Have you ever wondered what secrets a baby ape fossil might hold? Baby ape fossils are like time capsules, giving us a peek into the distant past. These tiny relics help scientists understand how apes evolved and how they relate to humans. Imagine holding a piece of history that’s millions of years old! These fossils can tell us about the environment, diet, and even the social behavior of ancient apes. They reveal how these creatures adapted to their surroundings and what challenges they faced. By studying these fossils, researchers can piece together the puzzle of evolution, shedding light on how life on Earth has changed over time. Baby ape fossils are not just bones; they are storytellers of the ancient world.
Key Takeaways:
- Baby ape fossils provide valuable insights into the early development and evolution of primates, helping scientists understand their physical characteristics, behaviors, and environments.
- These rare and fragile fossils offer a window into the past, shedding light on the evolutionary path that led to modern apes and humans, and inspiring new research in paleoanthropology.
What is a Baby Ape Fossil?
A baby ape fossil is a rare and fascinating discovery that provides insights into the early development and evolution of primates. These fossils can tell us about the physical characteristics, behaviors, and environments of ancient apes. Let's explore some intriguing facts about these ancient remnants.
-
Baby ape fossils are incredibly rare because young bones are more fragile and less likely to survive the fossilization process.
-
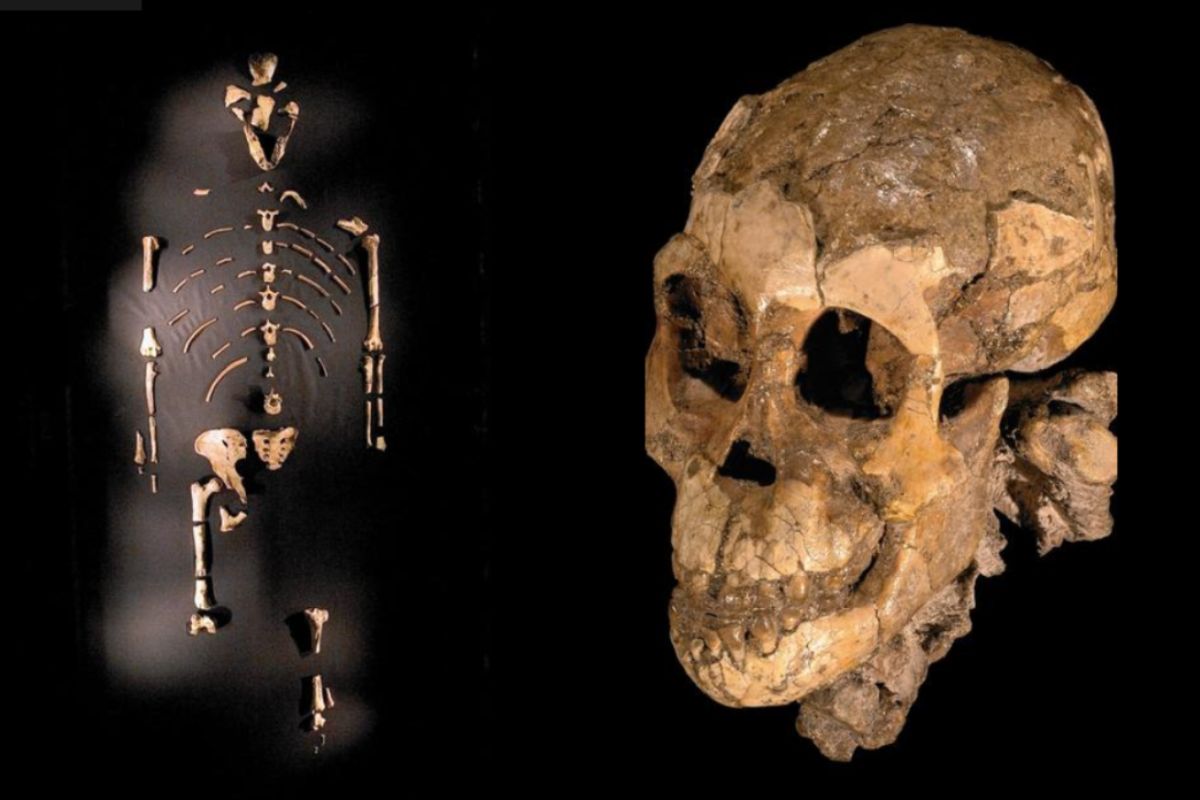
The first baby ape fossil was discovered in 2002 in Kenya, providing a glimpse into the life of a young ape from 13 million years ago.
-
This particular fossil belonged to a species called Nyanzapithecus alesi, which is believed to be an ancestor of modern apes and humans.
-
The skull of the Nyanzapithecus alesi was remarkably well-preserved, allowing scientists to study its brain size and structure.
-
The fossil's teeth were still developing, indicating the ape was less than two years old at the time of its death.
