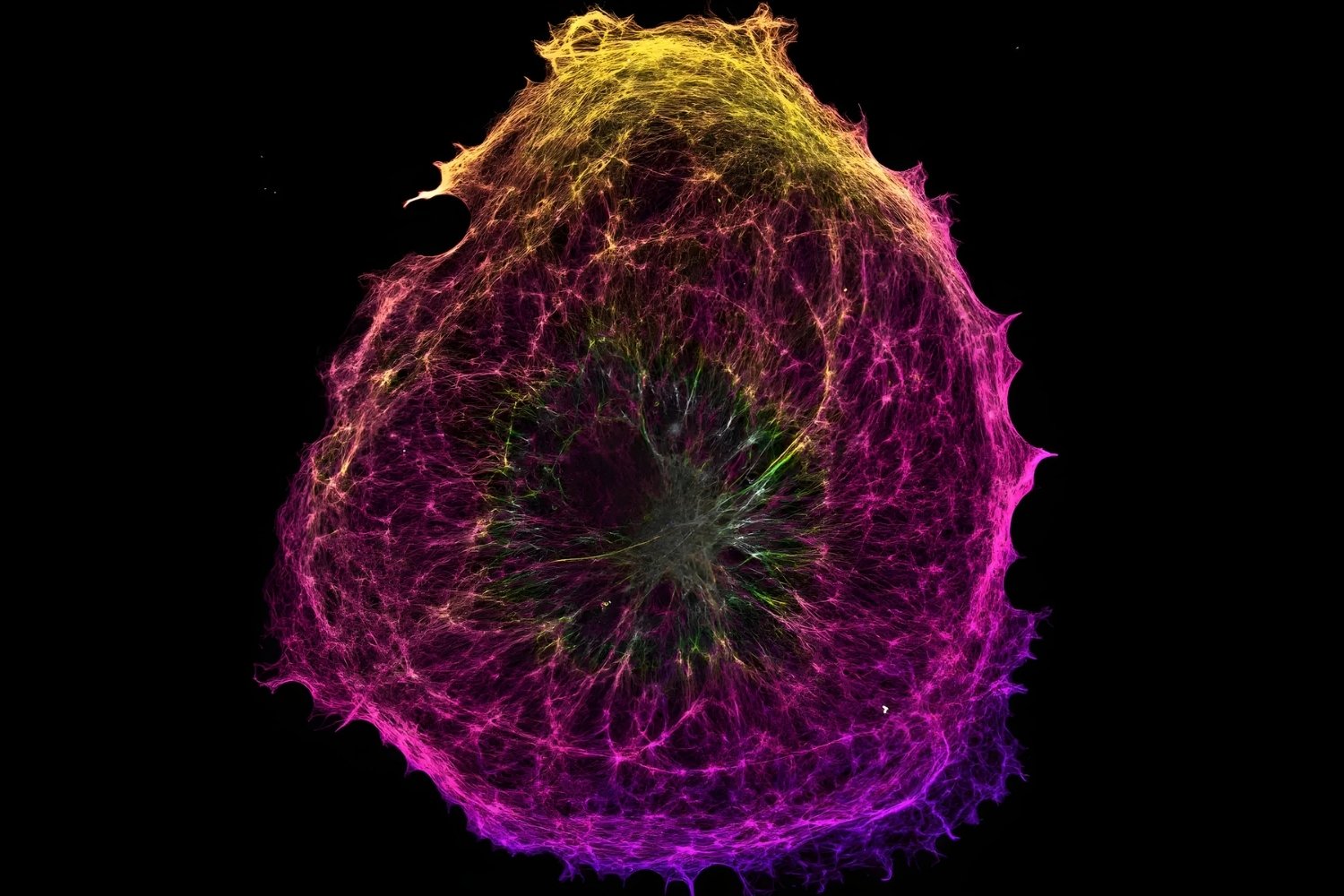
Microfilaments are tiny but mighty structures inside cells, playing a crucial role in various cellular functions. These slender threads, made of a protein called actin, are part of the cell's cytoskeleton. They help cells maintain their shape, move, and divide. Without microfilaments, cells would struggle to perform essential tasks like muscle contraction and cell signaling. They are also involved in processes like endocytosis, where cells engulf substances from their surroundings. Understanding microfilaments can provide insights into how cells work and how certain diseases develop. Ready to learn more? Here are 36 fascinating facts about microfilaments that will deepen your appreciation for these cellular powerhouses.
