of an ostrich egg.
Putting eggs in the fridge is not necessary.
Many countries outside of the U.S. place their eggs at room temperature. The problem with this preservation method is that once the eggs have been refrigerated, they must remain inside until ready for consumption.
This is to prevent the growth of bacteria that can penetrate the shell of the egg.
Homosexual black swans use females to attain their eggs.
According to research, most pairings of black swans are homosexual. It is often during mating season that homosexual pairs will invite a female and mate together.
Once an egg has been laid by the female, the males drive the female away and take care of the egg on their own.
A hen named Harriet has laid the world’s largest egg.
In 2010, a hen from the United Kingdom hatched an egg that measured 9.1 inches in diameter. This beat the previous record-holder which was only 8.6 inches in diameter.
There is a reason why chicken eggs are consumed rather than the eggs of other bird species.
To put it simply, chickens lay more eggs, and therefore are easier to mass-produce and distribute to people all around the world. They also require less nesting space compared to other bird species and do not have strong mothering instincts, making egg collection easier.
The most popular type of eggs are white eggs.
To be more precise, these eggs are more preferred by commercial producers due to the hen’s sizes being relatively smaller than those who lay brown eggs. These hens consume less food and take up less space while producing the same number of eggs.
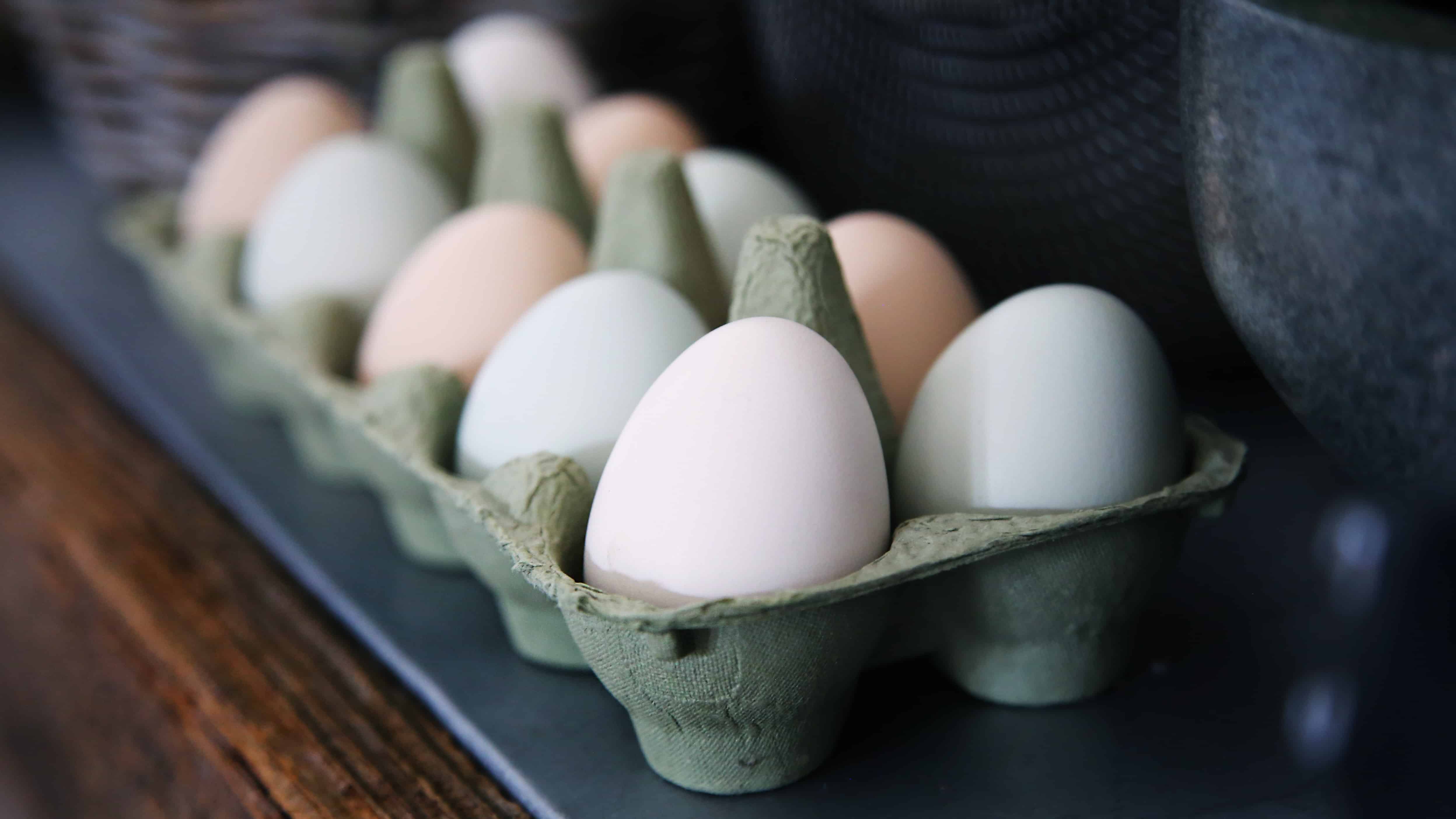

Most eggs laid today are from one common breed of chicken.
These hens are classified as White Leghorns for white eggs. Brown eggs commonly come from Rhode Island Reds and Barred Plymouth Rocks hens.
Cloudy egg whites indicate the eggs are at its freshest state.
The cloudiness is due to the natural presence of carbon dioxide that has not yet escaped through the shell of the egg. As the egg ages, the carbon dioxide slowly escapes the shell and results in a clearer and more transparent egg white.
Older eggs are easier to peel.
The reason for this is because older eggs have larger air cells inside them.
There is a way to tell the difference between hard-boiled and raw eggs without breaking them.
Simply spin the egg on a wide tabletop and observe its movement. If it wobbles, it means that the egg is raw because the liquid inside shifts.
