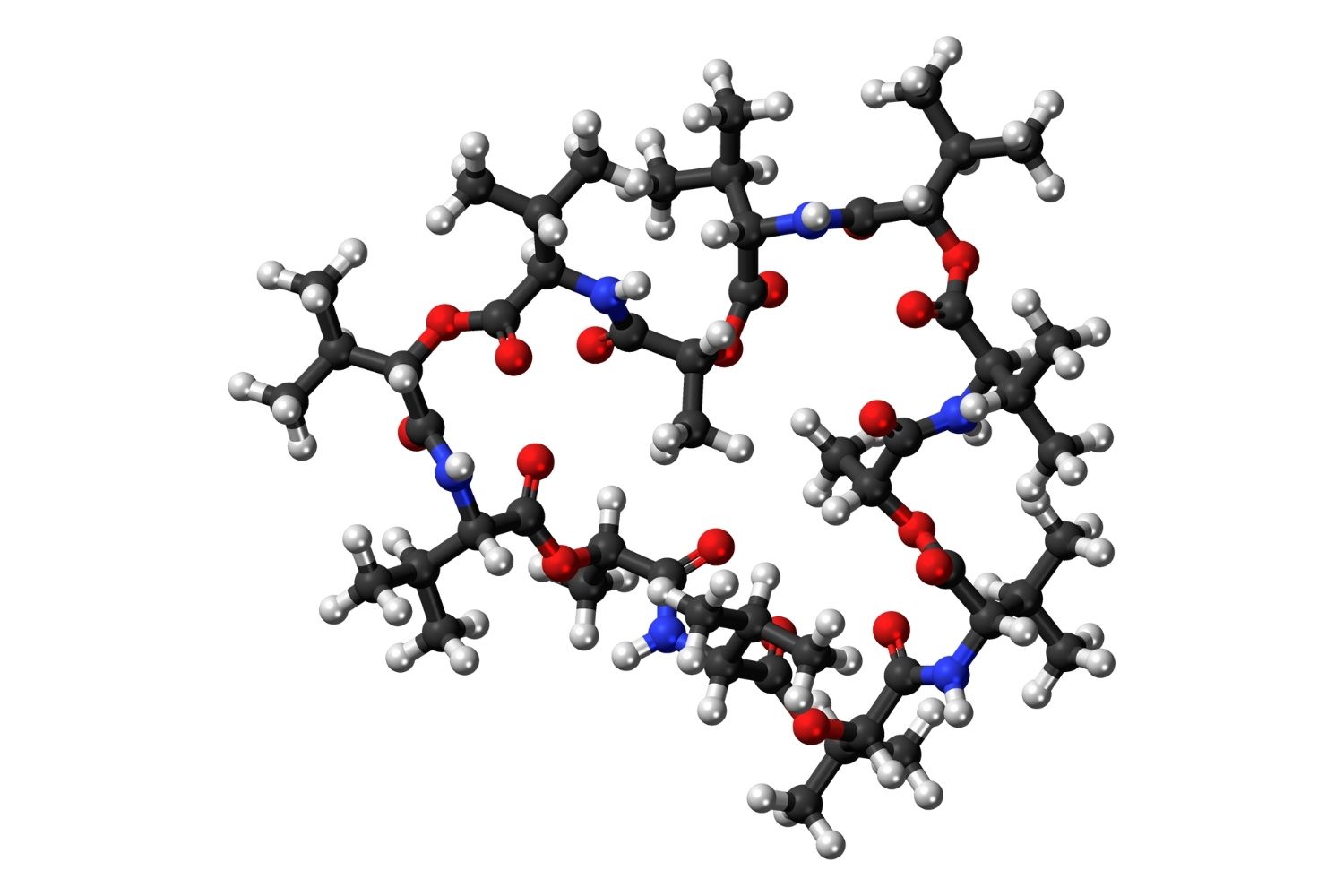
Valinomycin might sound like a character from a sci-fi movie, but it's actually a fascinating compound with some pretty cool properties. What is valinomycin? It's a naturally occurring antibiotic produced by certain bacteria, specifically Streptomyces species. This compound is a cyclic peptide, which means it's made up of amino acids linked in a circle. Valinomycin is known for its ability to transport potassium ions across cell membranes, making it a powerful tool in scientific research. Its unique structure allows it to selectively bind to potassium ions, facilitating their movement through lipid membranes. This property has made valinomycin a valuable asset in studies related to ion transport and membrane potential. Additionally, its ionophore capabilities have implications in various fields, including biochemistry and pharmacology. Understanding valinomycin's role in these processes can provide insights into cellular functions and potential therapeutic applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Valinomycin is a unique compound that can transport potassium ions and disrupt cell function. It has applications in research, but its toxicity prevents it from being used as a drug.
- Valinomycin's symmetrical structure and ability to mimic natural ion channels make it a valuable tool in studying cell processes and developing new materials. Despite its age, it continues to inspire scientific interest.
What is Valinomycin?
Valinomycin is a fascinating compound with a unique structure and intriguing properties. It's a type of antibiotic produced by certain bacteria and fungi. Let's dive into some interesting facts about this compound.
-
Valinomycin is a cyclic peptide. This means it forms a closed loop, which is quite different from the linear structure of most proteins.
