Curious about Mars missions? You're in the right place! Mars, our intriguing red neighbor, has captivated human imagination for centuries. From ancient astronomers to modern scientists, the quest to understand Mars has led to numerous missions, each with its own set of challenges and triumphs. Why are Mars missions important? They help us learn about the planet's history, climate, and potential for life. What have we discovered so far? From water traces to stunning landscapes, Mars missions have unveiled many secrets. Ready to dive into 27 fascinating facts about Mars missions? Let's embark on this cosmic journey together!
Key Takeaways:
- Mars missions have revealed fascinating discoveries, from ancient water to potential signs of life. Rovers, orbiters, and future plans all contribute to our understanding of the Red Planet.
- Sending humans to Mars is a long-term goal, with NASA, SpaceX, and other organizations working towards making it a reality. Challenges like thin atmosphere and communication delays must be overcome.
The Red Planet's Mystique
Mars has fascinated humans for centuries. Its reddish hue and proximity to Earth make it a prime candidate for exploration. Here are some intriguing facts about Mars missions.
-
The first successful Mars mission was NASA's Mariner 4 in 1965. It sent back the first close-up images of Mars, revealing a cratered surface.
-
The Soviet Union's Mars 3 was the first spacecraft to land on Mars in 1971. However, it lost communication just 20 seconds after landing.
-
NASA's Viking 1, launched in 1975, was the first successful lander to operate on Mars for an extended period. It sent back detailed images and data for over six years.
Rovers on Mars
Rovers have played a crucial role in exploring Mars. These robotic explorers have provided invaluable data about the planet's surface and atmosphere.
-
The Sojourner rover, part of NASA's Mars Pathfinder mission, was the first rover to explore Mars in 1997. It operated for 83 days, far exceeding its planned seven-day mission.
-
Spirit and Opportunity, twin rovers launched in 2003, were designed for 90-day missions. Spirit operated for over six years, while Opportunity lasted nearly 15 years.
-
Curiosity, launched in 2011, is still operational. It has traveled over 25 kilometers and discovered evidence of ancient water on Mars.
Orbiters and Their Contributions
Orbiters have provided a bird's-eye view of Mars, mapping its surface and studying its atmosphere.
-
Mars Odyssey, launched in 2001, holds the record for the longest continuously active spacecraft orbiting Mars. It has been mapping the planet's surface and detecting water ice.
-
The European Space Agency's Mars Express, launched in 2003, discovered methane in Mars' atmosphere, hinting at possible microbial life.
-
NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, launched in 2005, has sent back more data than all other Mars missions combined. It has captured high-resolution images of the planet's surface.
International Efforts
Mars exploration isn't limited to NASA. Other countries have also contributed to our understanding of the Red Planet.
-
India's Mars Orbiter Mission, also known as Mangalyaan, was launched in 2013. It made India the first country to successfully reach Mars on its first attempt.
-
The United Arab Emirates' Hope Probe, launched in 2020, aims to study Mars' atmosphere and climate. It is the first Arab mission to Mars.
-
China's Tianwen-1 mission, launched in 2020, includes an orbiter, lander, and rover. The rover, Zhurong, successfully landed on Mars in 2021.