Not all chicken eggs are created equally.
Some breeds of hens are capable of laying eggs almost every day. On the other hand, other breeds are only capable of laying eggs every other day or even once to twice per week.
Eating raw eggs won't help your health.
Most muscle heads believe that drinking raw eggs will help you gain muscle and give you more protein. This could not be further from the truth.
When you consume raw eggs, you only get 51% of the proteins that the egg contains. You are better off eating cooked eggs where you can get 91% of its benefits.
Iowa holds the top spot for most eggs laid in a year.
More than 14.8 billion eggs are produced in Iowa yearly. The next state to produce the next number of most eggs is Ohio at 7.9 billion eggs per year.
Eggs are a good source of nutrition for your eyes.
Eggs contain lutein which helps in preventing age-related cataracts and muscle degeneration.
Egg yolks naturally contain Vitamin D.
Most of the egg’s fats, vitamins, and minerals are found inside the yolk of an egg.

Produced eggs normally take 72 hours before reaching your supermarket.
Generally, farmers have a time limit of 30 days to get the eggs they produce to local markets and grocers. These stores then have another 30 days to sell them before being thrown out.
Apply the water test to an egg to determine its freshness.
Place the egg in a tall glass of water. Fresh eggs will always float while rotten ones will sink standing up.
The date on your egg carton does not indicate its expiration.
These eggs are usually edible for 3 to 4 weeks after this date. So make sure you don’t throw them out and use them while you still can.
Eggs are high in demand in the United States.
The average American consumes about 250 eggs a year. This equates to a consumption of 76.5 billion eggs in the United States per day.
There are different types of labels found on egg cartons.
Cage-free refers to hens that were raised in an environment outside of cages. Free-range means that the hens are free to roam around outdoors at some point. Certified organic eggs are from hens that are given a strict vegetarian diet. Natural labeled eggs don’t usually mean anything.
Eggs you find in stores do not hatch for a specific reason.
To fertilize an egg, a hen must mate with a rooster first. Only hens that have not mated are used to produce eggs made for human consumption.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.