Telomerase is a fascinating enzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular aging and cancer. Ever wondered why some cells seem to live forever while others age and die? The secret lies in telomerase. This enzyme helps maintain the length of telomeres, which are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. Without telomerase, these caps shorten over time, leading to cell aging and death. However, in cancer cells, telomerase activity is often ramped up, allowing them to divide indefinitely. Understanding telomerase can offer insights into aging, cancer treatments, and even potential anti-aging therapies. Ready to dive into 50 intriguing facts about this enzyme? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Telomerase, the "immortality enzyme," maintains chromosome ends and affects aging and cancer. It's like a cellular timekeeper, influencing how long cells live and dividing, with potential for anti-aging treatments.
- Telomerase is a hot topic in science and culture, inspiring stories of eternal youth. It's also a target for cancer research and anti-aging skincare products, showing its impact on health and popular imagination.
What is Telomerase?
Telomerase is a unique enzyme that plays a crucial role in cellular aging and cancer. It helps maintain the length of telomeres, which are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes. Understanding telomerase can provide insights into aging, cancer, and potential treatments.
- Telomerase is an enzyme that adds DNA sequence repeats to the ends of chromosomes, known as telomeres.
- Telomeres protect chromosomes from deterioration or fusion with neighboring chromosomes.
- Without telomerase, telomeres shorten with each cell division, leading to cellular aging.
- Telomerase activity is high in stem cells and germ cells, which need to divide frequently.
- Most somatic cells have low or undetectable telomerase activity, contributing to aging.
- Telomerase was discovered by Elizabeth Blackburn and Carol Greider in 1984.
- Blackburn and Greider, along with Jack Szostak, won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2009 for their work on telomeres and telomerase.
- Telomerase is composed of protein and RNA components.
- The RNA component of telomerase serves as a template for adding telomere sequences.
- Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) is the protein component that synthesizes DNA from the RNA template.
Telomerase and Aging
Telomerase has a significant impact on the aging process. Its role in maintaining telomere length can influence how quickly cells age and die.
- Shortened telomeres are associated with aging and age-related diseases.
- Telomerase activation in somatic cells could potentially slow down aging.
- Mice engineered to express telomerase in all tissues show delayed aging symptoms.
- However, overactive telomerase can increase the risk of cancer.
- Telomere length is considered a biomarker of biological aging.
- Lifestyle factors like stress, smoking, and poor diet can accelerate telomere shortening.
- Regular exercise and a healthy diet are linked to longer telomeres.
- Chronic inflammation can also lead to faster telomere shortening.
- Telomerase therapy is being explored as a potential anti-aging treatment.
- Some studies suggest that meditation and stress reduction can positively affect telomere length.
Telomerase and Cancer
Telomerase is often reactivated in cancer cells, allowing them to divide indefinitely. This makes it a target for cancer research and treatment.
- Approximately 85-90% of cancers show increased telomerase activity.
- Telomerase allows cancer cells to bypass the normal limits on cell division.
- Inhibiting telomerase could potentially stop cancer growth.
- Telomerase inhibitors are being tested in clinical trials as cancer treatments.
- Some cancers, like glioblastoma, are particularly dependent on telomerase.
- Telomerase reactivation is a hallmark of cancer.
- Cancer cells can also use alternative lengthening of telomeres (ALT) mechanisms.
- Telomerase-targeted therapies aim to selectively kill cancer cells without harming normal cells.
- Immunotherapy approaches are being developed to target telomerase-expressing cancer cells.
- Telomerase vaccines are another area of active research in cancer treatment.
Telomerase in Research and Medicine
Telomerase continues to be a focus of extensive research due to its implications for health and disease. Scientists are exploring various ways to harness its potential.
- Telomerase research has led to a better understanding of the aging process.
- Telomerase activity is measured using the telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) assay.
- Telomerase is being studied in the context of regenerative medicine.
- Stem cell therapies often involve manipulating telomerase activity.
- Telomerase gene therapy is a potential treatment for age-related diseases.
- Researchers are investigating telomerase's role in tissue repair and regeneration.
- Telomerase activators are being developed as potential supplements for health and longevity.
- Some natural compounds, like astragalus root, are believed to activate telomerase.
- Telomerase is also studied in the context of genetic disorders like dyskeratosis congenita.
- Understanding telomerase can help develop treatments for diseases caused by telomere dysfunction.
Interesting Facts about Telomerase
Beyond its scientific significance, telomerase has some fascinating aspects that capture the imagination.
- Telomerase is sometimes called the "immortality enzyme" due to its role in cell division.
- The discovery of telomerase challenged the belief that DNA replication was fully understood.
- Telomerase research has inspired science fiction stories about eternal youth.
- Some animals, like lobsters, have high telomerase activity and can live for decades.
- The study of telomerase has led to new insights into the biology of aging.
- Telomerase is a target for anti-aging cosmetics and skincare products.
