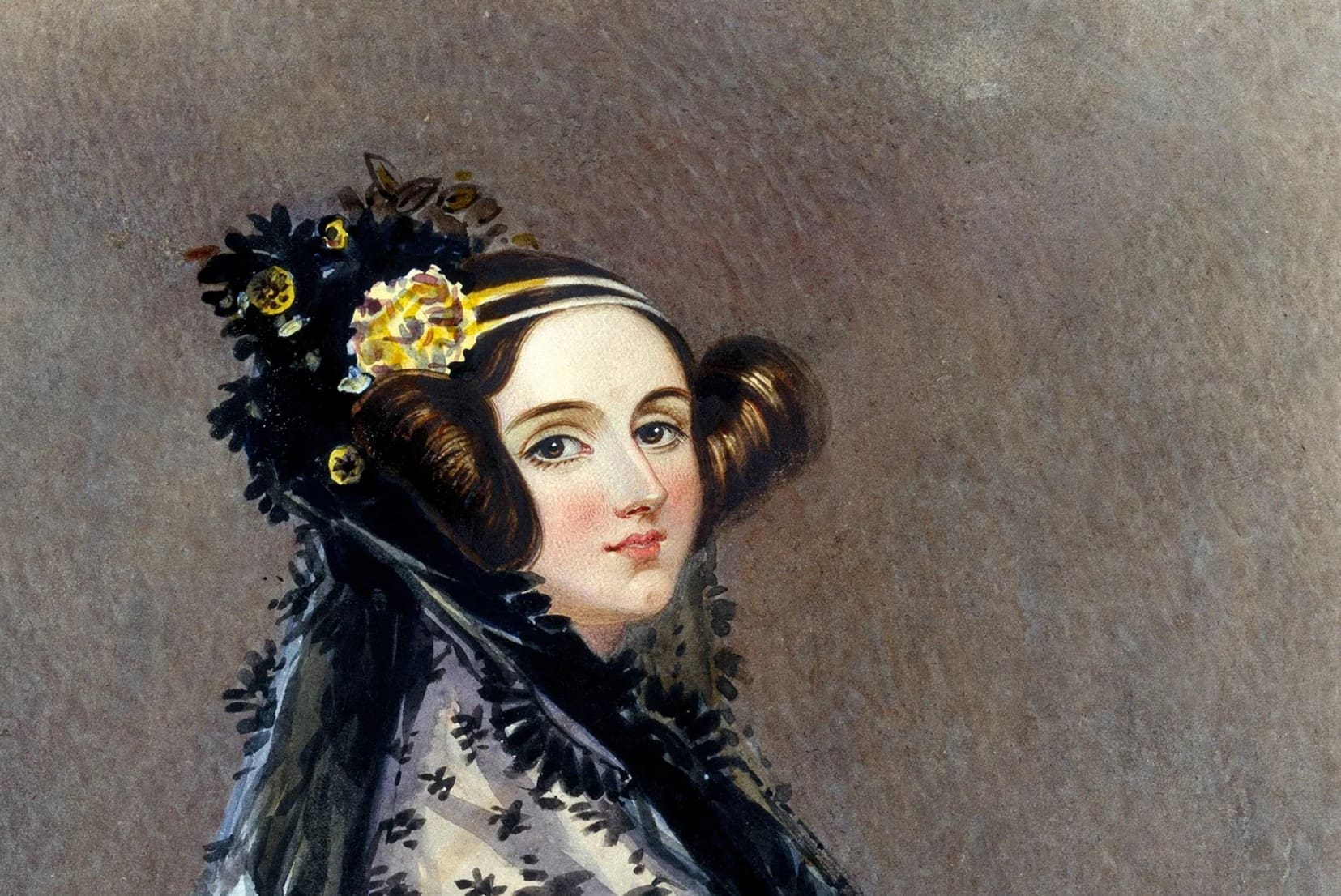
Ever wondered who kick-started the digital age, long before the first computer was even built? Ada Lovelace might just be the pioneer you're looking for. Born in 1815, this mathematician and writer became the world's first computer programmer, thanks to her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. But, how much do we really know about her? From her illustrious lineage to her visionary contributions that went unrecognized for decades, Ada's life is a treasure trove of fascinating facts. Ready to get your mind blown by some of the most intriguing tidbits about Ada Lovelace? Let's dive into the world of this 19th-century icon and uncover the legacy she left for future generations of tech enthusiasts and professionals alike.
Who Was Ada Lovelace?
