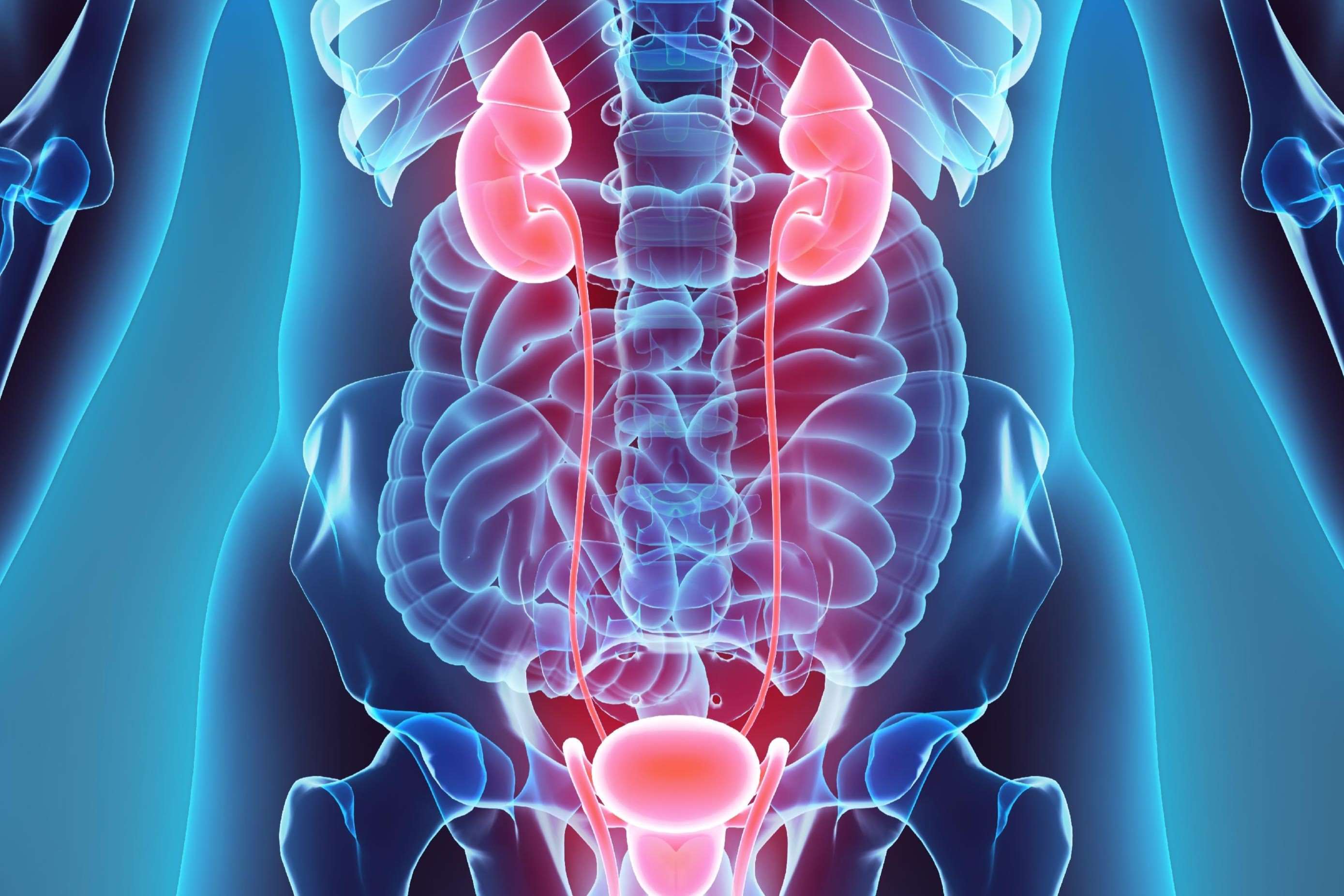
Did you know the renal pelvis and ureter play a crucial role in your body's plumbing system? These two structures are part of the urinary tract, ensuring waste is efficiently removed from the body. The renal pelvis acts like a funnel, collecting urine produced by the kidneys before it travels down the ureter. This tube-like structure then transports urine to the bladder, where it waits until you're ready to release it. Without this dynamic duo, your body would struggle to maintain a healthy balance of fluids and electrolytes. Understanding these components can help you appreciate how your body manages waste and keeps you feeling your best. Let's dive into some fascinating facts about the renal pelvis and ureter that highlight their importance in maintaining your health.
Key Takeaways:
- The renal pelvis and ureter work together to transport urine and maintain the body's fluid balance. They can be affected by kidney stones, infections, and other medical issues, so it's important to take care of them.
