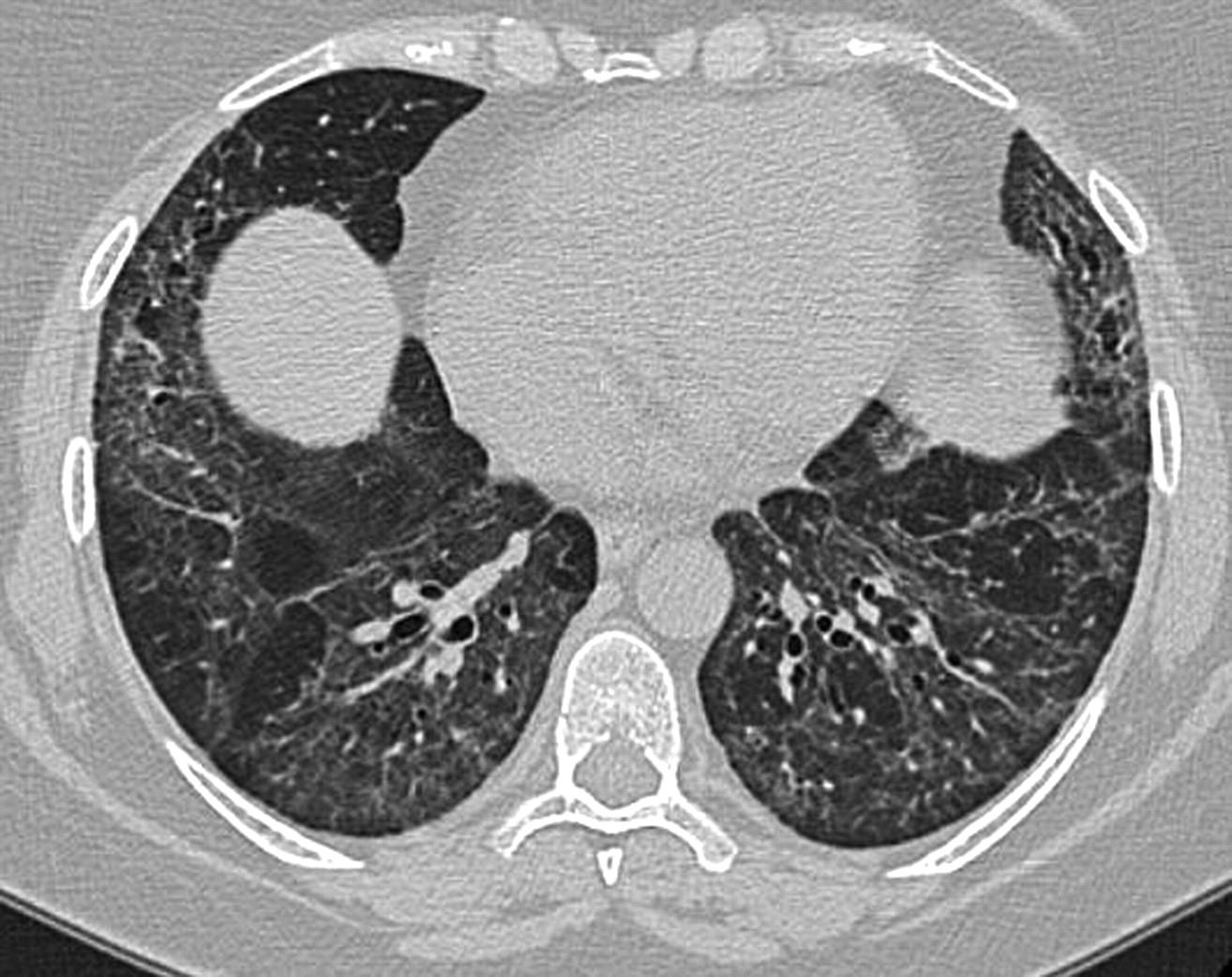
Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD), also known as interstitial lung disease, is a group of disorders causing scarring (fibrosis) of lung tissue. This scarring makes it hard for lungs to get enough oxygen. Symptoms often include shortness of breath, a dry cough, and fatigue. Causes can range from long-term exposure to hazardous materials like asbestos to autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Diagnosis usually involves imaging tests, lung function tests, and sometimes a lung biopsy. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression, often through medications, oxygen therapy, and lifestyle changes. Understanding DPLD is crucial for early detection and better management.