- The enzyme's name comes from "telos," the Greek word for "end," and "meros," meaning "part."
- Telomerase has been found in some single-celled organisms, like Tetrahymena.
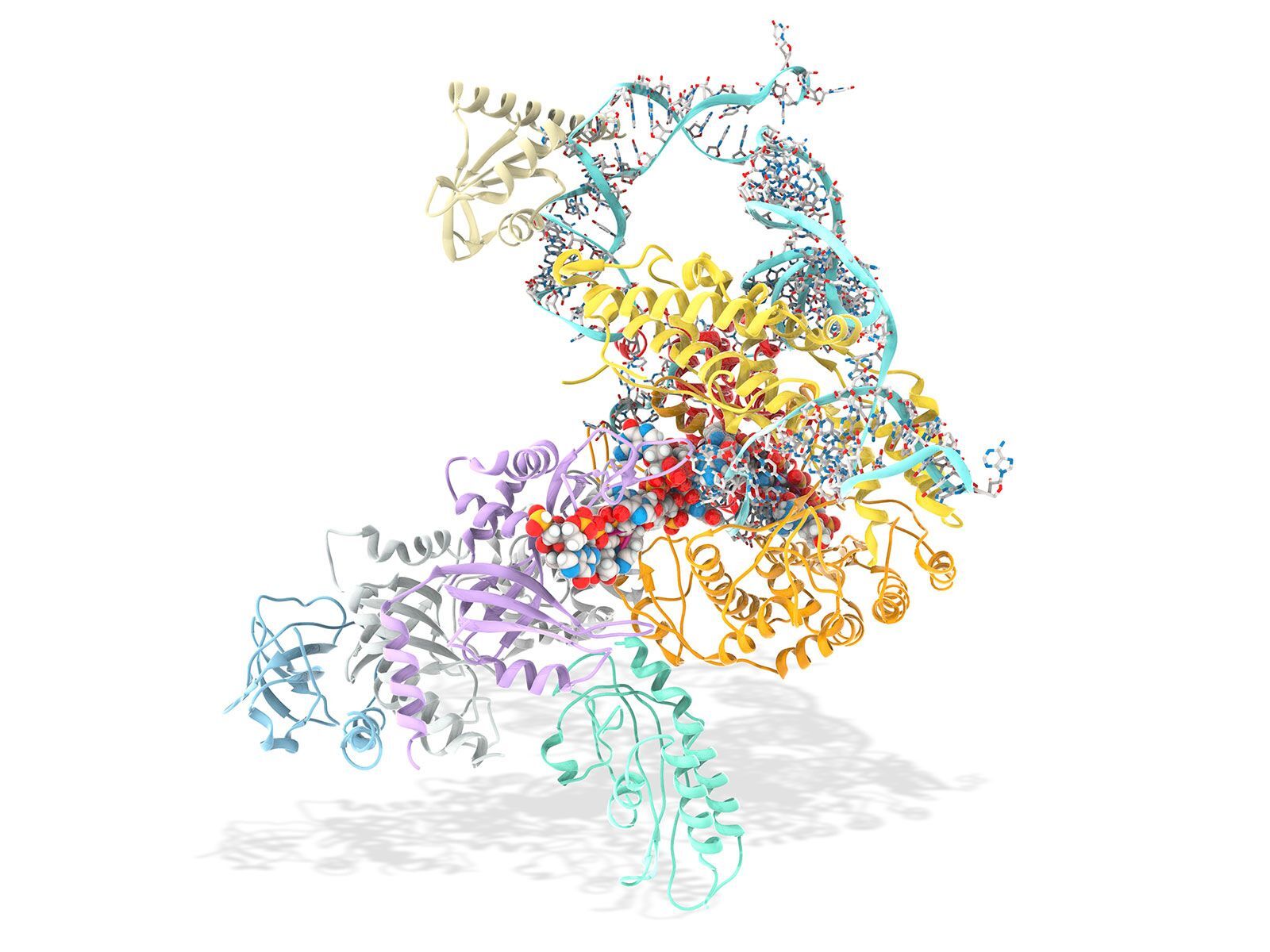
- The enzyme's structure was first visualized using cryo-electron microscopy.
- Telomerase continues to be a hot topic in both scientific research and popular culture.
The Power of Telomerase
Telomerase is a fascinating enzyme with a big role in cellular aging and health. It helps maintain telomeres, the protective caps on our chromosomes, which can impact how cells age and divide. Scientists are exploring telomerase for its potential in anti-aging therapies and cancer treatments. While boosting telomerase activity might slow aging, it could also increase cancer risk since cancer cells often hijack telomerase to keep dividing.
Understanding telomerase better could lead to breakthroughs in medicine, offering new ways to treat age-related diseases and cancer. It's a complex balance, but the possibilities are exciting. As research continues, we might unlock new secrets about how our cells work and how we can live healthier, longer lives. Telomerase isn't just a tiny enzyme; it's a key player in the story of life and aging.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