How Do Scientists Study Baby Ape Fossils?
Studying these fossils involves various techniques to understand their significance in evolutionary history. Researchers use advanced technology and methods to analyze these ancient remains.
-
CT scans are used to create detailed 3D images of the fossil without damaging it, revealing internal structures like brain cavities.
-
By examining the teeth, scientists can determine the age of the fossil and gain insights into the diet and growth patterns of the young ape.
-
The shape and size of the skull help researchers understand the evolutionary relationships between ancient apes and modern primates.
-
Fossilized bones can also provide clues about the environment in which the ape lived, such as the type of vegetation and climate.
-
Scientists compare baby ape fossils with those of other primates to trace evolutionary changes over millions of years.
What Do Baby Ape Fossils Tell Us About Evolution?
These fossils are crucial for understanding the evolutionary path that led to modern apes and humans. They offer a window into the past, showing how early primates adapted and evolved.
-
Baby ape fossils suggest that early primates had a slower growth rate compared to other mammals, similar to modern humans.
-
The brain size of the Nyanzapithecus alesi was smaller than that of modern apes, indicating a gradual increase in brain size over time.
-
The structure of the inner ear in the fossil suggests that early apes had a different sense of balance and movement compared to their modern counterparts.
-
The discovery of baby ape fossils supports the theory that Africa was a significant region for primate evolution.
-
These fossils help fill gaps in the fossil record, providing a more complete picture of how primates evolved over millions of years.
Why Are Baby Ape Fossils Important?
The importance of these fossils extends beyond just understanding primate evolution. They also offer insights into broader scientific questions about life on Earth.
-
Baby ape fossils help scientists understand the development of social behaviors in early primates, which can shed light on human social evolution.
-
By studying these fossils, researchers can learn about the impact of environmental changes on primate evolution.
-
The preservation of such fossils allows scientists to refine dating techniques and improve the accuracy of the fossil record.
-
These discoveries can inspire new research and exploration in paleoanthropology, leading to further breakthroughs in understanding human origins.
-
Baby ape fossils remind us of the interconnectedness of all life on Earth, highlighting the shared ancestry of humans and other primates.
Where Have Baby Ape Fossils Been Found?
The locations of these fossil discoveries provide clues about the habitats and distribution of ancient apes.
-
Most baby ape fossils have been found in Africa, particularly in regions like Kenya and Ethiopia, known for their rich fossil deposits.
-
The discovery of a baby ape fossil in the Tugen Hills of Kenya was a significant find, as it provided new insights into the Miocene epoch.
-
Some fossils have been unearthed in Asia, suggesting that early apes may have migrated between continents.
-
The Rift Valley in Africa is a hotspot for fossil discoveries, offering a wealth of information about early primate evolution.
-
Fossil sites in Europe have also yielded important finds, indicating that ancient apes once roamed across a wide geographical area.
What Challenges Do Scientists Face in Studying Baby Ape Fossils?
Researching these ancient remains is not without its difficulties. Scientists encounter various challenges when studying baby ape fossils.
-
The fragile nature of young bones makes them difficult to excavate and preserve without causing damage.
-
Limited fossil evidence means that researchers must rely on incomplete data to draw conclusions about early primates.
-
Dating fossils accurately can be challenging due to the complex geological processes that affect fossil sites.
-
Interpreting the behavior and lifestyle of ancient apes from fossil evidence requires careful analysis and often involves educated guesses.
-
Funding and resources for fossil research can be limited, hindering the ability to conduct extensive studies and excavations.
What Future Discoveries Could Baby Ape Fossils Lead To?
The study of these fossils continues to evolve, with new technologies and methods offering exciting possibilities for future discoveries.
-
Advances in genetic analysis could allow scientists to extract DNA from fossils, providing direct evidence of evolutionary relationships.
-
Improved imaging techniques may reveal previously hidden details in fossils, leading to new insights into early primate anatomy.
-
Collaborative research efforts across disciplines could uncover more fossil sites and expand our understanding of primate evolution.
-
Ongoing exploration in fossil-rich regions may lead to the discovery of new species, further enriching the fossil record.
-
As technology advances, scientists may develop new ways to simulate the environments in which ancient apes lived, offering a more comprehensive view of their world.
The Final Word on Baby Ape Fossils
Baby ape fossils are like time capsules, giving us a peek into the past. These tiny remnants tell us about the evolution of primates and how they relate to humans. Scientists learn a lot from these fossils, like how ancient apes moved, what they ate, and how they lived. Each discovery adds a piece to the puzzle of our ancestry. The more we find, the clearer the picture becomes. These fossils also help us understand how climate and environmental changes affected ancient species. As technology advances, researchers can uncover even more secrets hidden in these ancient bones. So, while they might be small, baby ape fossils have a big role in teaching us about the history of life on Earth. Keep an eye out for future discoveries that might change what we know about our ancient relatives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