Key Takeaways:
- Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD) encompasses over 200 lung disorders, causing scarring and breathing difficulties. Early detection and avoiding harmful substances are crucial for managing this condition effectively.
- Symptoms of DPLD include persistent dry cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Treatment options like corticosteroids and oxygen therapy can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
What is Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease?
Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD) is a group of lung disorders affecting the lung's interstitium, the tissue and space around the air sacs. These diseases cause scarring and inflammation, leading to breathing difficulties and reduced oxygen levels.
-
DPLD encompasses over 200 different lung disorders. This wide range includes conditions like idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and sarcoidosis.
-
The interstitium is crucial for gas exchange. Damage to this area impairs the lungs' ability to transfer oxygen to the blood.
-
Symptoms often include a persistent dry cough. This is one of the most common early signs of DPLD.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding what causes DPLD and the risk factors involved can help in early detection and management.
-
Exposure to environmental toxins is a significant risk factor. Substances like asbestos, silica dust, and certain gases can lead to DPLD.
-
Smoking increases the risk of developing DPLD. Smokers are more likely to develop lung diseases, including DPLD.
-
Genetics play a role in some cases. Family history can increase the likelihood of developing certain types of DPLD.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the diagnostic process is vital for managing DPLD effectively.
-
Shortness of breath is a common symptom. This usually worsens over time, especially during physical activity.
-
Fatigue and weight loss can also occur. These symptoms often accompany the respiratory issues.
-
High-resolution CT scans are crucial for diagnosis. They provide detailed images of the lungs, helping to identify the extent of the disease.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for DPLD, various treatments can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
Corticosteroids are often prescribed. These medications reduce inflammation in the lungs.
-
Oxygen therapy can be beneficial. It helps maintain adequate oxygen levels in the blood.
-
Lung transplantation may be an option for severe cases. This is considered when other treatments fail to improve the condition.
Living with DPLD
Managing daily life with DPLD involves several strategies to maintain health and well-being.
-
Regular exercise is important. It helps improve lung function and overall fitness.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs offer support. These programs provide education, exercise training, and nutritional advice.
-
Avoiding respiratory infections is crucial. Patients should get vaccinated against flu and pneumonia.
Prognosis and Outlook
The prognosis for DPLD varies depending on the specific type and severity of the disease.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis has a poor prognosis. The average survival time after diagnosis is 3-5 years.
-
Some types of DPLD can stabilize with treatment. Early intervention can slow disease progression.
-
Regular follow-ups with a pulmonologist are essential. Ongoing monitoring helps manage the disease effectively.
Research and Future Directions
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of DPLD.
-
Clinical trials are exploring new medications. These trials test the effectiveness of potential new treatments.
-
Genetic research is uncovering new insights. Understanding genetic factors can lead to targeted therapies.
-
Stem cell therapy is being investigated. This innovative approach holds promise for repairing lung tissue.
Support and Resources
Finding support and resources can help patients and their families cope with DPLD.
-
Support groups provide emotional assistance. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can be comforting.
-
Educational resources are available online. Websites like the American Lung Association offer valuable information.
-
Healthcare teams offer multidisciplinary support. This includes doctors, nurses, respiratory therapists, and social workers.
Prevention and Awareness
Raising awareness and taking preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing DPLD.
-
Avoiding exposure to harmful substances is key. This includes wearing protective gear in hazardous environments.
-
Quitting smoking significantly reduces risk. Smoking cessation programs can provide support.
-
Regular health check-ups can detect early signs. Early detection improves the chances of effective management.
Impact on Daily Life
DPLD affects various aspects of daily living, requiring adjustments and support.
-
Energy conservation techniques can help. Learning to manage energy levels is important for daily activities.
-
Nutritional support is often necessary. A balanced diet helps maintain strength and overall health.
-
Mental health support is crucial. Coping with a chronic illness can be challenging, and professional help can make a difference.
Final Thoughts on Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease
Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD) is a complex condition affecting the lung's interstitial space. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatments can make a big difference in managing the disease. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for better outcomes. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about the latest medical advancements can help those affected.
Remember, knowledge is power. The more you know about DPLD, the better equipped you'll be to handle it. If you or a loved one shows symptoms, don't hesitate to consult a healthcare professional. Stay proactive, stay informed, and take control of your health.
Thanks for reading, and we hope this information helps you understand DPLD better. Stay healthy!
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