Ada Lovelace, born Augusta Ada Byron on December 10, 1815, was an English mathematician and writer. She is best known for her work on Charles Babbage's proposed mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. Lovelace's notes on the engine include what is recognized as the first algorithm intended to be processed by a machine. Because of this, she is often regarded as the first computer programmer.
-
Ada was the only legitimate child of the poet Lord Byron and his wife Anne Isabella Milbanke, an heiress and a mathematician herself. Her parents separated when Ada was just a month old, and she never saw her father again.
-
From a young age, Ada showed a keen interest in mathematics and science, a passion encouraged by her mother, who hoped it would steer her away from the moody poetical inclinations of her father.
Ada Lovelace's Contributions to Computing
-
In 1833, Ada Lovelace met Charles Babbage, the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge. Babbage described to Ada his idea for an Analytical Engine, an early concept for a computer, which fascinated her.
-
Lovelace translated an article on the Analytical Engine from the original Italian, supplementing it with notes that were three times longer than the article itself. These notes contained what many consider the first computer program—a set of instructions for the Analytical Engine to calculate Bernoulli numbers.
-
Her work was published in 1843, under the initials A.A.L., making her one of the first women to publish a paper in the field of computer science.
The Legacy of Ada Lovelace
-
Ada Lovelace died at the young age of 36, on November 27, 1852, from uterine cancer. Despite her premature death, her contributions to computing have made her a lasting figure in the history of technology.
-
The U.S. Department of Defense named a newly developed computer language "Ada" in 1980 to honor Lovelace's contributions to computing.
-
October 13th is celebrated as Ada Lovelace Day, an international celebration of the achievements of women in science, technology, engineering, and maths (STEM).
Interesting Facts About Ada Lovelace
-
Ada was tutored by Mary Somerville, a renowned researcher and scientific writer of the 19th century, who introduced her to Babbage.
-
Despite her mathematical skills, Ada was also interested in music and described her approach to science as "poetical science," where imagination played a crucial role in her mathematical studies.
-
Lovelace speculated that the Analytical Engine could have applications beyond pure calculation, suggesting it might be capable of creating music and art, predicting the computer's potential to influence both science and the arts.
-
Ada Lovelace had a volatile relationship with her mother, who strictly monitored her actions and correspondence. Despite this, Ada pursued her interests in mathematics and science with fervor.
-
She was often ill throughout her life, suffering from various ailments like asthma and digestive issues, which were treated with the medical practices of the time, including regular bloodletting.
-
Ada's visionary work was not fully recognized during her lifetime. It wasn't until the mid-20th century that her contributions to computing were rediscovered and celebrated.
-
Lovelace's notes on the Analytical Engine were studied a century later as engineers and computer scientists began developing the first computers. Her work demonstrated foresight into the capabilities and future of computing machines.
-
Ada Lovelace's story has inspired numerous books, plays, and films, highlighting her as a pioneering woman in technology and a role model for women in STEM fields today.
-
Despite her aristocratic background, Ada's gambling habit led her to financial troubles. She tried to create mathematical schemes for large bets, which ultimately failed.
-
Ada Lovelace's correspondence with Charles Babbage was extensive, and their letters are preserved as important documents that provide insight into the early history of computing.
-
In recognition of her contributions, several awards, scholarships, and programs aimed at encouraging women to pursue careers in science and technology have been named after Ada Lovelace.
-
Lovelace's work is considered a crucial link in the chain of computer science history, connecting the conceptual beginnings of computing with the digital age.
-
Ada's interest in the Analytical Engine went beyond its mathematical capabilities; she envisioned a world where machines could assist in various forms of art and science, a testament to her forward-thinking and innovative mind.
-
Despite the societal constraints of her time, Ada Lovelace broke barriers and made significant contributions to a field that was in its infancy, laying the groundwork for future generations.
-
Her partnership with Charles Babbage was a fusion of creativity and scientific rigor, showcasing the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing technology.
-
Ada Lovelace's legacy endures, not only in the field of computing but also as a symbol of women's contributions to science and technology, challenging stereotypes and inspiring future generations.
A Glimpse Into Ada Lovelace's Legacy
Ada Lovelace's story is more than just a collection of interesting facts. It's a testament to the power of imagination and intellect. Her work laid the groundwork for modern computing, proving that women have always been at the forefront of technological innovation. Lovelace wasn't just the first computer programmer; she was a visionary who saw the potential for machines to go beyond mere calculation, to create art and music. Her legacy challenges us to think big and to see the beauty in numbers. As we look back on her contributions, let's also look forward to the future she helped shape. Ada Lovelace's life reminds us that in the realm of innovation, there are no limits to what can be achieved when creativity meets science.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.