-
It consists of 12 alternating amino acids and esters. These components create a ring structure that is highly specific in its function.
-
Valinomycin is known for its ionophore properties. It can transport potassium ions across cell membranes, making it a valuable tool in scientific research.
-
It was first isolated in 1955. Scientists discovered it in a strain of the bacterium Streptomyces fulvissimus.
-
Valinomycin has a high affinity for potassium ions. This specificity allows it to selectively transport potassium over other ions like sodium.
-
Its molecular formula is C54H90N6O18. This complex formula reflects its intricate structure.
-
Valinomycin is used in biochemistry and physiology studies. Researchers use it to study ion transport and membrane potential.
-
It can disrupt cellular processes. By altering ion gradients, valinomycin can affect cell function, which is why it's studied for its antibiotic properties.
-
Valinomycin is not used as a drug. Despite its antibiotic nature, it's not suitable for therapeutic use due to its toxicity.
-
It has a role in studying mitochondrial function. Scientists use it to understand how mitochondria manage ion transport.
How Does Valinomycin Work?
Understanding how valinomycin functions can shed light on its applications and significance in research.
-
Valinomycin forms a complex with potassium ions. This complex can easily pass through lipid membranes, facilitating ion transport.
-
It disrupts the electrochemical gradient. By moving potassium ions, valinomycin can alter the balance of charges across a membrane.
-
This disruption can lead to cell death. In bacteria, this makes valinomycin an effective antibiotic.
-
Valinomycin's action is passive. It doesn't require energy to transport ions, relying instead on concentration gradients.
-
It can be used to study ion channel function. Researchers use it to mimic or block natural ion channels in cells.
-
Valinomycin's selectivity is due to its structure. The size and shape of its ring allow it to fit potassium ions perfectly.
-
It can be used in artificial membranes. Scientists use it to create model systems for studying membrane dynamics.
-
Valinomycin can affect heart cells. By altering ion flow, it can influence heart muscle contraction.
-
It is used in electrophysiology experiments. Researchers study its effects on nerve and muscle cells.
-
Valinomycin can be a tool for studying apoptosis. Its ability to disrupt ion gradients can trigger programmed cell death.
Valinomycin in Research and Industry
Valinomycin's unique properties make it a valuable tool in various fields of study and industry.
-
It is used in biosensors. Valinomycin's ion-selective properties make it useful in detecting potassium levels.
-
Valinomycin can be used in agriculture. Its antibiotic properties have potential applications in controlling plant pathogens.
-
It is a model compound for studying ionophores. Researchers use it to understand how similar compounds work.
-
Valinomycin is studied for its potential in cancer research. Its ability to induce cell death makes it a candidate for cancer therapy studies.
-
It is used in the study of antibiotic resistance. Understanding how valinomycin works can help develop new antibiotics.
-
Valinomycin can be synthesized in the lab. This allows researchers to study its structure and function in detail.
-
It is used in the development of new materials. Scientists explore its potential in creating ion-selective membranes.
-
Valinomycin is a tool for studying cellular respiration. Its effects on ion gradients can help understand energy production in cells.
-
It is used in the study of neurobiology. Researchers use it to explore how neurons manage ion flow.
-
Valinomycin can be used in environmental monitoring. Its ability to detect potassium can help assess soil and water quality.
Interesting Facts About Valinomycin
Beyond its scientific applications, valinomycin has some intriguing aspects worth noting.
-
Valinomycin has a unique smell. Some describe it as having a sweet, earthy aroma.
-
It is a natural product. Despite its complex structure, valinomycin is produced by microorganisms in nature.
-
Valinomycin's structure is highly symmetrical. This symmetry contributes to its stability and function.
-
It has been studied for over 60 years. Despite its age, valinomycin continues to be a subject of scientific interest.
-
Valinomycin can be toxic to humans. Its ability to disrupt ion gradients makes it dangerous if ingested or inhaled.
-
It is used in educational settings. Valinomycin is a classic example in biochemistry courses for studying ion transport.
-
Valinomycin's discovery was accidental. Scientists were initially studying soil bacteria when they found it.
-
It has inspired the development of synthetic ionophores. Researchers use valinomycin as a template for designing new compounds.
-
Valinomycin's production is a complex process. The bacteria that produce it require specific conditions to synthesize it.
-
It remains a valuable tool in modern science. Despite advances in technology, valinomycin's unique properties keep it relevant in research.
Valinomycin: A Fascinating Compound
Valinomycin, a potent antibiotic, is a fascinating compound with a unique structure and function. Its ability to selectively transport potassium ions across cell membranes makes it a valuable tool in scientific research. This cyclic peptide, produced by certain Streptomyces bacteria, has applications in biochemistry and pharmacology. Its role in disrupting ion gradients helps researchers understand cellular processes and develop new therapies.
However, valinomycin's potency also means it can be toxic, requiring careful handling in laboratory settings. Its use in studying mitochondrial function and apoptosis highlights its importance in advancing our understanding of cell biology. While not used directly as a therapeutic agent due to its toxicity, valinomycin's contributions to science are undeniable. This compound continues to intrigue researchers, offering insights into the complex world of cellular mechanisms and potential pathways for future medical advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
