Ever wondered about the oldest human fossil? You're in for a treat! The oldest known human fossil, Homo sapiens, dates back around 300,000 years. Found in Jebel Irhoud, Morocco, this discovery has reshaped our understanding of human evolution. These ancient bones reveal that early humans had a mix of modern and primitive features. Imagine a face similar to ours but with a more robust build. This fossil challenges previous beliefs that modern humans originated solely in East Africa. Instead, it suggests a more complex story of our origins. Ready to dive into more intriguing facts? Let's get started!
Key Takeaways:
- Ancient human fossils, like Lucy and Turkana Boy, provide insights into our evolution, tool use, and diet, shaping our understanding of human history and culture.
- Modern technology, such as CT scans and DNA analysis, has revolutionized the study of ancient human fossils, uncovering new discoveries and enhancing our understanding of human evolution.
Oldest Human Fossils: An Overview
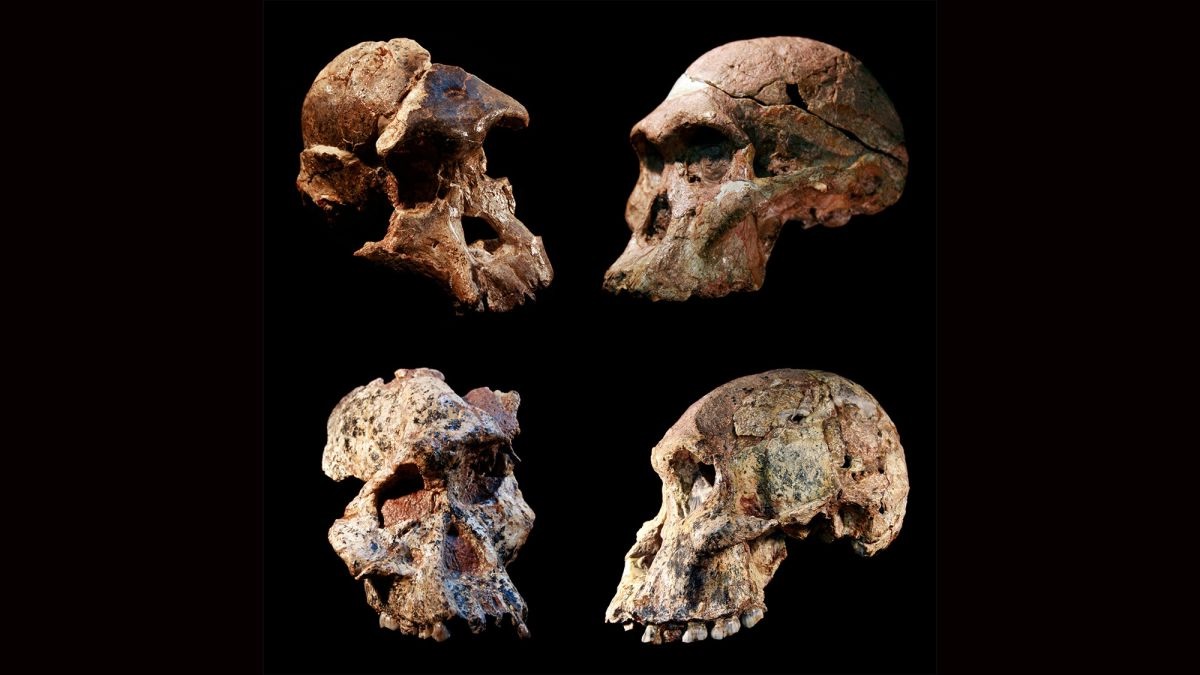
Human fossils provide a window into our ancient past. They help us understand our evolution, migration, and adaptation. Here are some fascinating facts about the oldest human fossils.
-
Oldest Known Fossil: The oldest known human fossil is a jawbone found in Ethiopia, dating back about 2.8 million years. This discovery pushed back the timeline of human evolution.
-
Lucy: Lucy, a famous Australopithecus afarensis skeleton, was discovered in 1974 in Ethiopia. She lived around 3.2 million years ago and is one of the most complete skeletons of an early human ancestor.
-
Homo Habilis: Homo habilis, known as "handy man," lived about 2.4 to 1.4 million years ago. They were among the first to use stone tools.
-
Turkana Boy: Discovered in Kenya, Turkana Boy is a nearly complete skeleton of a Homo erectus youth. He lived around 1.6 million years ago and provides insight into the growth and development of early humans.
Discoveries in Africa
Africa is often called the cradle of humankind. Many significant fossils have been unearthed here, shedding light on our origins.
-
Ardi: Ardipithecus ramidus, nicknamed Ardi, was discovered in Ethiopia. She lived about 4.4 million years ago and walked upright, though she also climbed trees.
-
Taung Child: The Taung Child, an Australopithecus africanus fossil, was found in South Africa in 1924. This discovery was crucial in understanding early human development.
-
Laetoli Footprints: These footprints, found in Tanzania, are about 3.6 million years old. They show that early humans walked upright.