- The renal pelvis and ureter have evolved to meet the needs of different species, showcasing nature's adaptability. From handling large volumes of water in aquatic animals to conserving water in desert-dwelling species, these structures play crucial roles in survival.
Understanding the Renal Pelvis and Ureter
The renal pelvis and ureter play crucial roles in the urinary system. They work together to transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Let's explore some fascinating facts about these essential structures.
-
The renal pelvis is a funnel-shaped structure located at the center of each kidney. It collects urine produced by the kidney before it moves to the ureter.
-
The ureter is a muscular tube that connects the renal pelvis to the bladder. It measures about 10 to 12 inches in length in adults.
-
Urine moves through the ureter by a process called peristalsis. This involves rhythmic contractions of the ureter's muscular walls.
-
The renal pelvis and ureter are lined with a special type of tissue called transitional epithelium. This tissue can stretch and contract, allowing it to handle varying volumes of urine.
-
The ureter has three natural constrictions where kidney stones are more likely to get stuck. These are at the junction with the renal pelvis, where it crosses the pelvic brim, and where it enters the bladder.
Functions and Importance
The renal pelvis and ureter are not just passive conduits for urine. They have specific functions that are vital for maintaining the body's fluid balance.
-
The renal pelvis acts as a reservoir, temporarily holding urine until it is ready to be transported to the bladder.
-
The ureter's muscular walls help propel urine toward the bladder, preventing backflow that could lead to infections.
-
The ureter's ability to contract and relax helps maintain a steady flow of urine, even when the body is in different positions or during physical activity.
-
The renal pelvis and ureter work together to ensure that urine is efficiently removed from the body, which is crucial for eliminating waste products and maintaining electrolyte balance.
-
Any obstruction or damage to the ureter can lead to serious health issues, including hydronephrosis, where urine backs up into the kidney, causing swelling and potential damage.
Health and Medical Insights
Understanding the health aspects of the renal pelvis and ureter can help in recognizing and addressing potential medical issues.
-
Kidney stones are one of the most common problems affecting the renal pelvis and ureter. They can cause severe pain and may require medical intervention to remove.
-
Ureteral strictures, or narrowing of the ureter, can occur due to injury, surgery, or inflammation. This can lead to difficulty in urine flow and may require surgical correction.
-
Infections of the urinary tract, such as pyelonephritis, can affect the renal pelvis and ureter, leading to symptoms like fever, back pain, and frequent urination.
-
Congenital abnormalities, such as a duplicated ureter, can occur in some individuals. This condition may require monitoring or treatment if it affects urine flow.
-
Advances in medical imaging, like CT scans and ultrasounds, have made it easier to diagnose issues related to the renal pelvis and ureter.
Interesting Tidbits
Beyond their medical significance, the renal pelvis and ureter have some intriguing aspects worth noting.
-
The term "renal pelvis" comes from the Latin word "pelvis," meaning basin, reflecting its shape and function.
-
The ureter's ability to transport urine against gravity is a remarkable example of the body's engineering.
-
In some animals, the ureter has evolved to have unique adaptations. For example, in birds, the ureter directly connects to the cloaca, bypassing a bladder.
-
The study of the renal pelvis and ureter is part of a broader field known as urology, which focuses on the urinary tract and male reproductive organs.
-
Research into the renal pelvis and ureter continues to advance, with scientists exploring new ways to treat and prevent related diseases.
Evolution and Adaptation
The renal pelvis and ureter have evolved over time to meet the needs of different species, showcasing nature's adaptability.
-
In aquatic animals, the renal pelvis and ureter have adapted to handle large volumes of water, helping to maintain salt balance.
-
In desert-dwelling animals, these structures are highly efficient at conserving water, allowing them to survive in arid environments.
-
The evolution of the renal pelvis and ureter in mammals has enabled them to thrive in diverse habitats, from rainforests to tundras.
-
Some reptiles have a renal pelvis that is less developed, reflecting their lower water requirements compared to mammals.
-
The study of these evolutionary adaptations provides insights into how organisms have survived and thrived in various ecological niches.
Final Thoughts on Renal Pelvis and Ureter
Understanding the renal pelvis and ureter is crucial for grasping how our bodies manage waste. These structures play a vital role in the urinary system, acting as pathways for urine to travel from the kidneys to the bladder. Any issues here, like kidney stones or infections, can lead to significant discomfort and health problems. Staying hydrated and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help keep these organs functioning well. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider ensure any potential issues are caught early. Knowledge about these parts of the body empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining their health. By appreciating the complexity and importance of the renal pelvis and ureter, we can better understand the body's inner workings and the importance of taking care of it. Keep these facts in mind for a healthier future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
