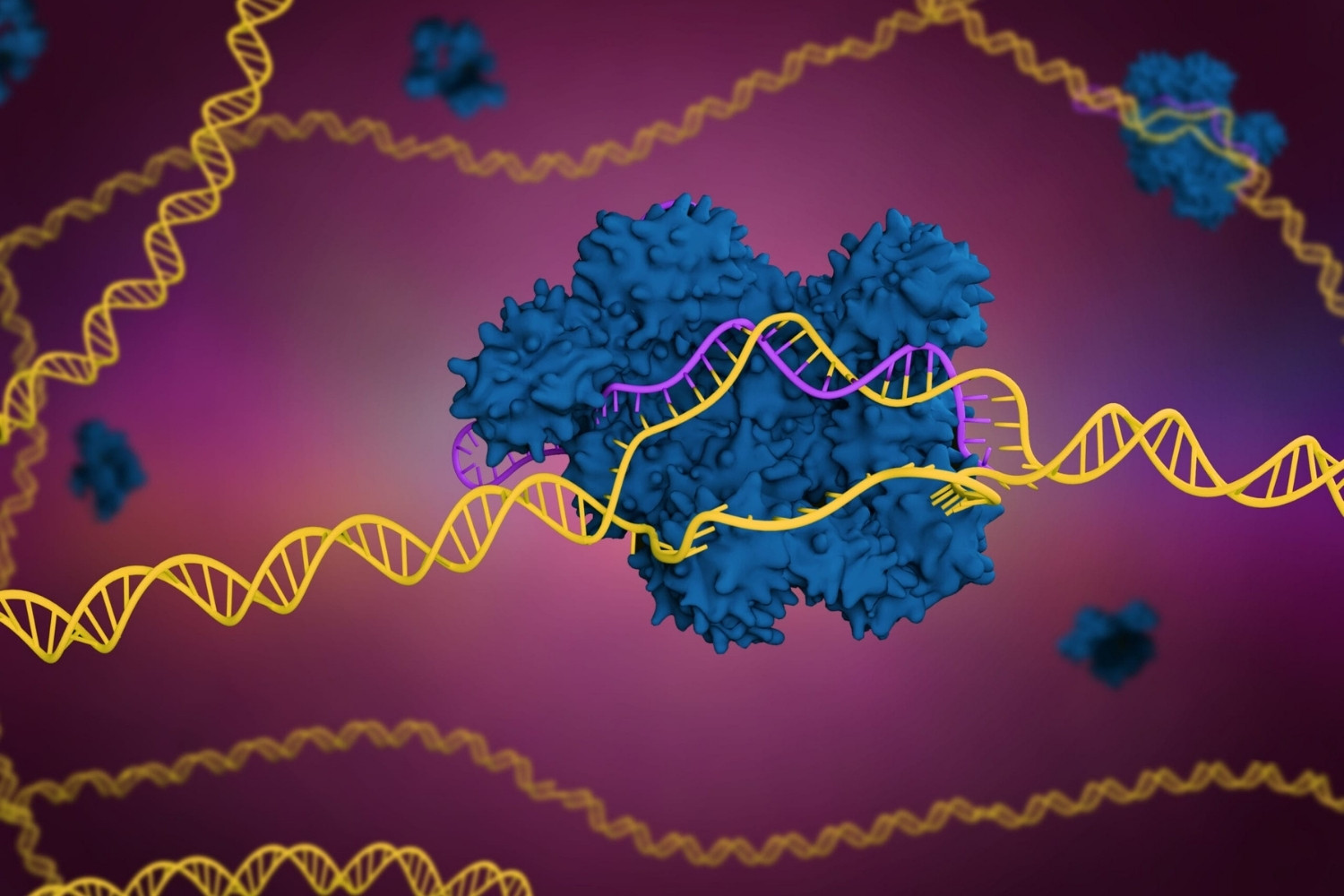
CRISPR-Cas9 has revolutionized genetics, offering a powerful tool for editing DNA. But what exactly is CRISPR-Cas9? CRISPR stands for "Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats," and Cas9 is a protein that acts like molecular scissors. Together, they allow scientists to cut and modify DNA with unprecedented precision. This technology holds promise for treating genetic disorders, improving crops, and even combating diseases like cancer. However, it's not without controversy. Ethical questions arise about its potential misuse and long-term effects. Understanding CRISPR-Cas9's capabilities and limitations is crucial for navigating its future applications. Ready to dive into 34 fascinating facts about this groundbreaking technology? Let's get started!
What is CRISPR-Cas9?
CRISPR-Cas9 is a groundbreaking technology in the field of genetics. It allows scientists to edit genes with precision, opening up possibilities for treating genetic disorders, improving crops, and much more. Here are some fascinating facts about CRISPR-Cas9.
-
CRISPR stands for "Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats." These are sequences of DNA found in the genomes of bacteria and archaea.
-
Cas9 is an enzyme that acts like a pair of molecular scissors, capable of cutting DNA strands at specific locations.
-
The CRISPR-Cas9 system was adapted from a natural defense mechanism used by bacteria to fend off viruses.