-
Olduvai Gorge: This site in Tanzania has yielded many important fossils, including those of Homo habilis and Paranthropus boisei, dating back 1.75 million years.
European Fossil Finds
Europe has also been a rich source of ancient human fossils, offering a glimpse into the lives of our ancestors who migrated out of Africa.
-
Neanderthals: Neanderthals lived in Europe and parts of Asia from about 400,000 to 40,000 years ago. Their fossils have been found in many locations, including Germany and Spain.
-
Atapuerca: The Atapuerca site in Spain has produced fossils of Homo antecessor, one of the earliest known human species in Europe, dating back around 1.2 million years.
-
Cro-Magnon: Cro-Magnon fossils, found in France, are about 30,000 years old. They are among the earliest modern humans in Europe.
Asian Fossil Discoveries
Asia has provided key fossils that help trace the spread of early humans across the globe.
-
Peking Man: Peking Man, a Homo erectus fossil, was discovered in China and dates back about 750,000 years. This find was crucial in understanding human migration.
-
Denisovans: Denisovan fossils, found in Siberia, are from a previously unknown group of ancient humans. They lived around 50,000 years ago and interbred with both Neanderthals and modern humans.
-
Java Man: Java Man, another Homo erectus fossil, was found in Indonesia. He lived about 1.5 million years ago and is one of the first human fossils discovered outside Africa.
Fossils in the Americas
The Americas have fewer ancient human fossils, but the discoveries made are still significant.
-
Kennewick Man: Kennewick Man, found in Washington State, is about 9,000 years old. His remains have provided valuable information about early inhabitants of North America.
-
Luzia Woman: Luzia Woman, discovered in Brazil, is around 11,500 years old. She is one of the oldest known human skeletons in the Americas.
Fossil Dating Techniques
Understanding how scientists date these ancient fossils is crucial for piecing together our history.
-
Radiocarbon Dating: This method measures the decay of carbon-14 in organic materials, useful for dating fossils up to 50,000 years old.
-
Potassium-Argon Dating: Used for older fossils, this technique measures the decay of potassium-40 to argon-40 in volcanic rock.
-
Thermoluminescence: This method dates the last time an object was heated. It’s useful for dating ancient tools and pottery.
-
Electron Spin Resonance: This technique measures trapped electrons in bones and teeth, helping date fossils up to 2 million years old.
Fossil Preservation
The conditions under which fossils are preserved can tell us much about the environment in which early humans lived.
-
Permafrost: Fossils found in permafrost, like those in Siberia, are often well-preserved due to the cold temperatures.
-
Caves: Many fossils are found in caves, where conditions can protect bones from the elements.
-
Sedimentary Rock: Fossils in sedimentary rock layers can be dated by the age of the surrounding rock, providing a timeline for the fossil.
-
Tar Pits: Fossils found in tar pits, like those in La Brea, California, are often well-preserved due to the tar’s preservative properties.
Impact on Understanding Human Evolution
These fossils have significantly impacted our understanding of human evolution, migration, and adaptation.
-
Bipedalism: Fossils like Lucy and the Laetoli footprints show that early humans walked upright millions of years ago.
-
Tool Use: Homo habilis fossils indicate that early humans used tools, a significant step in our evolution.
-
Brain Size: Fossils show a gradual increase in brain size over millions of years, reflecting the development of complex thought and culture.
-
Diet: Fossilized teeth and bones provide clues about the diet of early humans, from plant-based diets to the inclusion of meat.
Fossil Discoveries and Modern Technology
Modern technology has revolutionized the study of ancient human fossils, providing new insights and discoveries.
-
CT Scans: CT scans allow scientists to examine fossils in detail without damaging them, revealing internal structures.
-
DNA Analysis: Ancient DNA analysis has provided information about the relationships between different human species and their migrations.
-
3D Printing: 3D printing technology enables the creation of accurate replicas of fossils for study and display.
-
Virtual Reality: Virtual reality allows researchers to explore fossil sites and reconstructions of ancient environments in immersive detail.
Famous Fossil Hunters
Many of the most significant fossil discoveries were made by dedicated fossil hunters and paleontologists.
-
Mary Leakey: Mary Leakey discovered the Laetoli footprints and many other important fossils in Africa.
-
Louis Leakey: Louis Leakey, along with his wife Mary, made numerous discoveries that advanced our understanding of human evolution.
-
Donald Johanson: Donald Johanson discovered Lucy, one of the most famous early human fossils, in Ethiopia.
The Final Word on Ancient Human Fossils
Ancient human fossils give us a peek into our distant past. They show how early humans lived, adapted, and evolved. These fossils, like the famous Lucy and the Turkana Boy, are more than just old bones. They tell stories of survival, migration, and development. Each discovery adds a piece to the puzzle of human history.
Understanding these fossils helps scientists trace the journey of human evolution. It connects us to our ancestors and highlights the incredible journey of our species. From Homo habilis to Homo sapiens, each fossil is a chapter in the story of humanity.
So next time you hear about a new fossil find, remember, it's not just a scientific discovery. It's a link to our shared past, a reminder of where we come from, and a clue to where we might be headed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