Future Mars Missions
The quest to explore Mars continues with ambitious plans for the future.
-
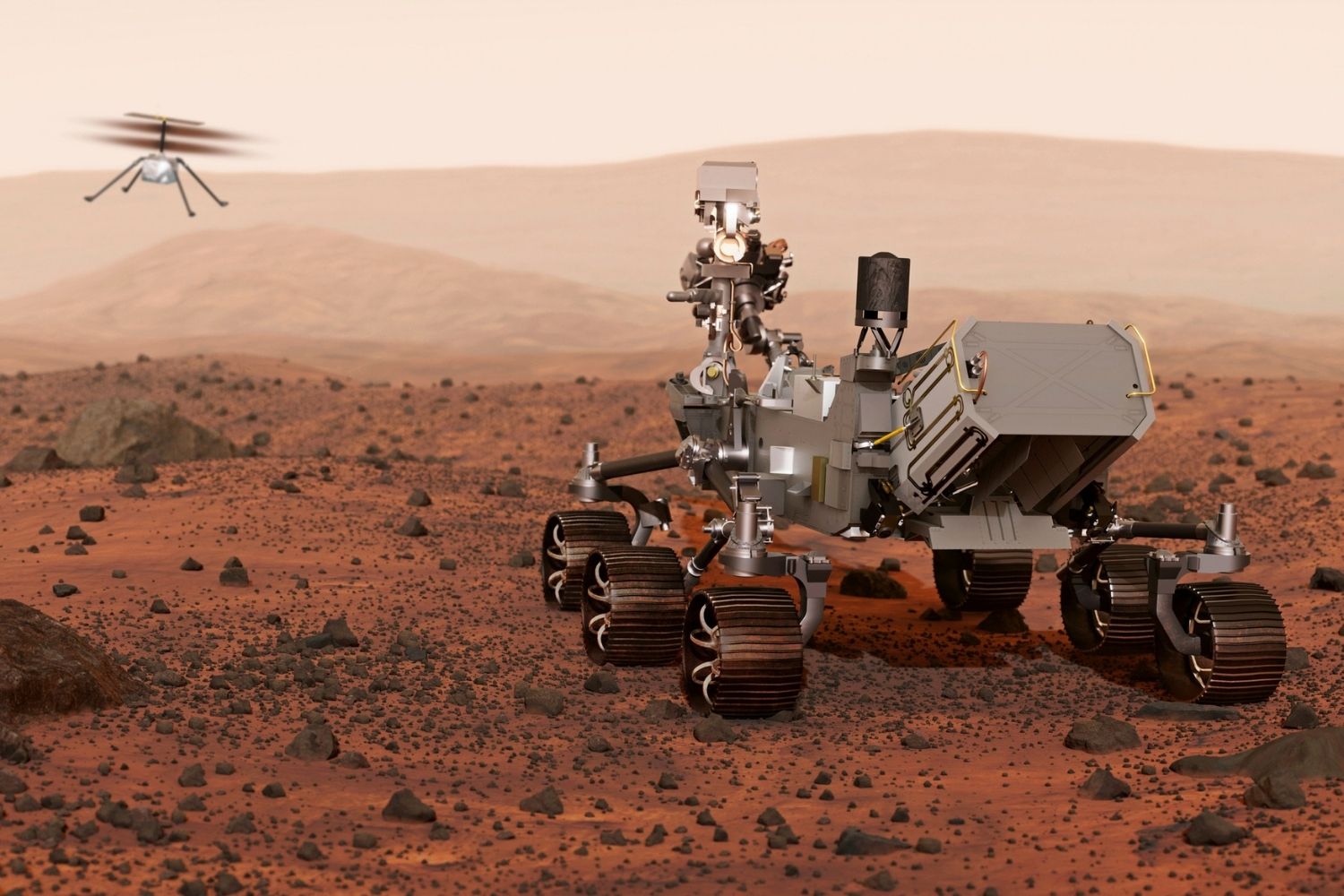
NASA's Perseverance rover, launched in 2020, is searching for signs of ancient life and collecting samples for future return to Earth.
-
The European Space Agency and Russia's Roscosmos are collaborating on the ExoMars mission. It aims to search for signs of past life and understand the planet's geochemical environment.
-
SpaceX plans to send humans to Mars with its Starship spacecraft. The goal is to establish a self-sustaining colony on the Red Planet.
Challenges of Mars Missions
Exploring Mars is no easy feat. Numerous challenges must be overcome to ensure mission success.
-
The thin Martian atmosphere makes landing difficult. Parachutes and retro rockets are used to slow down spacecraft during descent.
-
Mars' dust storms can last for months and cover the entire planet. These storms can interfere with solar-powered equipment.
-
Communication delays between Earth and Mars can be up to 24 minutes. This delay requires rovers to operate autonomously.
Scientific Discoveries
Mars missions have led to groundbreaking discoveries that have reshaped our understanding of the planet.
-
Evidence of liquid water was found by the Mars Global Surveyor in 2000. This discovery suggested that Mars could have once supported life.
-
Curiosity discovered organic molecules in Martian soil, indicating that the building blocks of life might exist on Mars.
-
The InSight lander, launched in 2018, detected Marsquakes, providing insights into the planet's interior structure.
Mars and the Search for Life
The search for life on Mars is a primary goal of many missions. Scientists are looking for signs of past or present life.
-
Viking 1 and 2 conducted experiments to detect microbial life in Martian soil. The results were inconclusive but sparked ongoing interest in the search for life.
-
The discovery of recurring slope lineae by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter suggests that liquid water might still flow on Mars today.
-
Perseverance is equipped with instruments to search for biosignatures, or signs of past life, in Martian rocks.
Human Missions to Mars
Sending humans to Mars is a long-term goal for space agencies and private companies.
-
NASA's Artemis program aims to return humans to the Moon by 2024 as a stepping stone for future Mars missions.
-
SpaceX's Starship is designed to carry up to 100 people to Mars. The company plans to conduct uncrewed test flights before sending humans.
-
The Mars Society advocates for human exploration and settlement of Mars. They conduct simulations and research to prepare for future missions.
Mars Missions: A Glimpse into the Future
Mars missions have shown us just how far human curiosity and technology can go. From the Viking landers in the '70s to the Perseverance rover today, each mission has brought us closer to understanding the Red Planet. These missions aren't just about exploring another world; they're about pushing the boundaries of what's possible. The discoveries made on Mars could pave the way for future space exploration and even potential colonization. With each mission, we learn more about Mars' climate, geology, and potential for life. This knowledge not only satisfies our curiosity but also prepares us for the challenges of living on another planet. As we look to the future, Mars missions will continue to inspire and drive innovation, proving that the sky isn't the limit—it's just the beginning.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
