When it comes to the fascinating world of animals, turtles often capture our attention with their distinct appearance and intriguing behaviors. These amazing creatures have been around for millions of years, adapting and thriving in various environments across the globe.
In this article, we will delve into the world of turtles and explore some fascinating facts about their unique brain structure and functionality. From their ability to navigate with precision to their remarkable memory skills, turtles have a lot more going on inside their shells than meets the eye.
So, if you’re ready to embark on a journey of discovery and learn some intriguing turtle brain facts, let’s dive right in!
Key Takeaways:
- Turtles have a smart brain structure that helps them remember places, solve problems, and live a long time. Their brains also help them see well, smell, and find their way using the Earth’s magnetic field.
- Turtles are not just slow and steady; they’re also smart and emotional! Their brains help them do cool things like remember where they live, sense the Earth’s magnetic field, and live for a really long time.
Turtles have a unique brain structure.
Turtles possess a brain structure that sets them apart from other animals. Their brains are characterized by a three-part division known as the triune brain, which consists of the reptilian complex, the limbic system, and the neocortex.
Turtles have excellent spatial memory.
One remarkable aspect of turtle brains is their exceptional spatial memory. Turtles have the ability to remember specific locations and navigate intricate environments, allowing them to return to their nesting sites or favored feeding areas with precision.
Turtles are capable of learning and problem-solving.
Contrary to popular belief, turtles possess a level of intelligence that enables them to learn and solve problems. They can be trained to recognize certain stimuli and respond accordingly, showcasing their cognitive abilities.
Turtles have a highly developed visual system.
Turtle brains have a well-developed visual system, enabling them to perceive their surroundings with great clarity. Their vision plays a crucial role in hunting, foraging, and identifying predators.
Turtles have a keen sense of smell.
The olfactory system of turtles allows them to detect scents and navigate their surroundings. Their sense of smell aids in finding food sources, identifying mates, and recognizing their own nesting sites.
Turtles exhibit complex behaviors influenced by their brain function.
Due to their unique brain structure, turtles exhibit a wide range of complex behaviors. From courtship rituals to territorial displays, their brain function plays a pivotal role in shaping their behavioral patterns.
Turtles can experience emotions to an extent.
Recent scientific studies suggest that turtles may possess the capacity to experience basic emotions. While their emotional range may not be as extensive as that of mammals, they have been observed displaying behaviors indicative of basic emotional states.
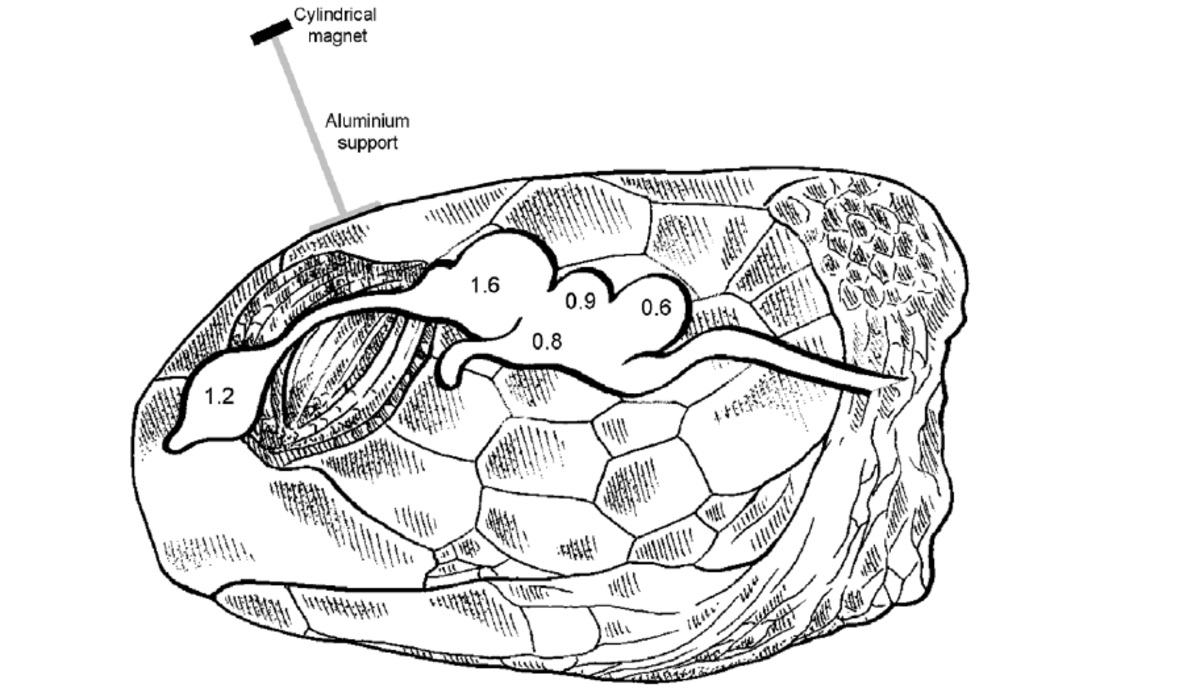
Turtles have a remarkable ability to navigate using the Earth’s magnetic field.