-
In 2012, Jennifer Doudna and Emmanuelle Charpentier published a paper demonstrating how CRISPR-Cas9 could be used for gene editing, revolutionizing genetic research.
How Does CRISPR-Cas9 Work?
Understanding the mechanics behind CRISPR-Cas9 can be complex, but it's fascinating. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how this technology operates.
-
Scientists design a small piece of RNA with a matching sequence to the target DNA. This RNA guides Cas9 to the exact location in the genome.
-
Once the guide RNA finds its target, Cas9 cuts the DNA at that specific spot.
-
The cell then tries to repair the cut, and during this process, scientists can introduce new genetic material or disable a gene.
-
This method allows for precise editing, making it possible to add, remove, or alter DNA sequences in living organisms.
Applications of CRISPR-Cas9
CRISPR-Cas9 has a wide range of applications that extend beyond just gene editing. Its potential uses are vast and varied.
-
One of the most promising applications is in treating genetic disorders such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell anemia, and muscular dystrophy.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 is being used to develop crops that are more resistant to pests, diseases, and environmental conditions.
-
Scientists are exploring the use of CRISPR-Cas9 to create gene drives, which could help control populations of disease-carrying insects like mosquitoes.
-
Researchers are investigating how CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to modify the genes of livestock to improve their health and productivity.
Ethical Considerations
With great power comes great responsibility. The ethical implications of CRISPR-Cas9 are a hot topic of debate among scientists, ethicists, and the public.
-
One major concern is the potential for "designer babies," where genetic editing could be used to enhance physical or intellectual traits.
-
There are fears that CRISPR-Cas9 could be used to create biological weapons or harmful organisms.
-
The possibility of unintended consequences, such as off-target effects where the wrong part of the genome is edited, raises safety concerns.
-
Ethical guidelines and regulations are being developed to ensure that CRISPR-Cas9 is used responsibly and safely.
Success Stories
Despite the challenges, there have been numerous success stories showcasing the potential of CRISPR-Cas9.
-
In 2017, scientists used CRISPR-Cas9 to correct a genetic mutation in human embryos that causes hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a heart condition.
-
Researchers have successfully used CRISPR-Cas9 to treat mice with muscular dystrophy, showing promise for future human treatments.
-
In agriculture, CRISPR-Cas9 has been used to create a strain of wheat that is resistant to powdery mildew, a common fungal disease.
-
Scientists have developed a type of rice that can grow in salty soils, potentially increasing food production in areas with poor soil quality.
Future Prospects
The future of CRISPR-Cas9 is bright, with ongoing research and new discoveries being made regularly. Here are some exciting prospects.
-
Scientists are working on improving the accuracy and efficiency of CRISPR-Cas9 to minimize off-target effects.
-
There is ongoing research into using CRISPR-Cas9 for gene therapy to treat a wide range of diseases, including cancer and HIV.
-
Researchers are exploring the potential of CRISPR-Cas9 to extend human lifespan by targeting genes associated with aging.
-
The technology could be used to revive extinct species by editing the genes of closely related living species.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its potential, CRISPR-Cas9 faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
-
One major challenge is the delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 components into the cells of living organisms, which can be difficult and inefficient.
-
Off-target effects remain a significant concern, as unintended edits can have harmful consequences.
-
There is a need for better understanding of the long-term effects of gene editing on organisms and their offspring.
-
Regulatory hurdles and ethical concerns can slow down the progress and application of CRISPR-Cas9 technology.
CRISPR-Cas9 in Popular Culture
CRISPR-Cas9 has captured the imagination of the public and has been featured in various forms of media.
-
The technology was prominently featured in the 2018 documentary "Human Nature," which explores its potential and ethical implications.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 has been a topic of discussion in numerous science fiction novels, highlighting both its promise and potential dangers.
-
The technology has been covered extensively in news articles, podcasts, and television programs, bringing it into the mainstream consciousness.
-
Educational programs and online courses about CRISPR-Cas9 are becoming increasingly popular, helping to inform and educate the public.
Fun Facts About CRISPR-Cas9
Beyond its scientific and ethical implications, CRISPR-Cas9 has some fun and quirky aspects worth noting.
-
The name "CRISPR" was coined by Francisco Mojica, a Spanish microbiologist who discovered the sequences in the 1990s.
-
CRISPR-Cas9 has been used to create genetically modified pets, such as glow-in-the-dark fish and pigs with altered coat colors.
The Future of CRISPR-Cas9
CRISPR-Cas9 has revolutionized genetics. This gene-editing tool offers potential cures for genetic disorders, cancer, and even HIV. Researchers are exploring its use in agriculture to create disease-resistant crops, which could help combat food shortages. However, ethical concerns remain. The possibility of "designer babies" and unintended genetic consequences raises questions about how far we should go.
Despite these challenges, the benefits are undeniable. CRISPR-Cas9 could lead to breakthroughs in medicine and agriculture, improving lives worldwide. As research continues, it's crucial to balance innovation with ethical considerations. The future of CRISPR-Cas9 is bright, but it requires careful navigation to ensure its responsible use.
Stay informed and engaged with developments in this exciting field. The journey of CRISPR-Cas9 is just beginning, and its impact will likely be felt for generations to come.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