What Are Microfilaments?
Microfilaments, also known as actin filaments, are essential components of the cell's cytoskeleton. They play a crucial role in maintaining the cell's shape, enabling movement, and facilitating various cellular processes. Here are some fascinating facts about these tiny but mighty structures.
- Microfilaments are primarily composed of a protein called actin.
- Actin is one of the most abundant proteins in eukaryotic cells.
- These filaments are about 7 nanometers in diameter.
- They are the thinnest filaments in the cytoskeleton.
- Microfilaments can rapidly assemble and disassemble, allowing cells to change shape quickly.
Functions of Microfilaments
Microfilaments are involved in a variety of cellular functions. They are not just structural elements; they actively participate in many processes.
- They help in cell division by forming the contractile ring during cytokinesis.
- Microfilaments are crucial for muscle contraction.
- They aid in cell motility, allowing cells to move by forming structures like lamellipodia and filopodia.
- These filaments are involved in intracellular transport, moving organelles and vesicles within the cell.
- They play a role in maintaining cell shape by providing mechanical support.
Microfilaments in Muscle Cells
Muscle cells have a unique structure and function, largely due to the presence of microfilaments. These filaments are integral to muscle contraction and movement.
- Actin filaments interact with myosin filaments to produce muscle contraction.
- The sliding filament theory explains how actin and myosin filaments slide past each other to shorten the muscle.
- Microfilaments in muscle cells are organized into repeating units called sarcomeres.
- Sarcomeres are the basic functional units of muscle fibers.
- The arrangement of actin and myosin filaments gives skeletal muscles their striated appearance.
Microfilaments in Non-Muscle Cells
While muscle cells are a well-known example, microfilaments are also vital in non-muscle cells. They contribute to various cellular activities beyond muscle contraction.
- In non-muscle cells, microfilaments are involved in cell signaling pathways.
- They help in the formation of cell junctions, which connect cells to each other.
- Microfilaments are essential for endocytosis, the process by which cells engulf external substances.
- They participate in exocytosis, where cells expel materials.
- These filaments are involved in the formation of microvilli, which increase the surface area of cells for absorption.
Microfilament Dynamics
The dynamic nature of microfilaments allows cells to adapt to their environment and perform various functions efficiently.
- Microfilaments undergo polymerization, where actin monomers join to form a filament.
- Depolymerization is the process where actin filaments break down into monomers.
- The balance between polymerization and depolymerization is regulated by actin-binding proteins.
- Tropomyosin is an actin-binding protein that stabilizes microfilaments.
- Profilin promotes the addition of actin monomers to the growing filament.
Microfilaments and Disease
Abnormalities in microfilaments can lead to various diseases and health conditions. Understanding these connections can help in developing treatments.
- Mutations in actin genes can cause congenital myopathies, a group of muscle disorders.
- Defects in actin-binding proteins are linked to certain types of cancer.
- Microfilament dysfunction is associated with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's.
- Some pathogens exploit microfilaments to enter and move within host cells.
- Research on microfilaments is ongoing to develop therapies for these conditions.
Microfilaments in Research
Microfilaments are a hot topic in scientific research. They offer insights into cell biology and potential medical applications.
- Fluorescent tagging of actin allows scientists to visualize microfilaments in live cells.
- Advanced microscopy techniques have revealed the detailed structure of microfilaments.
- Studies on microfilaments have contributed to our understanding of cell mechanics.
- Research on actin dynamics has implications for cancer treatment.
- Microfilament studies are helping to develop new drugs for muscle diseases.
- Understanding microfilaments can lead to innovations in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Microfilaments: The Unsung Heroes of Cells
Microfilaments play a crucial role in the life of cells. These tiny structures, made of actin, are essential for cell movement, shape, and division. Without them, cells couldn't perform many of their vital functions. They help in muscle contraction, cell signaling, and even in the immune response. Microfilaments are dynamic, constantly assembling and disassembling to meet the cell's needs. They work closely with other cellular components like microtubules and intermediate filaments to maintain the cell's integrity and function. Understanding microfilaments gives us insight into how cells operate and adapt. So next time you think about the complexity of life, remember these tiny but mighty structures. They might be small, but their impact is enormous.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