Turtle brains contain magnetite, a mineral that enables them to sense the Earth’s magnetic field. This extraordinary ability helps them orient themselves during long-distance migrations and locate their preferred nesting beaches.
Turtles have a slow metabolic rate compared to other animals.
Turtle brains contribute to their slow metabolic rate, allowing them to survive in environments with limited resources. Their ability to conserve energy and adapt to harsh conditions has contributed to their success as a species.
Turtles exhibit long lifespans thanks to their brain function.
The unique brain function and physiological processes of turtles contribute to their incredible longevity. Some turtle species have been known to live for over a hundred years, making them one of the longest-living creatures on Earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, turtles are truly fascinating creatures with unique brain capabilities. From their ability to navigate the Earth’s magnetic fields to their remarkable memory, turtles have proven to be extraordinary animals. Their intricate brains allow them to adapt to various environments and survive in both land and water habitats. Understanding the brain of a turtle not only deepens our appreciation for these reptiles but also sheds light on the intricate nature of animal cognition as a whole.
FAQs
1. How big is the brain of a turtle?
The size of a turtle’s brain depends on its species and age. Generally, turtle brains are relatively small compared to their body size.
2. Can turtles recognize humans?
While turtles may not have the same level of recognition as mammals, some studies suggest that they can distinguish between familiar and unfamiliar individuals based on visual and olfactory cues.
3. Do turtles have good memory?
Turtles have remarkable memory capabilities. They can remember specific locations, such as nesting sites or food sources, and can even remember individuals they have encountered before.
4. Can turtles learn tricks or commands?
Turtles have the capacity to learn through conditioning and repetition. While they may not perform complex tricks like dogs, they can be trained to respond to certain commands and associate stimuli with rewards.
5. Are turtles intelligent?
Turtles exhibit different forms of intelligence, particularly in terms of problem-solving, memory, and navigation. Their specific cognitive abilities may vary based on their species and environmental demands.
6. How do turtle brains differ from other reptiles?
Turtle brains possess unique features, such as an enlarged olfactory region, which is crucial for their sense of smell. Additionally, the size and shape of their brains differ across species, reflecting their varied behaviors and adaptations.
7. Can turtles feel emotions?
While it is difficult to know for certain, research suggests that turtles may experience basic emotions like fear or pleasure. However, their emotional experiences are likely to be more primitive compared to mammals.
8. Are there any differences in brain function between land and aquatic turtles?
Land turtles tend to have a more developed visual processing area of the brain, as they rely heavily on their vision for survival. Aquatic turtles, on the other hand, have an enhanced ability to navigate underwater environments.
9. Can turtles recognize themselves in a mirror?
Currently, there is limited research on whether turtles can recognize themselves in a mirror. However, some experiments suggest that certain species of turtles may show signs of self-awareness.
10. What is the impact of environmental factors on turtle brain development?
Environmental factors, such as temperature and light exposure, can significantly impact the development of a turtle’s brain. These factors can affect navigation abilities, memory formation, and overall cognitive functioning.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
